Comprehensive Guide to Managing Eczema Symptoms
Eczema is a persistent skin condition causing itching, redness, and cracking. This guide explains symptoms, triggers, and both natural and medical treatments to control and soothe flare-ups. While no cure exists, proper skin care and lifestyle changes can significantly improve quality of life for sufferers. Learn about effective remedies, medications, and preventive measures to manage eczema effectively and maintain healthy skin.
Sponsored
Understanding Eczema: Key Insights
Eczema is a chronic skin disorder characterized by inflamed, itchy, cracked, and sometimes sore patches of skin. It includes various conditions such as atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, dyshidrotic eczema, neurodermatitis, and stasis dermatitis. Symptoms can fluctuate, occurring frequently or sporadically, impacting quality of life. Although no cure exists, effective management aims to soothe irritation and prevent flare-ups. For many sufferers, natural treatments combined with medical advice can significantly improve skin health and comfort.
Important Facts about Eczema
Dietary triggers like dairy and nuts may provoke symptoms.
Age influences symptom presentation; common signs include itchy, red patches.
Environmental factors such as pollen, dust, and smoke can worsen symptoms.
There is no definitive cure; treatments focus on symptom relief and skin restoration. It is not contagious.
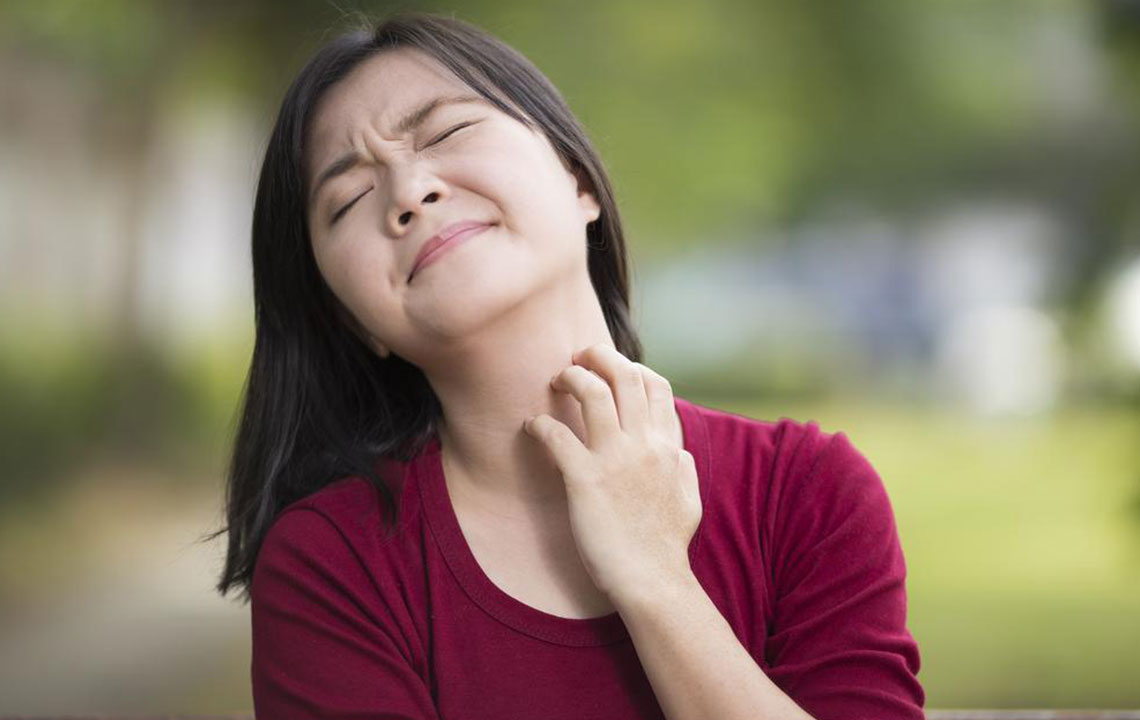
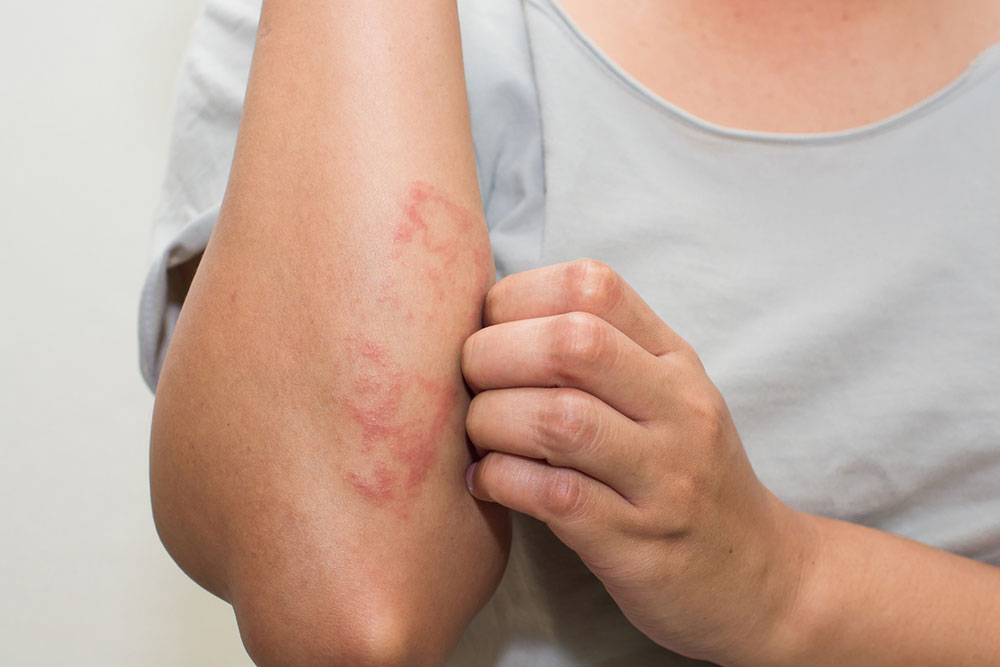
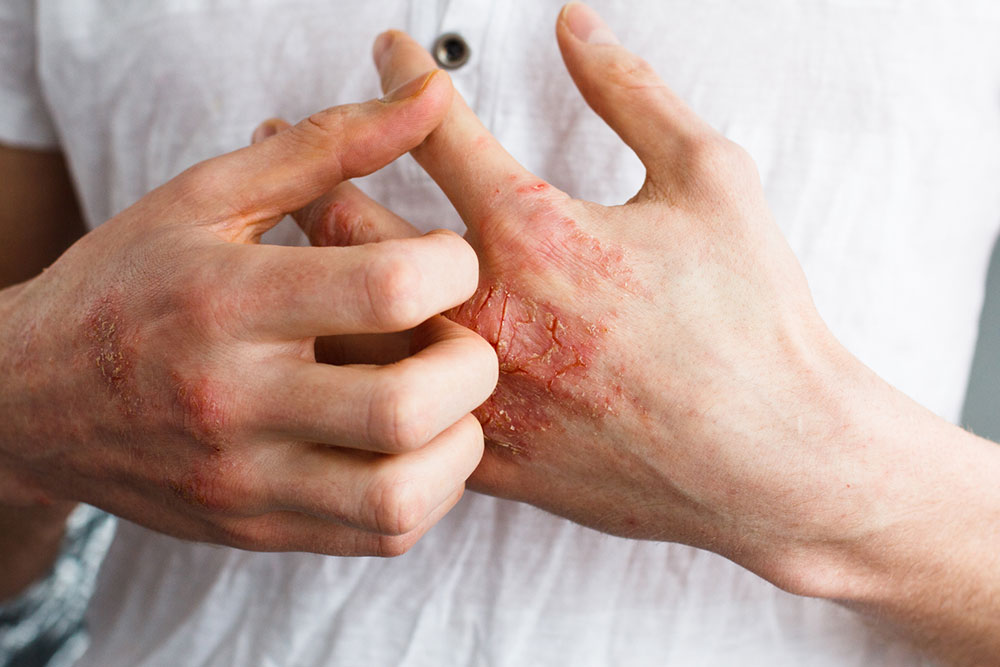
Recognizing Eczema Symptoms
Small bumps that may ooze liquid during flare-ups.
Rough, dry, cracked skin that can become inflamed.
Discolored patches on face, hands, feet, neck, or scalp.
Swelling and irritation from itching.
