Recognizing and Managing Lupus: Symptoms and Prevention Tips
Lupus is a complex autoimmune disorder affecting various body parts. Recognizing symptoms like fatigue, rashes, and joint pain early helps in effective management. Treatment options include medications such as steroids and immunosuppressants. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle with proper diet, sun protection, and regular exercise can significantly improve life quality. Consulting healthcare professionals promptly is crucial for controlling this unpredictable disease and preventing complications.
Sponsored
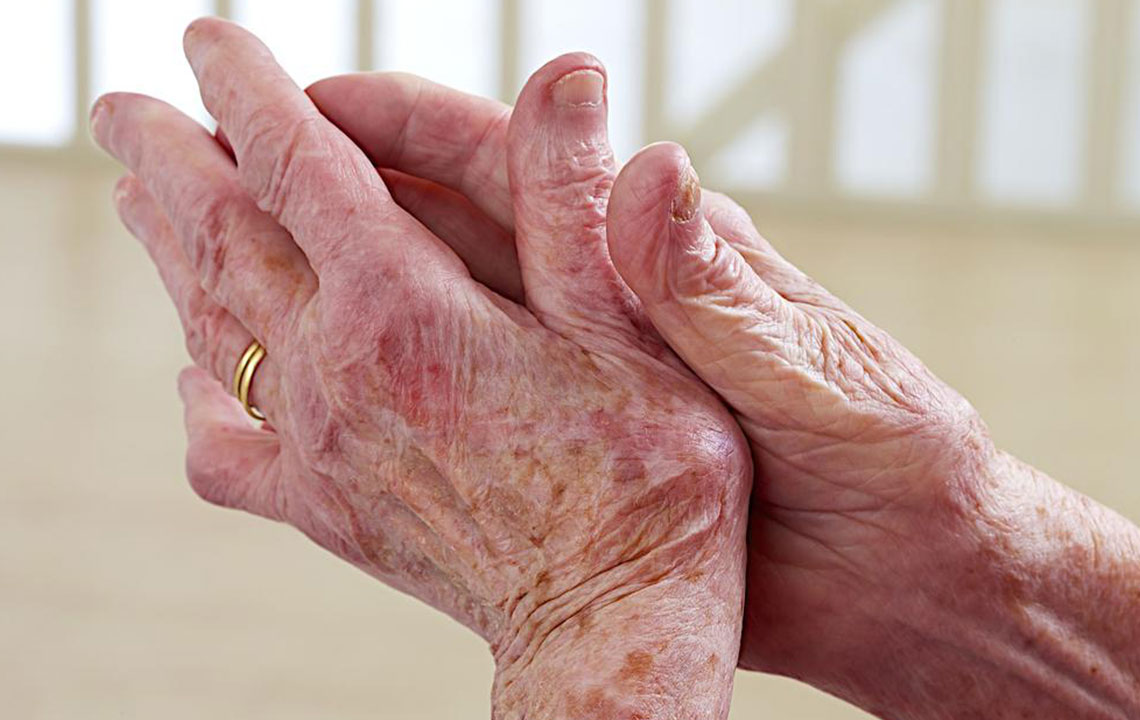
Lupus, scientifically called Systemic Lupus Erythematosus, is a long-term autoimmune disease that targets various parts of the body. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues. Although genetic factors and lifestyle can influence its development, family history is not always a determining factor. According to the Lupus Foundation of America, approximately 1.6 million Americans live with lupus. The condition affects both sexes, mainly women aged 14 to 45 years.
Common lupus symptoms include:
Extreme fatigue – Persistent tiredness is often the first sign, with energy gradually decreasing.
Low-grade fever – Occasional mild fever (99°F-101°F) may signal inflammation or infection, requiring medical attention.
Muscle and joint pain – Stiffness and swelling in joints, especially mornings, with reddish skin and discomfort during movement.
