Comprehensive Guide to Eczema Symptoms, Causes, Types, and Treatments
This comprehensive guide explores eczema, detailing its symptoms, causes, various types, and modern treatment options. It emphasizes the importance of identifying triggers like irritants and allergens to effectively manage the condition. Proper skincare, avoiding triggers, and medical interventions can help control flare-ups, alleviating discomfort and improving quality of life for eczema sufferers. Education on different eczema types provides tailored approaches for each individual, promoting long-term skin health and well-being.
Sponsored

Understanding Eczema: Symptoms, Causes, Variations, and Management
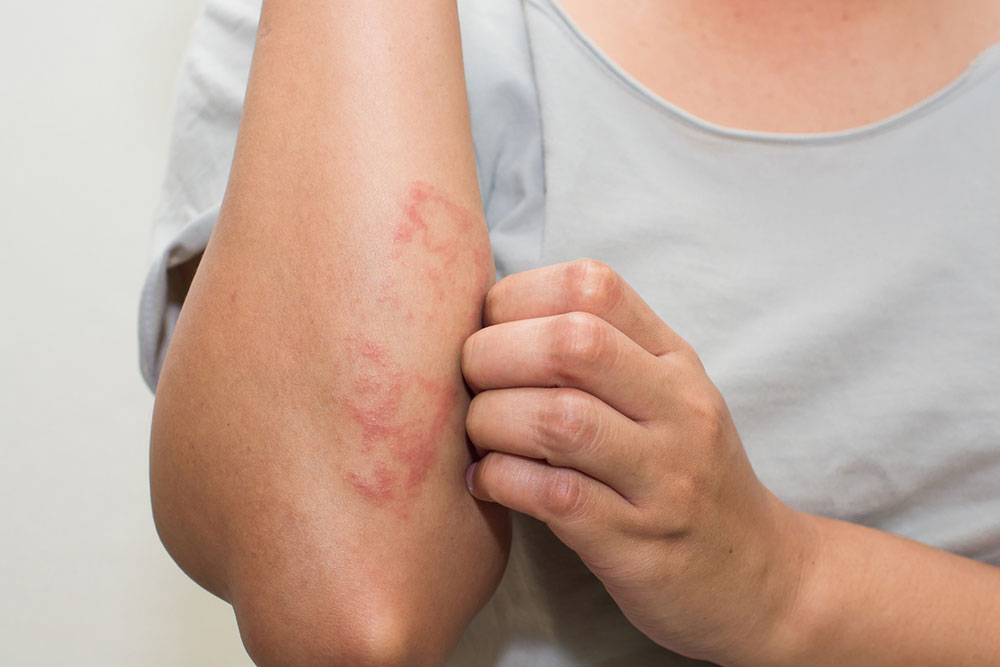
Eczema refers to a group of skin disorders characterized by red, bumpy rashes that can be itchy and uncomfortable. Various types exist, and recognizing the symptoms is crucial for effective treatment and management.
This common skin condition can be managed successfully once the triggers are identified. While irritating, understanding its causes helps in avoiding exacerbations, improving quality of life.
