Effective Strategies to Reduce LDL Cholesterol Levels
Learn practical and effective methods to lower LDL cholesterol naturally through diet, exercise, and lifestyle changes. Reducing LDL levels can decrease the risk of heart disease, improve overall health, and potentially eliminate the need for medication. Implementing healthy eating habits, increasing physical activity, quitting smoking, managing weight, and limiting alcohol intake are essential steps toward a healthier heart. Consult your doctor for personalized guidance and support your journey to better cardiovascular health with these proven strategies.
Sponsored

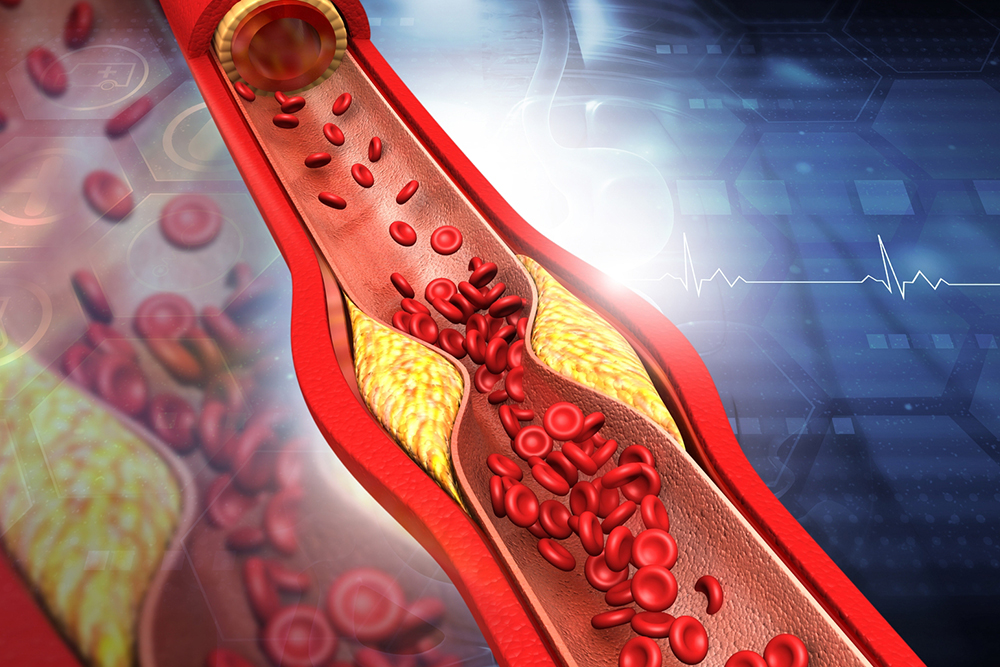
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL), often called the "bad" cholesterol, tends to accumulate in arterial walls, narrowing blood flow. This buildup can cause artery hardening, increasing the risk of heart attacks and other cardiovascular problems.
Factors Contributing to Elevated LDL Unhealthy diets, stress, pollution, sedentary lifestyles, and genetics are primary factors that raise LDL levels.
Indicators of High LDL High LDL usually produces no symptoms; only blood testing can detect elevated cholesterol levels.
How to Lower Bad Cholesterol Naturally Adopting simple lifestyle changes can significantly reduce LDL levels and potentially eliminate the need for medication. Here are practical tips:
Adopt Heart-Healthy Eating Habits: Even if you have an unhealthy diet history, changing your food choices can dramatically impact your cholesterol. Focus on nutritious, balanced meals.
Choose Healthy Fats: Limit saturated fats found in red meat and full-fat dairy. Instead, opt for lean meats, skimmed dairy, and monounsaturated fats in olive or canola oils. Keep saturated fat intake under 7% of daily calories.
Avoid Trans Fats: Trans fats, common in processed snacks and fried foods, raise bad cholesterol and lower good cholesterol, posing severe heart risks. Read labels carefully and steer clear of partially hydrogenated oils.
Incorporate heart-friendly foods like leafy greens, fruits, oatmeal, nuts, fish oils, and high-fiber, low-fat options into your diet.
Increase Physical Activity: Regular exercise can help lower LDL. Even brief, consistent activity like brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or climbing stairs can make a difference. Group workouts or exercising with friends enhance motivation.
Quit Smoking: Quitting smoking boosts HDL and alleviates blood pressure, reducing heart attack risk. Exposure to cigarette smoke, active or passive, harms heart health.
Manage Weight: Extra body weight elevates LDL levels. Adopt healthy eating habits, prefer homemade meals, include fruits, and opt for baked snacks to facilitate weight management.
Limit Alcohol Intake: Moderate alcohol consumption may improve HDL, but excess alcohol can lead to high blood pressure, liver issues, and cardiovascular disease. It's best to drink sparingly or avoid altogether.
Don't wait to take control of your cholesterol levels. Combine lifestyle improvements with medical advice if necessary. Patience is key; gradually, these changes can lead to healthier arteries and a happier heart. Consult your healthcare provider if lifestyle modifications alone aren't enough to manage your LDL levels.