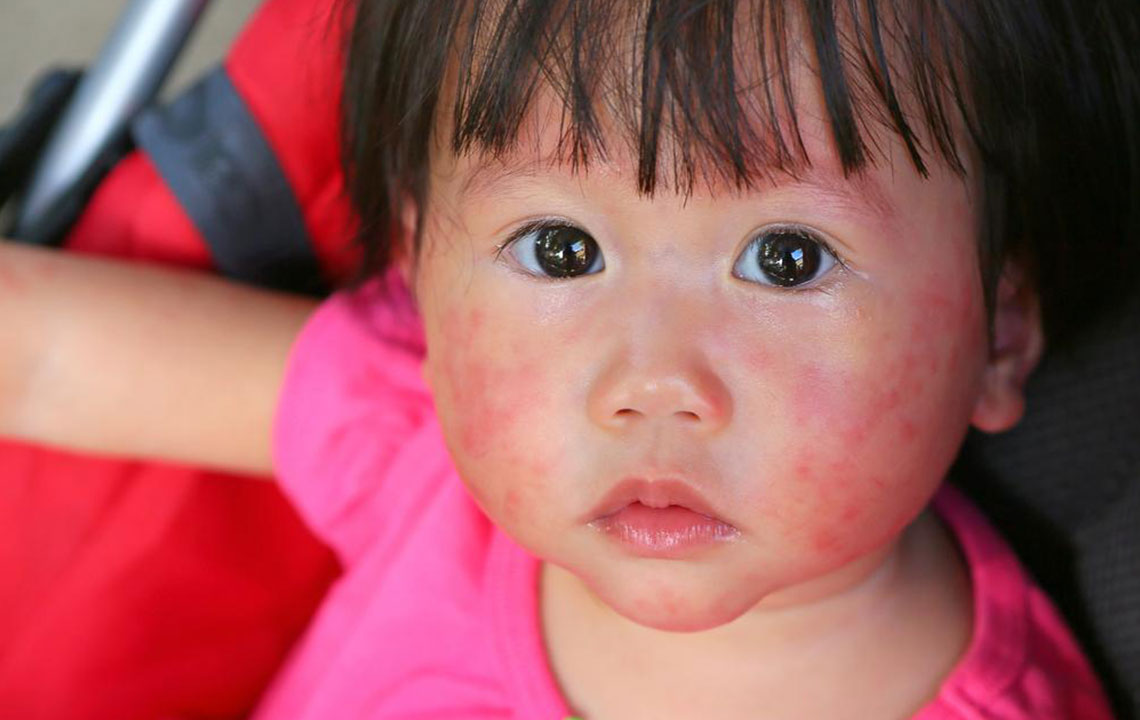
Butterfly rash – Redness and irritation on cheeks and nose, often worsened by sunlight.
Chest discomfort – Pulmonary inflammation can cause chest pain, especially when breathing.
Other symptoms include dry eyes due to Sjogren’s syndrome, gastrointestinal issues like heartburn, hair thinning or loss, and hormonal changes leading to decreased libido and irregular periods. Lupus can also affect blood vessels and impair vision.
Managing Lupus Effectively
Lupus treatment varies, as the condition is unpredictable. It depends on factors such as age and health status. While some cases may not require medication, severe cases need ongoing treatment. Common therapies involve:
Steroids – Topically or systemically for rashes and inflammation, used at low doses to minimize side effects.
Plaquenil – To control joint and muscle symptoms.
Cytoxan – Chemotherapy agent targeting kidney and brain involvement.
Imuran – For serious symptoms and organ rejection prevention.
Rheumatrex – Used in skin and joint conditions, especially if other drugs are ineffective.
CellCept – Suppresses immune response, aiding transplant success.
Rituxan – For refractory cases, including lymphoma and rheumatoid arthritis.
Enhancing Life with Lupus
Regular exercise like walking and swimming boosts energy and strengthens bones.
An appropriate diet and sufficient rest are crucial for managing symptoms.
Avoid alcohol and smoking, as they interfere with medications and harm health.
Protect yourself from sun exposure by wearing sunglasses, applying sunscreen, and avoiding peak sunlight hours.
Monitor low-grade fevers as potential signs of internal infection.
Maintain open communication with your healthcare provider and adhere to prescribed treatments.
Understanding early signs and seeking prompt diagnosis can improve quality of life, even though a complete cure remains elusive.