Effective Strategies for Managing Shingles
Learn about the effective treatments and natural remedies for shingles, a painful rash caused by the reactivation of the Varicella Zoster virus. This article covers antiviral medications, home care tips, and lifestyle adjustments to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications. Early intervention is crucial for managing pain and reducing risks of long-term issues such as postherpetic neuralgia. Natural remedies like soothing baths and dietary changes can complement medical treatments, supporting faster recovery. Understanding these management strategies helps those affected regain comfort and health.
Sponsored
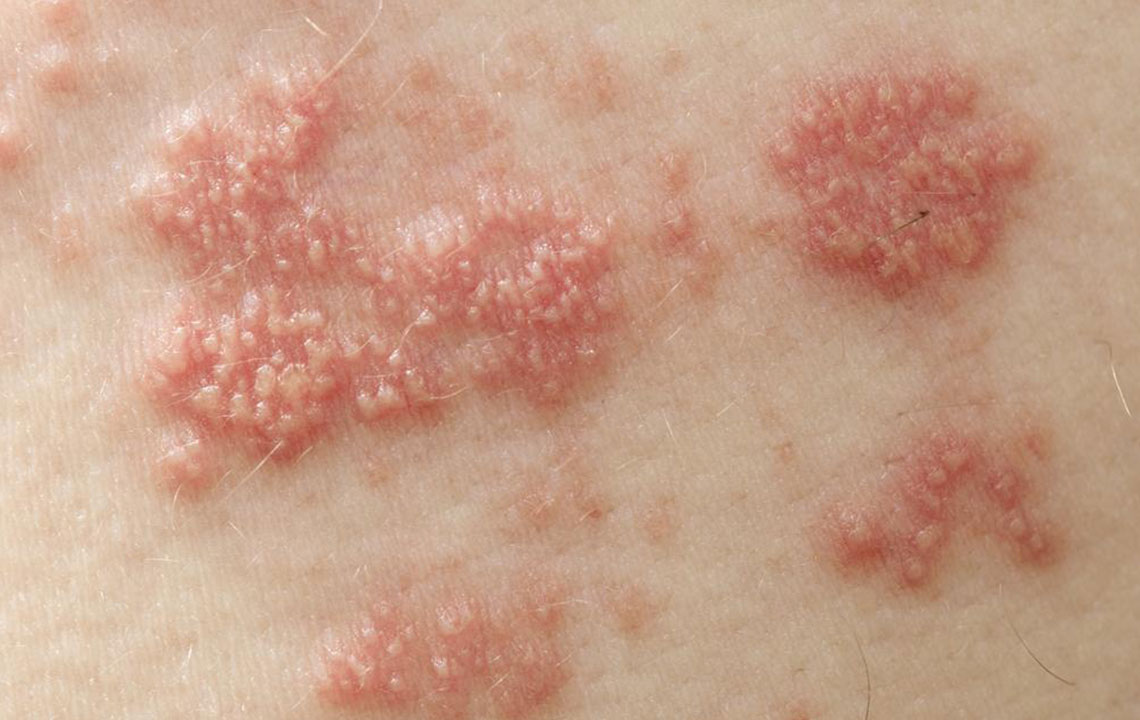
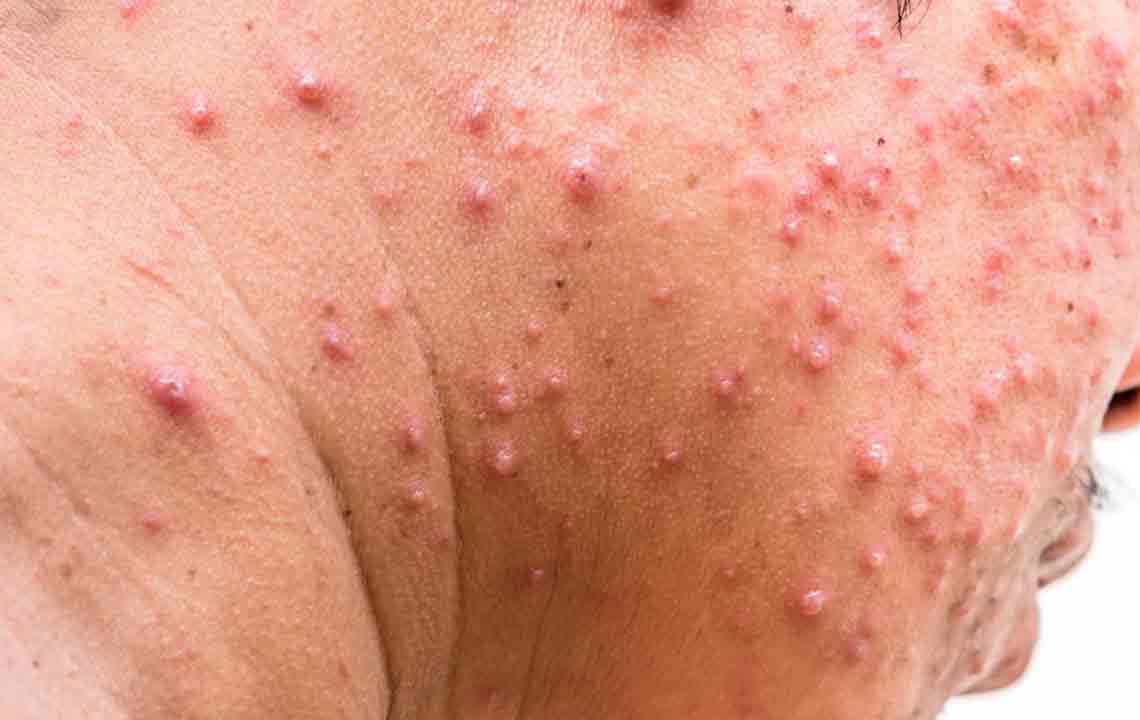
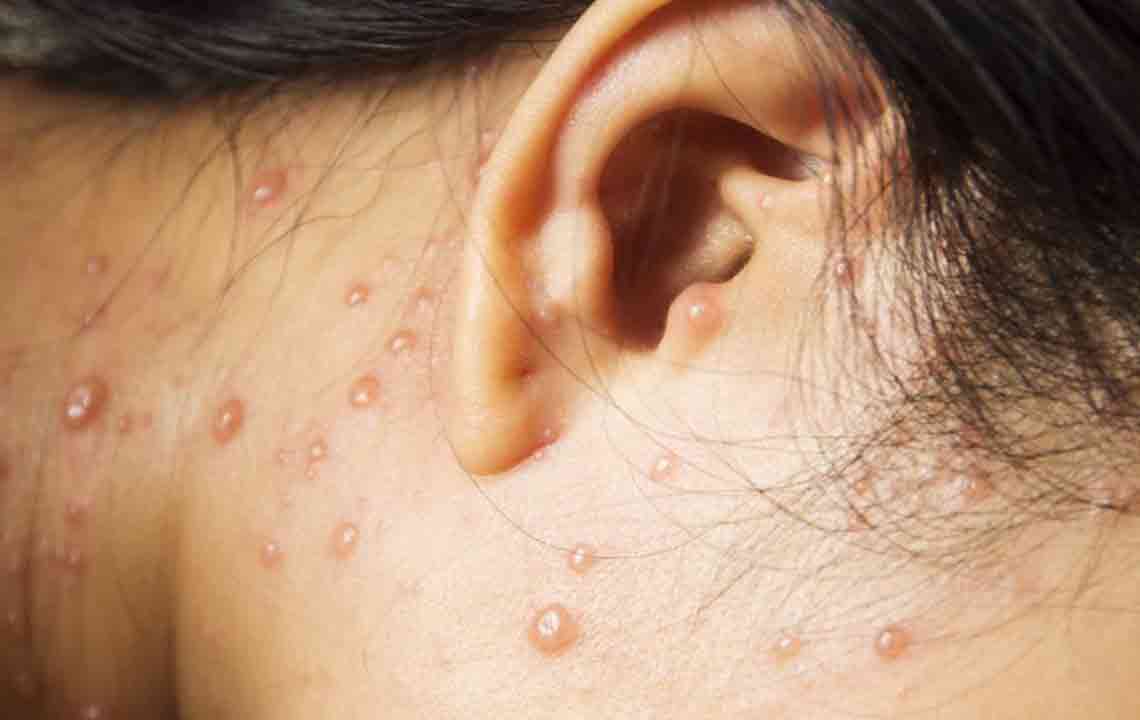
Shingles is a skin condition caused by the reactivation of the Varicella Zoster virus, resulting in a painful rash that often appears as a band or strip on the face or body. Also known as herpes zoster, this condition commonly affects older adults or those with weakened immune systems due to stress or injury.
The virus stays dormant in nerve roots after chickenpox recovery but can reactivate later, especially when immunity wanes. While the exact cause remains unclear, reactivation leads to shingles. It can be contagious to those who haven't had chickenpox or vaccination, spreading the virus through contact with the rash.
The primary triggers include the virus re-emerging after years of dormancy, usually triggered by immune suppression.
There is no definitive cure for shingles, but treatments can ease symptoms and reduce duration.
