Effective Strategies for Managing Eczema
Learn about comprehensive strategies for managing eczema, including medications, phototherapy, and skin care tips. Effective treatment depends on individual symptoms and medical advice, aiming to reduce itching, prevent flare-ups, and promote skin healing. Always consult healthcare providers for personalized care to ensure safe and effective management of eczema.
Sponsored
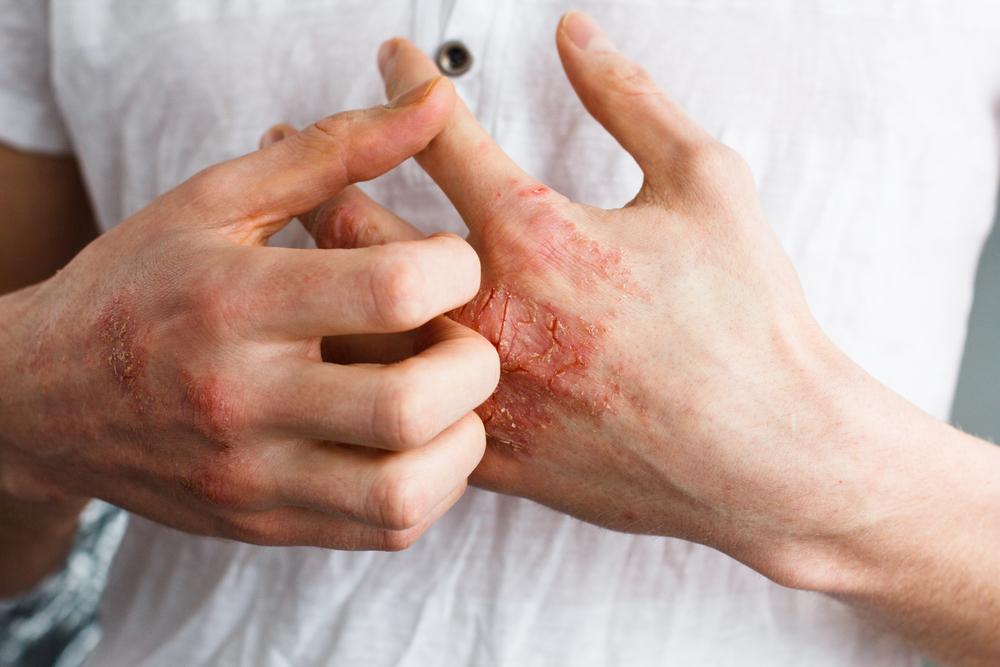
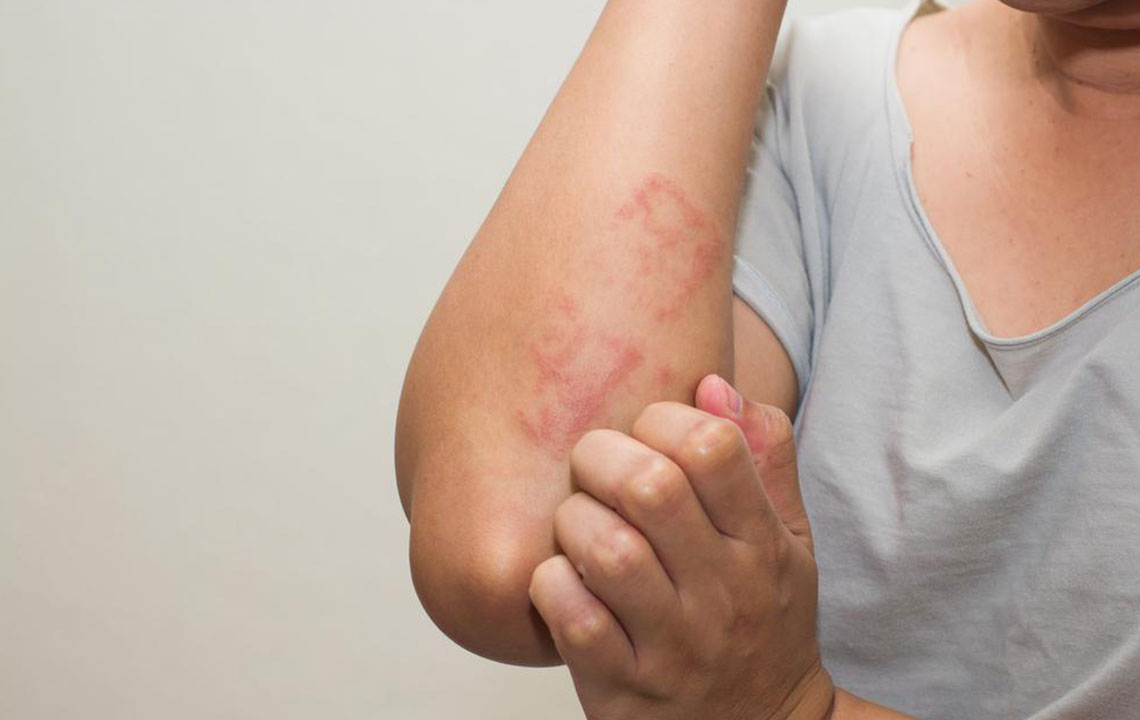
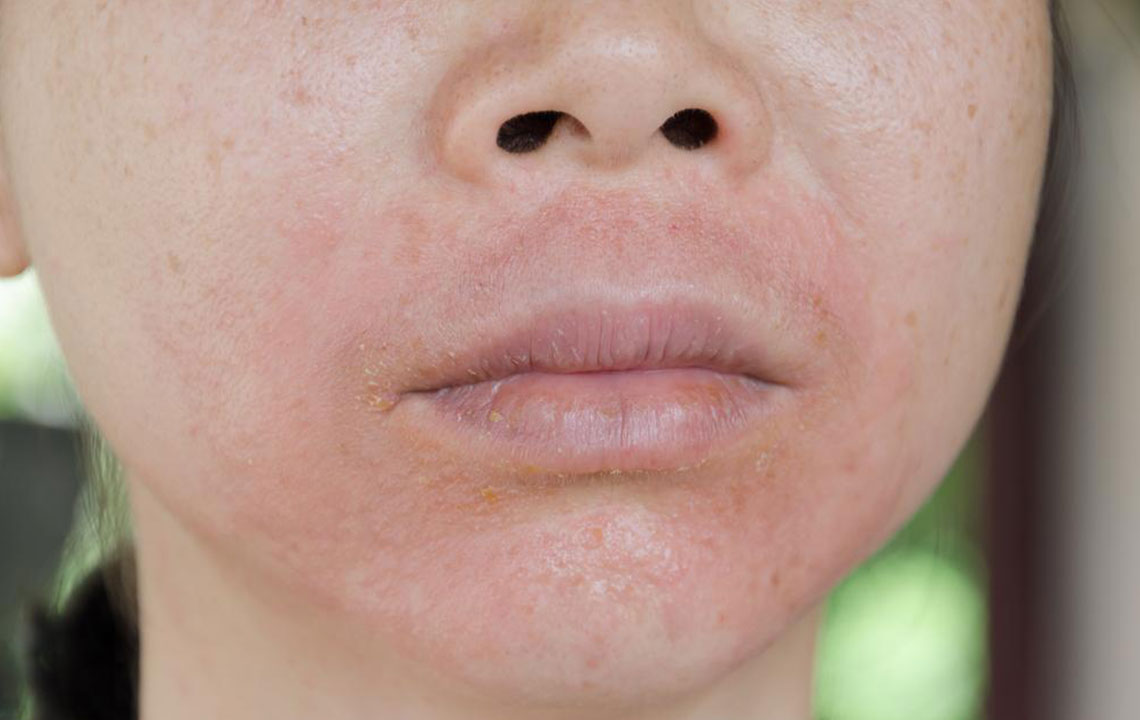
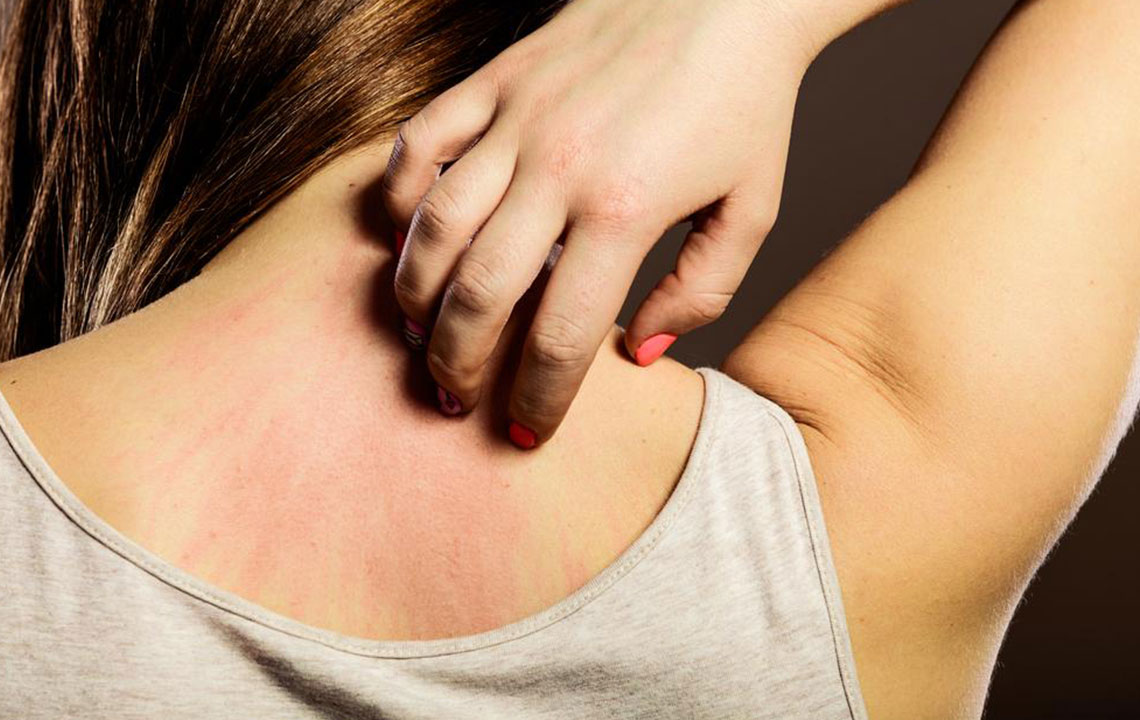
Eczema is a common inflammatory skin condition characterized by red, itchy patches that often appear on the face, chest, or other areas. To alleviate symptoms, consulting a healthcare professional is essential. They may recommend various treatments, including medicated ointments or other therapies, to provide relief.
The goal of eczema management includes
