Recognizing Early Symptoms of Lupus: Key Indicators to Watch For
This article highlights key early signs of lupus, including dry mouth, fatigue, skin rashes, and joint pain. Recognizing these symptoms aids in timely diagnosis and management, preventing severe complications. Understanding lupus indicators can significantly improve patient outcomes and promote early intervention.
Sponsored
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells, causing widespread damage. This disruption hampers immune function, increasing susceptibility to infections and leading to serious health issues. Early detection of lupus is crucial to prevent complications, making awareness of its symptoms essential.
Dry mouth and eyes: Malfunction of tear and saliva glands results in persistent dryness, often mistaken for minor infections or autoimmune disorders.
This symptom may develop gradually and be confused with other autoimmune conditions, emphasizing the importance of medical consultation.
Chronic fatigue: Persistent tiredness that doesn't improve with rest can be an early warning sign, even if you sleep well.
Unexplained fever: Recurrent, low-grade fevers with no apparent cause can indicate immune system trouble.
Thyroid dysfunction: Autoimmune impacts on the thyroid gland can lead to metabolic issues affecting overall health.
Hair shedding: Thinning hair, scalp inflammation, or loss of facial hair may mark early lupus activity.
Digestive symptoms: Heartburn, acid reflux, and gastrointestinal discomfort can signal underlying autoimmune involvement.
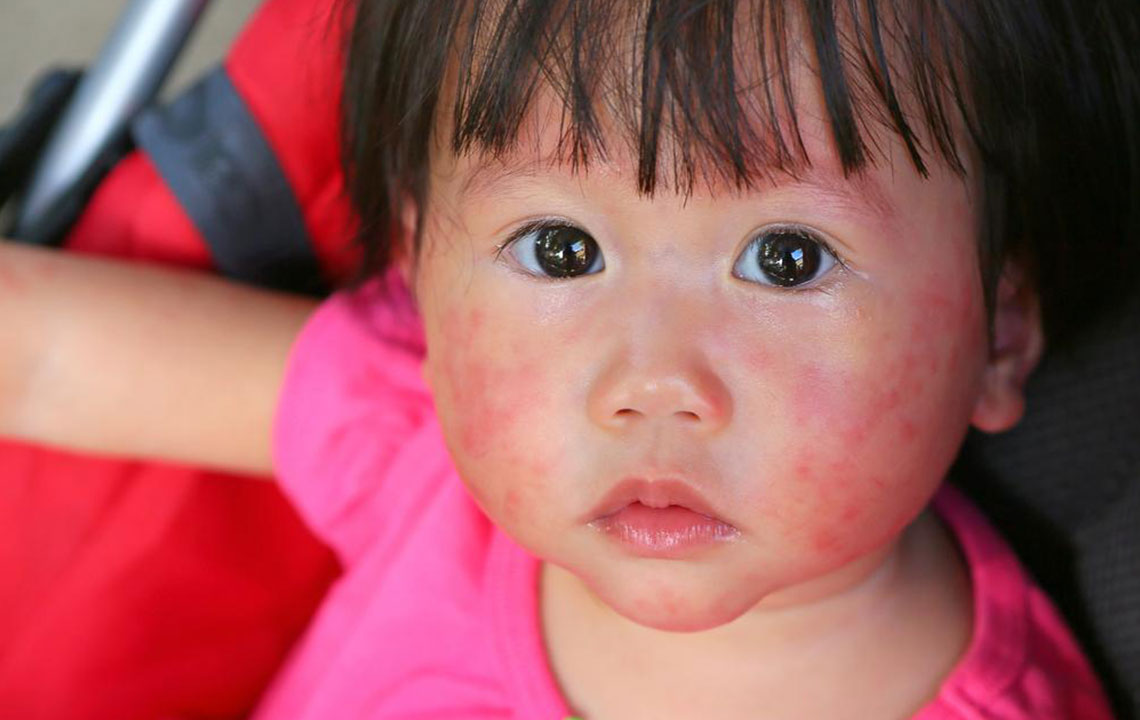
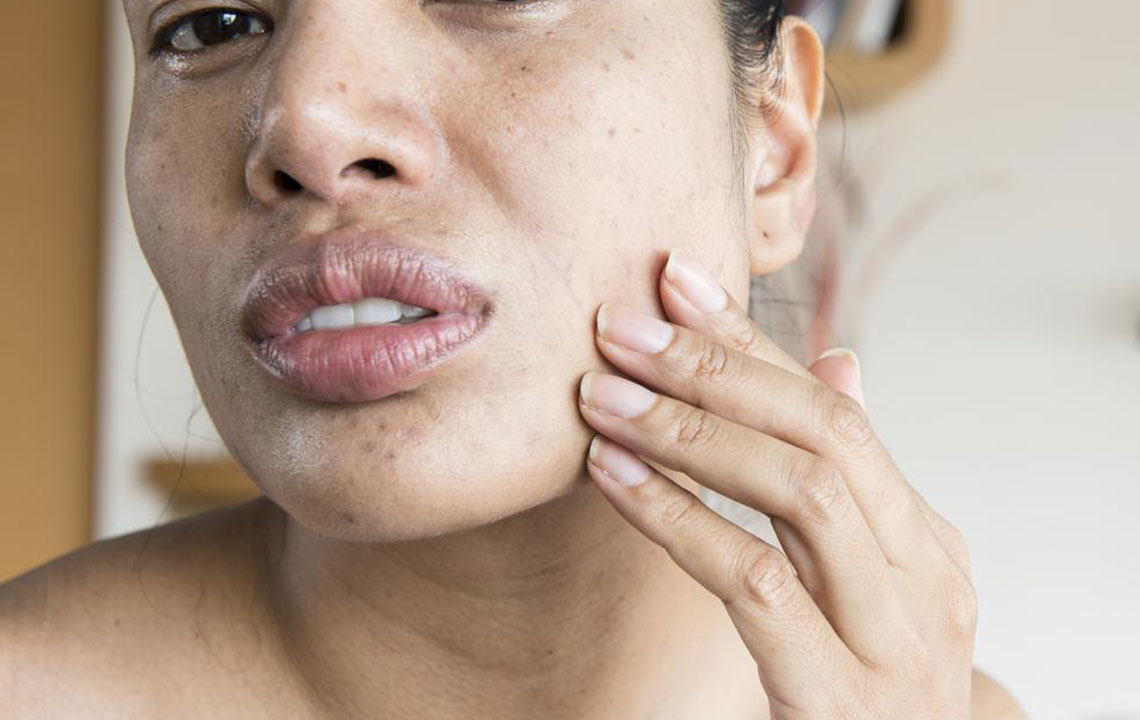
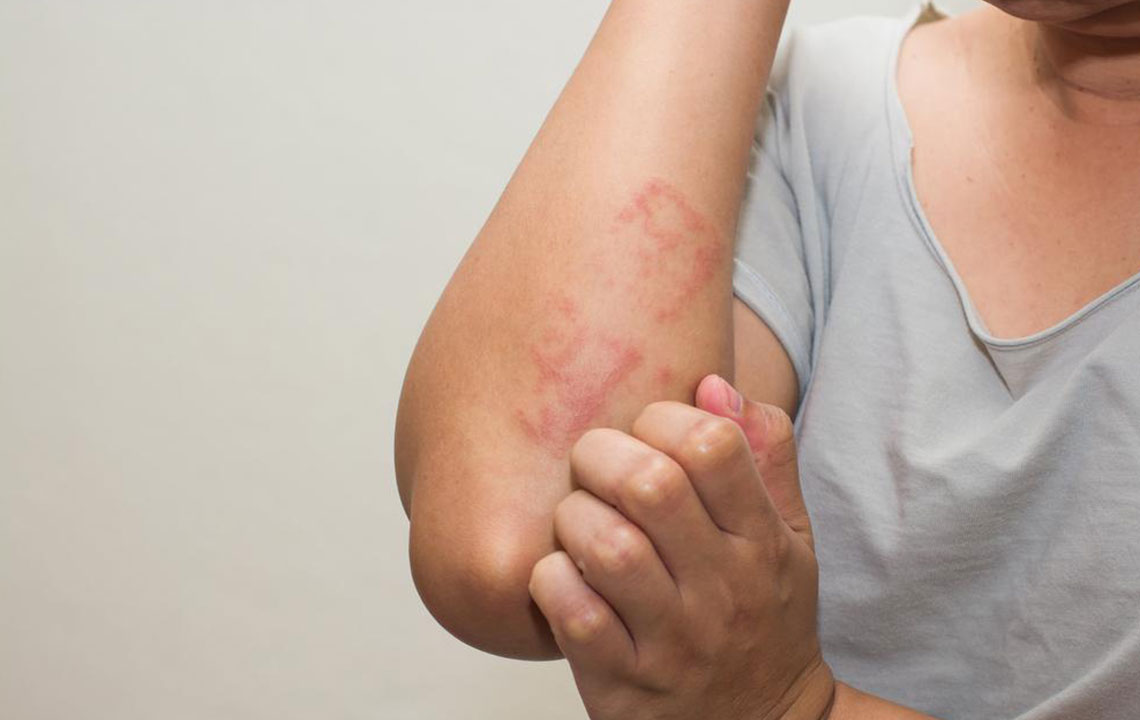
Skin rashes: Butterfly-shaped rash across the cheeks and nose is a hallmark sign, affecting about half of lupus patients.