Signs of Eczema
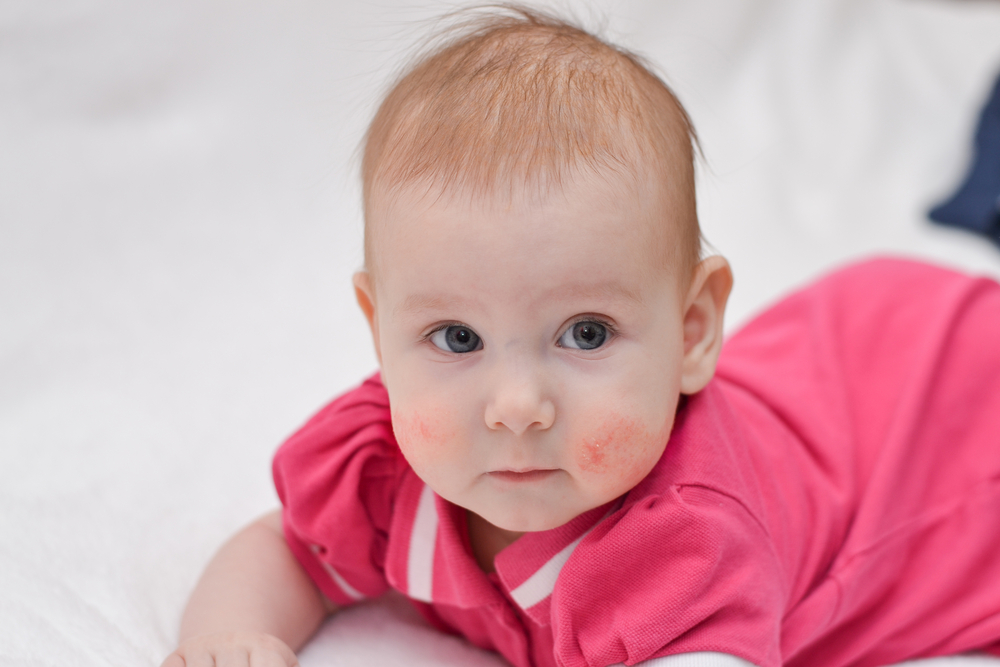
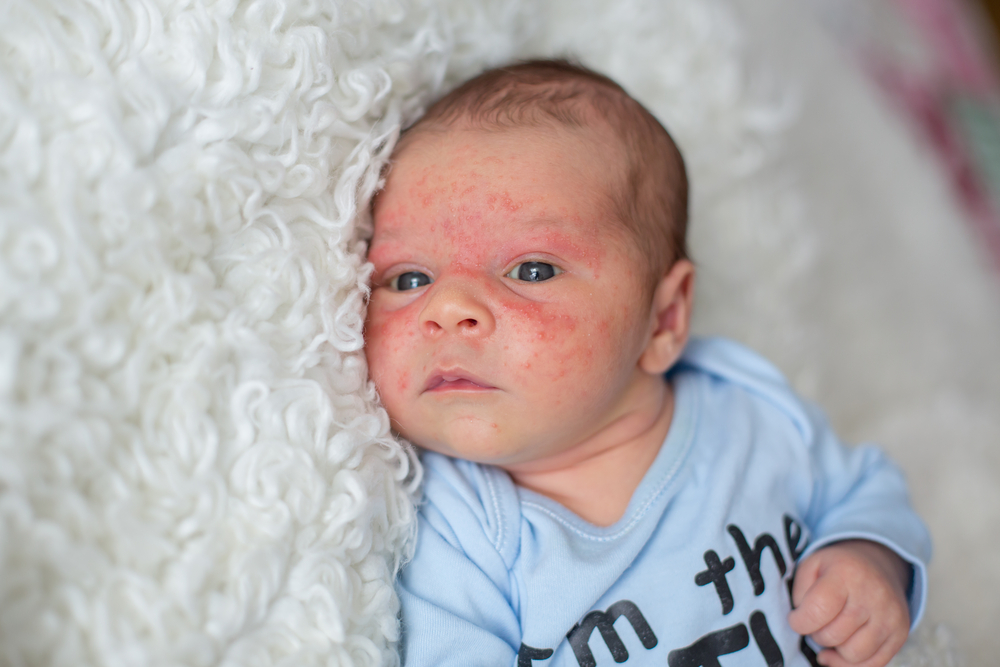
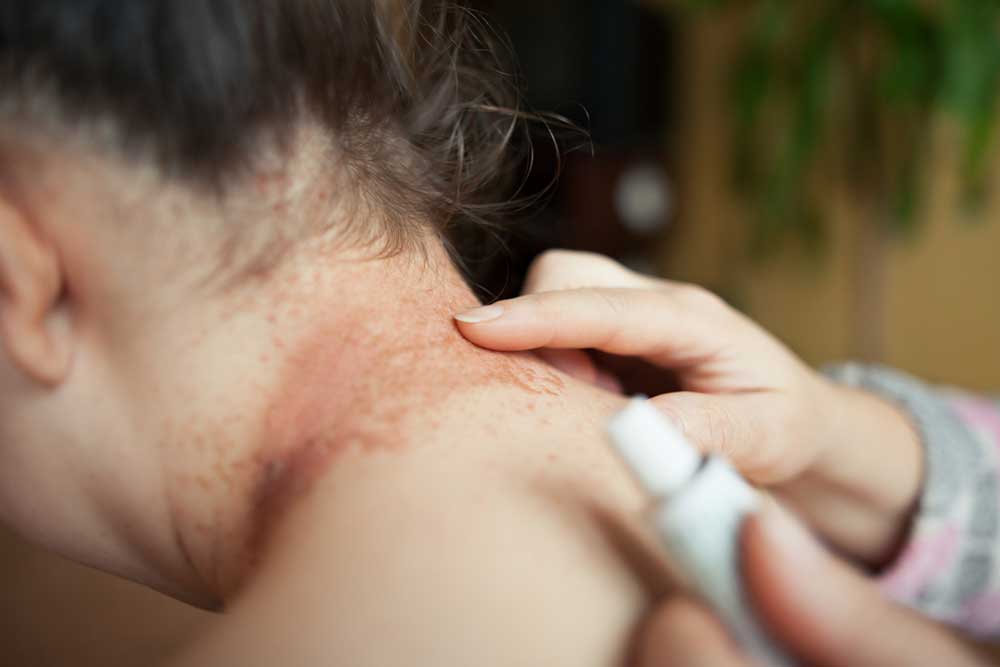
Typically, eczema begins with inflamed, red patches on the skin. The affected areas may become dry, thickened, and scaly, often accompanied by intense itching. The color of the rash varies depending on skin tone—appearing red in lighter skin and darker or lighter patches in darker skin. Scratching can lead to blisters and possible infections.
Common symptoms include redness, dryness, itching, dark patches, leathery skin, oozing blisters, and severe discomfort. Eczema can be triggered by an immune response to irritants like rough clothing, extreme temperatures, or allergens such as pet dander, soaps, or detergents. It is important to note that eczema is not contagious.
Types of Eczema
Atopic Dermatitis: Frequently impacting individuals with allergies like asthma, this form appears on the face, neck, ankles, and behind elbows, often beginning in childhood.
Stasis Dermatitis: Happens in people with circulatory problems, producing rashes primarily on the lower legs.
Scabies: Caused by mite infestation, mimicking other eczema forms with itchy rashes.
Fungal Dermatitis: Fungal infections that can appear similar to eczema; microscopic skin tests can confirm the presence of fungus.
Pompholyx: Characterized by blisters on palms, soles, or sides of fingers and toes.
Nummular Eczema: More common in older adults, presenting as round, scaly patches on the lower legs.
Lichen Simplex Chronicus: Leads to thickened skin, mainly on the neck and shins.
Seborrheic Dermatitis: Affects facial areas, scalp, and chest, often causing oozing in infants.
Xerotic Eczema: Dry, cracked skin prone to oozing, typically in arid conditions.
Allergic Contact Dermatitis: Results from repeated allergen exposure causing localized eczema reactions.
Management and Treatment Options
Keeping skin moisturized is vital to prevent dryness and itchiness. Regular gentle cleansing, moisturizing lotions, and topical corticosteroids can reduce symptoms. For infections, antibiotics may be necessary. For oozing sores, mild cleaning solutions and air drying help. Severe cases may require antihistamines, phototherapy, Tar treatments, or immunosuppressants like cyclosporine. Proper treatment and avoiding known triggers are central to living comfortably with eczema.
By understanding and avoiding triggers such as harsh soaps, rough fabrics, extreme weather, and certain foods, sufferers can minimize flare-ups. Consulting healthcare professionals helps establish personalized strategies to manage symptoms effectively, ensuring a better quality of life.