Treatment options focus on alleviating symptoms and preventing complications. Antiviral medications are most effective if started within three days of symptom onset, helping shorten the illness and lower the risk of postherpetic neuralgia. For persistent pain, doctors might recommend antidepressants or topical creams. In severe cases, corticosteroids may be prescribed, especially if antiviral therapy isn't sufficient.
Postherpetic neuralgia, a common complication causing prolonged pain, affects a minority of shingles patients and can be alleviated with over-the-counter medications like topical anesthetics and antidepressants. In complicated cases like disseminated zoster, antiviral and antibiotic treatments are used to prevent further spread and organ involvement. Eye-related shingles require antiviral therapy along with rest and soothing compresses to protect vision. Inner nerve involvement may demand specialized treatments based on severity and location.
Natural remedies and home care can also support shingles recovery:
Soothing baths with colloidal oatmeal or cornstarch can help reduce discomfort. Use lukewarm water to avoid aggravating blisters.
Applying cool, damp compresses to affected areas can provide relief and reduce inflammation, but avoid using ice directly on the skin.
Applying a paste made from cornstarch and baking soda can help relieve itching. Apply for 15 minutes and repeat as needed.
Eating a nutrient-rich diet with vitamins A, B-12, C, and E enhances immune function. Incorporate citrus fruits, leafy greens, eggs, poultry, and tomatoes to support recovery.