Understanding Tendonitis: Causes, Symptoms, Stages, and Treatment Strategies
This article provides a comprehensive overview of tendonitis, highlighting its causes, symptoms, progression stages, and treatment options. Emphasizing early management and preventive measures, it guides readers on how to handle tendon inflammation effectively and when to seek medical intervention to avoid complications like ruptures requiring surgery.
Sponsored
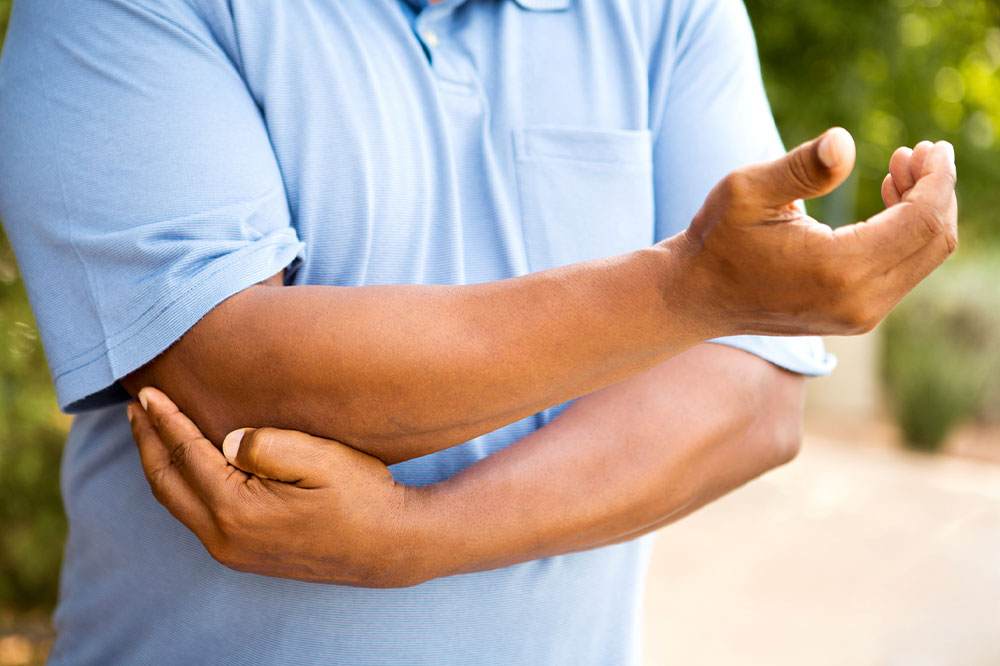

Tendonitis involves inflammation of the tendons, which are fibrous cords connecting muscles to bones. This condition commonly affects joints in the shoulders, elbows, wrists, knees, and heels. Early treatment is vital to prevent progression and potential tendon rupture, which might require surgery.
Causes of Tendonitis
Tendonitis typically results from repetitive stress on tendons, often due to overuse in sports or work activities. As with aging, tendons lose flexibility, increasing vulnerability. It frequently affects areas like the thumb base and elbows, causing discomfort and inflammation.
Recognizing Symptoms
Symptoms include pain that worsens with movement, joint stiffness, swelling, redness, and difficulty performing daily tasks such as gripping or turning doorknobs. Moving the affected wrist might produce a crackling sensation.
Progression of Tendonitis
The severity of tendonitis varies across stages. In early stages, fatigue may occur with activity, but performance remains unaffected. As it advances, discomfort persists through all activity phases, leading to reduced movement and functionality. Severe cases involve constant pain, swelling, and altered movement patterns, often requiring complete rest.
Non-invasive Management Options
Rest, ice application, compression, and elevation are essential. Avoid activities that strain the tendon and use supportive wrist braces if needed. Physical therapy focusing on stretching and strengthening can help. Proper technique during sports and work can prevent worsening. If symptoms persist, consulting a healthcare provider is recommended.
Surgical Intervention
Surgery may be necessary in severe cases, involving tendon realignment, removal of bone spurs, or calcium deposits. Chronic inflammation, especially in tendons like the Achilles or rotator cuff, may lead to rupture. Early diagnosis and treatment are key to recovery and avoiding permanent damage.