Comprehensive Guide to Asthma Testing and Diagnosis
This article provides a detailed overview of asthma testing methods, including spirometry, peak flow measurement, allergy testing, immune panels, and imaging. It highlights how these diagnostics help determine asthma presence and severity, guiding effective treatment plans. The guide emphasizes the importance of accurate testing for proper management and highlights common procedures used by healthcare providers to diagnose asthma effectively.
Sponsored
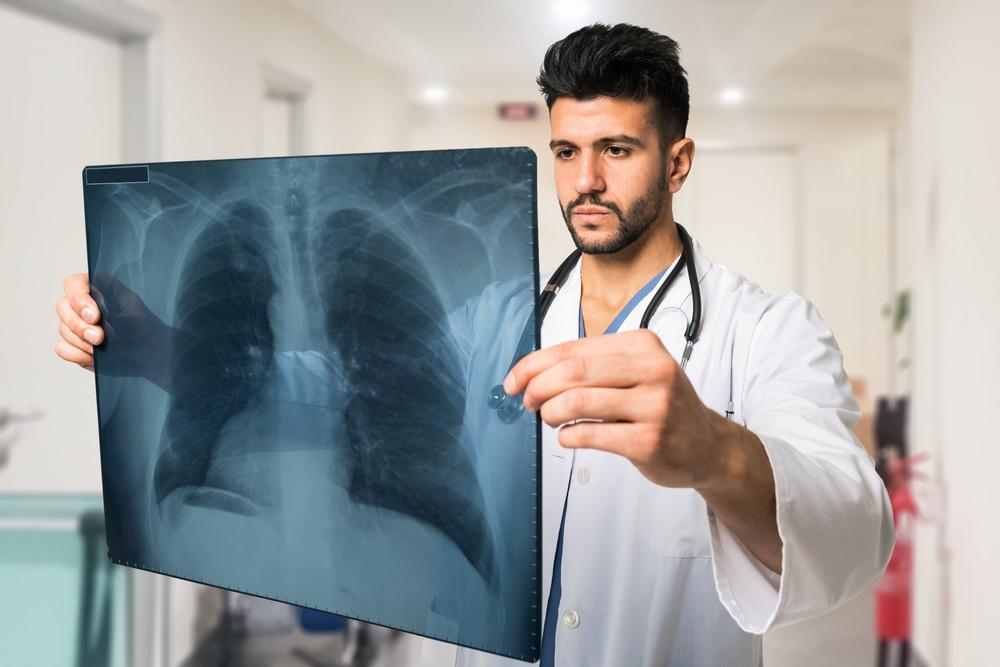
Doctors utilize various tests to accurately identify asthma and assess its severity.
Spirometry
Spirometry measures lung function by having patients breathe into a device that records airflow. It calculates Forced Expiratory Volume (FEV) and Total Lung Capacity (FVC). Reduced FEV and FEV:FVC ratios indicate airflow restriction typical of asthma. Administering bronchodilators before testing can show improvements, confirming diagnosis.
Peak Flow Monitoring
A handheld peak flow meter measures how much air you can exhale forcefully. Consistent readings help evaluate control levels, with color codes indicating soundness of asthma management.
Allergy Evaluation
Suspected allergic asthma prompts allergy testing. Symptoms often worsen after allergen exposure, linked to Immunoglobulin E (IgE) activity, which causes lung inflammation and constriction. Skin prick tests and blood IgE levels help identify specific allergies.
Immune Assessment
Blood tests may show elevated White Blood Cells and eosinophils, indicating inflammation associated with allergic responses.
Imaging Studies
Chest X-rays can reveal lung hyperinflation and exclude other conditions. These imaging techniques support comprehensive asthma diagnosis.