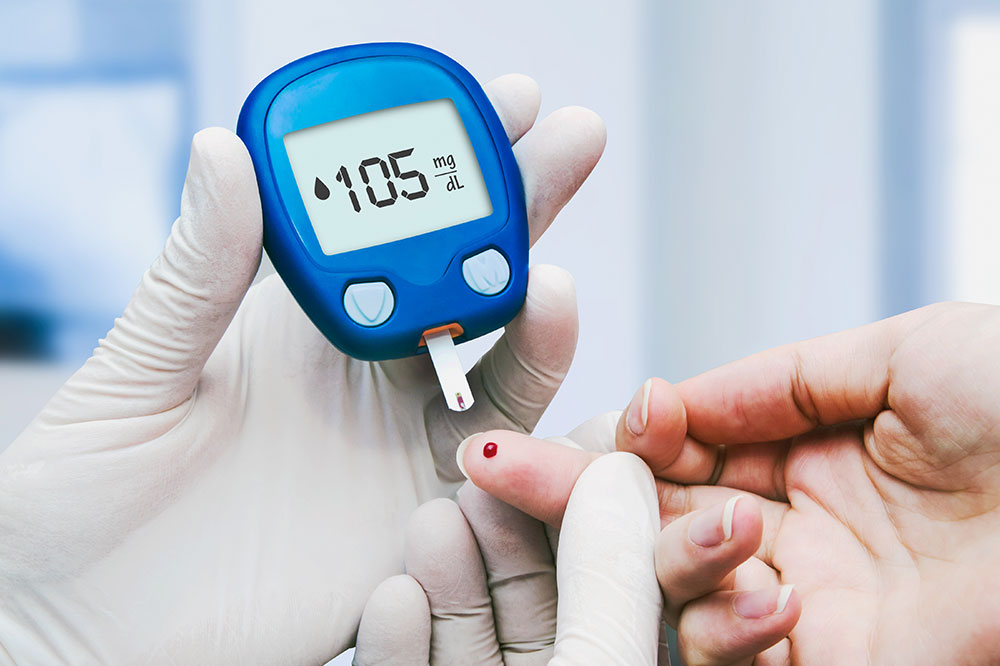
Understanding the Different Types of Diabetes and Their Management
Explore the various types of diabetes, including Type 1, Type 2, and gestational diabetes. Learn about their causes, symptoms, and management strategies. The article emphasizes lifestyle changes, medication, and the importance of regular health checks in controlling blood sugar levels, as a permanent cure remains undiscovered. Proper understanding and management are crucial to reduce health risks associated with this widespread condition.
Sponsored
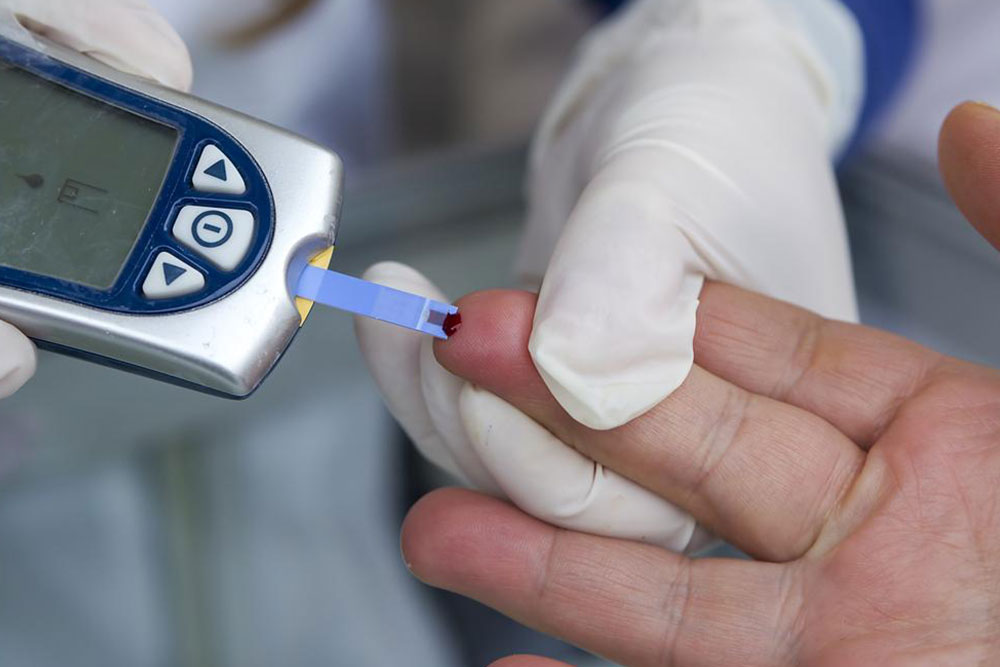
Diabetes is a prevalent chronic condition affecting many individuals worldwide, potentially leading to serious health issues if unmanaged. It involves disruptions in insulin production or utilization. Insulin, produced by pancreatic beta cells, is essential for converting sugar in the bloodstream into energy. In diabetes, inadequate insulin causes sugar to accumulate in the blood, increasing risks such as kidney damage and heart problems. Managing blood sugar through regular monitoring, medication, diet, and exercise is crucial as there is currently no cure for the disease.
Physical activity and a balanced diet help control blood sugar levels. There are primarily two main types of diabetes: Type 1 and Type 2, along with a rare form called gestational diabetes.
Type 1 Diabetes
Usually diagnosed during childhood or adolescence, though it can occur in adults, this form occurs when the immune system attacks pancreatic beta cells, resulting in little or no insulin production. Sometimes called LADA in adults, this condition requires insulin therapy and careful meal planning for blood sugar control. Approximately 10% of diabetics have Type 1 diabetes.
Type 2 Diabetes
Characterized by the body's inability to effectively use insulin (insulin resistance) or insufficient insulin production, Type 2 is the most common form, affecting around 90% of diabetics. It often develops in adulthood but can also occur in children, especially with genetic predisposition. Management involves lifestyle changes, medication, and insulin therapy when necessary.
Gestational Diabetes
A temporary condition during pregnancy, affecting approximately 2-4% of pregnant women, gestational diabetes increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes for both mother and child. Blood sugar testing during pregnancy assists diagnosis, and treatment includes diet, exercise, and monitoring, with medication if blood sugar levels become dangerously high.
Despite extensive research, a definitive cure for diabetes remains elusive. Until then, maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise are vital in managing the disease and preventing complications.