Persistent rashes causing discomfort.
Managing Eczema Effectively
Although a cure remains unavailable, treatments aim to reduce inflammation and prevent outbreaks. Approaches depend on age and severity, with some individuals experiencing remission over time. Lifestyle adjustments and natural remedies can help control symptoms and improve skin condition.
Home Strategies for Eczema Relief
Use vegetable shortening: A moisturizer that restores dry, flaky skin.
Incorporate turmeric: Its active compound, curcumin, reduces inflammation and speeds healing.
Apply tea tree oil: Its antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties ease itching and soothe skin.
Eat flaxseeds: Rich in omega-3 fatty acids to fight inflammation.
Consume fermented cod liver oil: Supports healthy skin and reduces inflammation.
Take magnesium baths: Combine magnesium flakes, sea salt, and essential oils to calm inflamed skin.
Enjoy probiotics: Foods like kefir and miso may decrease flare-ups.
Medical Options
Topical corticosteroids: Reduce inflammation and soothe irritated skin.
Systemic corticosteroids: Prescribed for severe cases, but caution is advised against long-term use.
Antiviral and antifungal medications: Treat infections associated with eczema.
Antibiotics: Address bacterial skin infections.
Antihistamines: Minimize itching and improve sleep.
Barrier repair moisturizers: Keep skin hydrated and protected.
Calcineurin inhibitors: Suppress immune response to reduce inflammation.
Phototherapy: Controlled UV exposure to manage symptoms under medical supervision.
Recognizing and adopting suitable treatments can help manage eczema effectively, even though it cannot be fully cured. Continued skin care and avoiding triggers are essential to prevent flare-ups and maintain healthy skin.