Comprehensive Strategies for Managing Multiple Sclerosis
This article explores comprehensive approaches to managing multiple sclerosis, highlighting medical treatments, therapies, and lifestyle strategies to enhance patient well-being and quality of life. It covers symptom control, psychological support, and supportive care to navigate the complex complications of MS effectively.
Sponsored

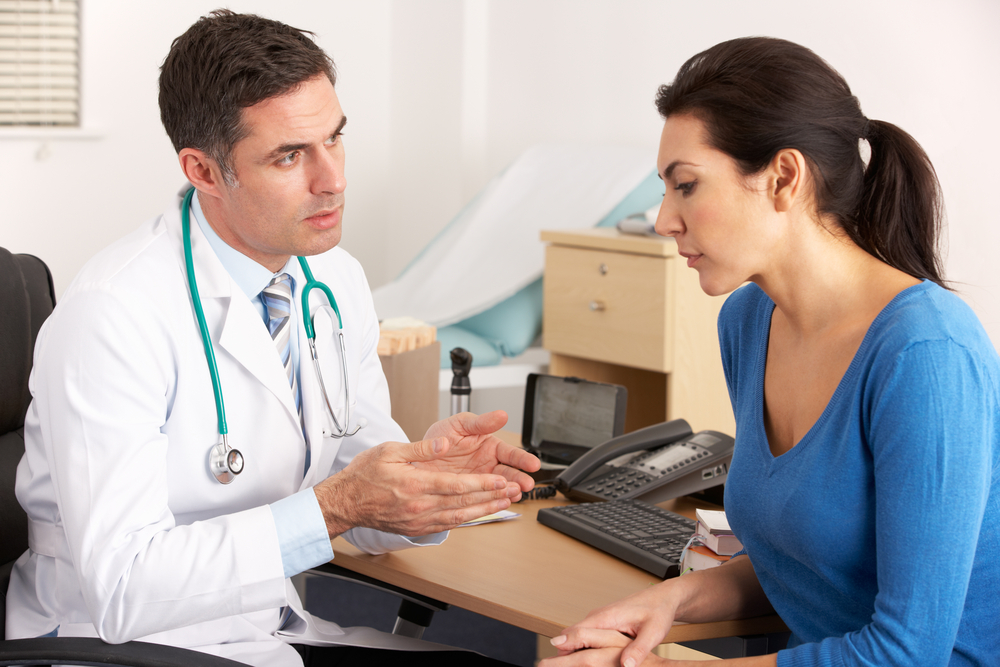
Effective Treatment and Support for Multiple Sclerosis Patients
Multiple sclerosis profoundly impacts various aspects of a patient's life, often reducing their overall well-being. The condition leads to multi-systemic complications, making management challenging.
Common Complications of Multiple Sclerosis Include:
Persistent tremors and depression
Muscle spasms and temperature sensitivity
Chronic pain and sexual health issues
Bladder problems and fatigue
Urinary infections and cognitive decline
Constipation and fecal incontinence
This article reviews both medical and lifestyle approaches to managing each complication effectively.
Handling tremors: These are prevalent among MS patients. Management strategies include devices such as weighted utensils, deep brain stimulation, or surgical interventions like thalamic surgery. Medications like Clonazepam, Mysoline, Ondansetron, and Propranolol may also be prescribed.
Addressing muscle spasms: Regular stretching, physiotherapy, and occupational therapy support symptom control. Spasmolytic drugs such as Diazepam, Baclofen, Dantrolene, and Tizanidine help relax muscles.
Managing pain: Chronic pain treatment involves anticonvulsants, antidepressants, and anti-arrhythmic drugs like Gabapentin, Phenytoin, and Carbamazepine, which are taken in doses ranging from 100 to 1000 mg daily. Potassium channel blockers like 4-aminopyridines can alleviate weakness.
Treating bladder issues: Strategies include fluid restriction at night, frequent voiding, and pelvic exercises such as Kegels. When necessary, medications like oxybutynin and propantheline may be used alongside pseudoephedrine. To prevent urinary infections, patient should increase acidic fluid intake, including orange and cranberry juices, and antibiotics or catheterization may be employed.
Addressing constipation and fecal incontinence: Dietary modifications such as increased fluid and fiber intake, stool softeners, and laxatives are effective for constipation. Fecal incontinence can be mitigated by reducing fiber consumption.
Combatting depression: Disease impact may lead to feelings of hopelessness or suicidal thoughts. Psychological counseling, psychiatric treatment, support groups, and therapy can help. Medications like Fluoxetine, Sertraline, and Amitriptyline are often prescribed.
Managing heat sensitivity: Patients should avoid heat exposure, use cooling methods such as ice packs, and maintain cool environments with air conditioning.
Treating sexual dysfunction: Solutions include lubricants, sexual aids, and medications like Sildenafil (Viagra), to improve intimacy.
Reducing fatigue: Assistance with daily activities and stimulants like methylphenidate can help lessen fatigue's impact on quality of life.
Addressing cognitive issues: Memory lapses and decreased concentration can be managed with drugs such as Donepezil, which enhance neurotransmitter activity.
It is crucial to support MS patients with social and occupational therapy, helping them retain independence and improve life quality. Professional services can assist in maximizing remaining motor functions and improving mental outlook, fostering better living conditions despite disabilities.