Understanding and Managing B Cell Lymphoma Symptoms and Therapies
This article covers the key symptoms of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and outlines effective treatment options. Recognizing early signs like lumps, itching, weight loss, and night sweats can lead to prompt diagnosis. Treatment primarily involves chemotherapy regimens such as R-CHOP, with options tailored to individual health and disease stage. With advances in therapy and early detection, most patients have a high chance of remission. Understanding the differences between lymphoma types and seeking immediate medical attention are vital steps toward successful management of this aggressive cancer.
Sponsored

Recognizing Symptoms and Exploring Treatment Options for B Cell Lymphoma
B cell lymphoma, particularly diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), originates in lymphocytes, which are vital white blood cells. It commonly manifests as enlarging lumps in areas such as the neck, groin, or underarms, and can spread rapidly throughout the body. Fortunately, with prompt diagnosis and treatment, many patients achieve remission. Studies show that about 75% of those treated become disease-free. Ongoing research aims to enhance treatment success rates even further.
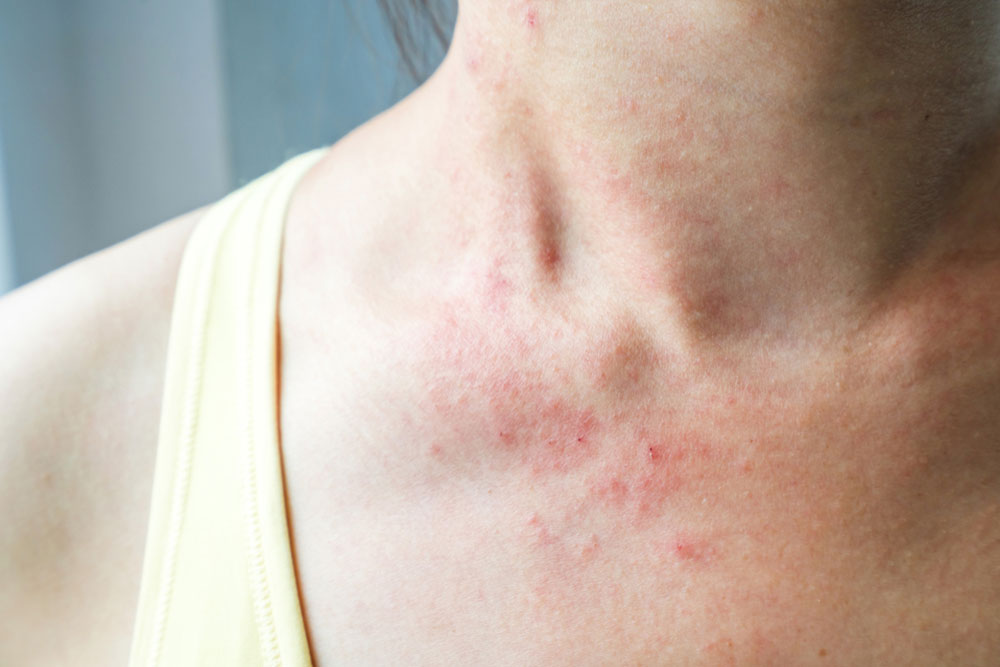
Signs of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
The initial indicator usually appears as a noticeable lump that may grow quickly, sometimes causing discomfort. In some cases, the disease affects other organs like the stomach. Common symptoms include:
Itching
Difficulty breathing or coughing
Unintentional weight loss
Fever
Night sweats that soak clothing
Abdominal or chest pain with pressure
Therapies for Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
Due to its rapid progression, early medical intervention is crucial. Treatment plans are tailored based on factors such as age, overall health, and disease stage. Common therapies include chemotherapy and radiation, often combined in a regimen known as 'R-CHOP', which involves various medications administered over three weeks. For aggressive cases, additional drugs like etoposide may be incorporated. Understanding the differences between Hodgkin’s and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma is essential, as they require distinct treatment strategies. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is the most prevalent type of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Immediate consultation with a healthcare professional if symptoms appear can significantly improve outcomes.