Essential Guide to Electrical Cable Types and Selection
Learn about the key types of electrical cables, including their sizes, color codes, and voltage categories. This guide helps in choosing the right cables for safe and effective electrical projects, covering low, medium, and high voltage options.
Sponsored
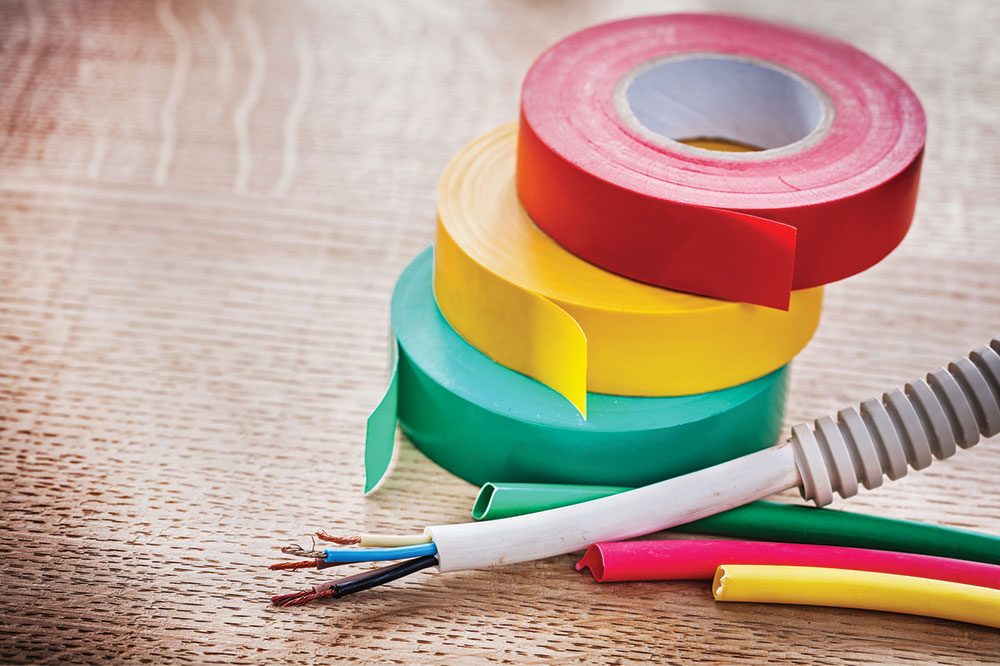

Electrical cables consist of multiple conductors enclosed in a protective sheath, facilitating energy transfer between points. These cables vary in design, materials, colors, and sizes based on their application. When planning an electrical setup, choosing the right cable is crucial. Understanding key aspects such as cable gauge, color coding, and voltage capacity will help ensure safety and efficiency.
Cable Gauge and Size
The size of an electrical cable relates to the thickness of its internal wires, with lower gauge numbers indicating thicker conductors. The number of wires and their gauges are often combined, like a 10/3 cable with three 10-gauge conductors. Ground wires are typically labeled with a 'G'.
Color Coding
Insulation color indicates respectives functions—neutral, active, or grounding. Different regions may have distinct color standards, but generally, active wires avoid light blue, yellow, green, or black. Awareness of local color codes aids proper wiring and safety.
Voltage Ratings
Electrical cables are classified based on their voltage capacity:
Low Voltage These cables handle up to 750V or 1000V, used for household wiring, industrial applications, and renewable energy systems. Types include armored, fire-resistant, solar, and rubber cables.
Medium Voltage Ranging from 1kV to 36kV, these cables connect substations to transformers. Common types include RHZ1, HEPRZ1, and MV-90.
High Voltage Above 36kV, these cables transmit electricity from power plants to substations, used in large-scale power distribution.
Grasping these concepts can assist in selecting appropriate cables, ensuring safe, reliable electrical installations.