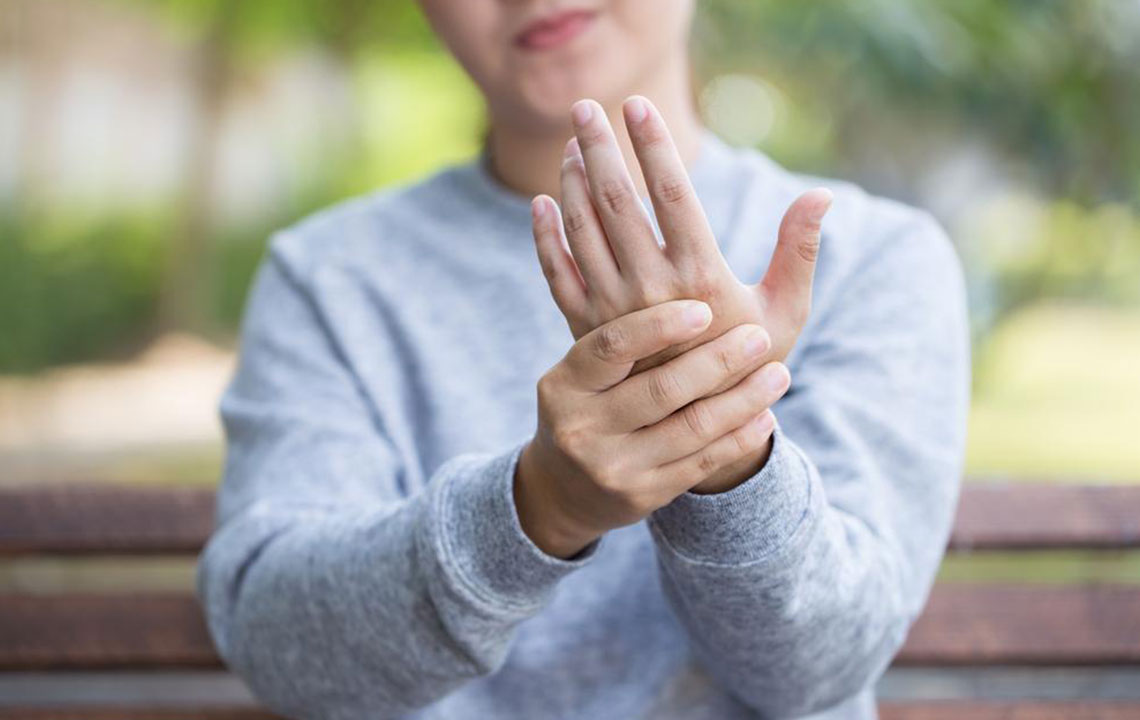
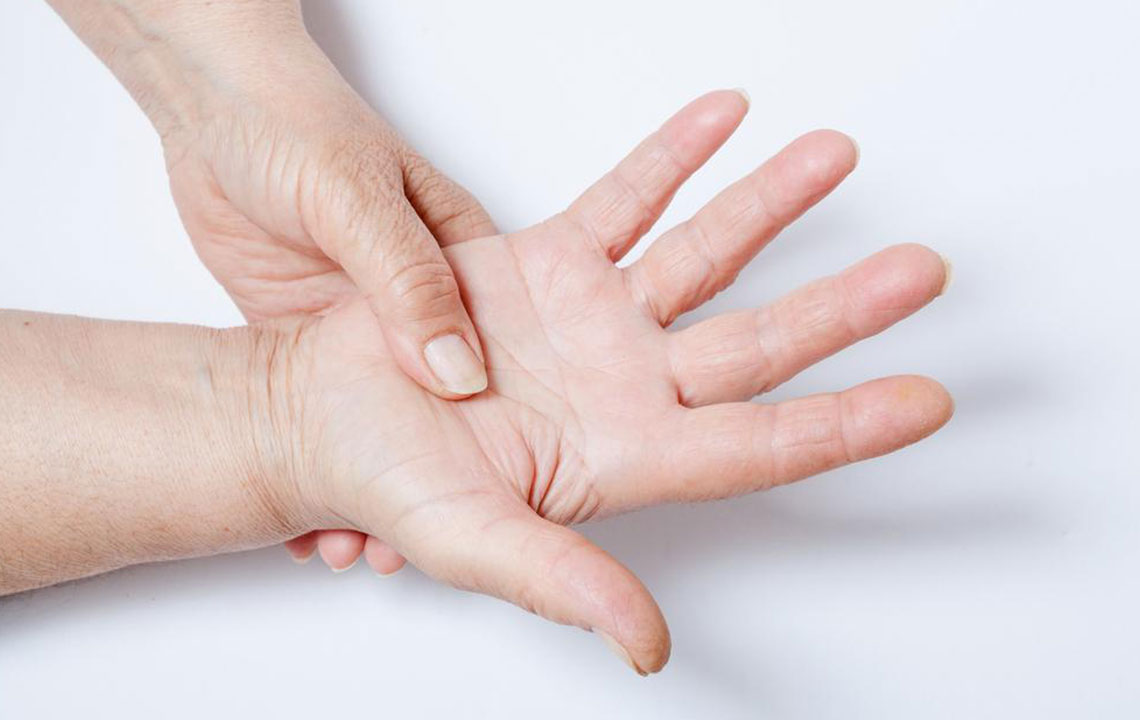
Joint discomfort: Pain, stiffness, and swelling in joints often prompt medical evaluation.
Kidney inflammation: Nephritis causes impaired kidney function, including toxin filtration and waste removal.
Chest pain: Inflammation of pulmonary vessels leads to chest discomfort, often described as pleurisy.