reducing itching,
preventing flare-ups,
promoting skin healing, and
avoiding infections.
Treatment choices depend on individual symptoms, medical history, and age, often combining multiple approaches for optimal results.
Additionally, maintaining skin hygiene and moisture is crucial.
Management Methods
Eczema control involves several strategies.
Medications
Proper use of medications can accelerate recovery, but treatments differ based on individual cases. Doctors often prescribe a combination of therapies.
Eczema creams, corticosteroid ointments, foams, and solutions containing hydrocortisone help reduce inflammation and itching. Mild options are available over the counter, while stronger formulations require prescriptions.
The potency of steroids depends on the severity and affected areas. For mild eczema, over-the-counter hydrocortisone is often sufficient.
NSAID topical ointments offer non-steroidal anti-inflammatory relief, suitable for mild to moderate cases, effective for individuals over 2 years old.
Barrier repair moisturizers, available with or without a prescription, help restore skin moisture and repair damage. Consult your healthcare provider to select the right product, especially if fragrances cause irritation.
antibiotics may be necessary if bacterial infection develops due to scratching.
Antihistamines taken at night can reduce itching and improve sleep quality.
Phototherapy
Moderate to severe eczema can be treated with controlled ultraviolet (UV) light exposure, which helps regulate immune response. Care must be taken to avoid excessive UV exposure to prevent skin aging and cancer risk. Typical therapies include UV light therapy and PUVA.
In addition to medical treatments, proper skin care at home is vital. Always discuss with your doctor before trying new creams, moisturizers, or light therapies.