Managing Asthma Effectively
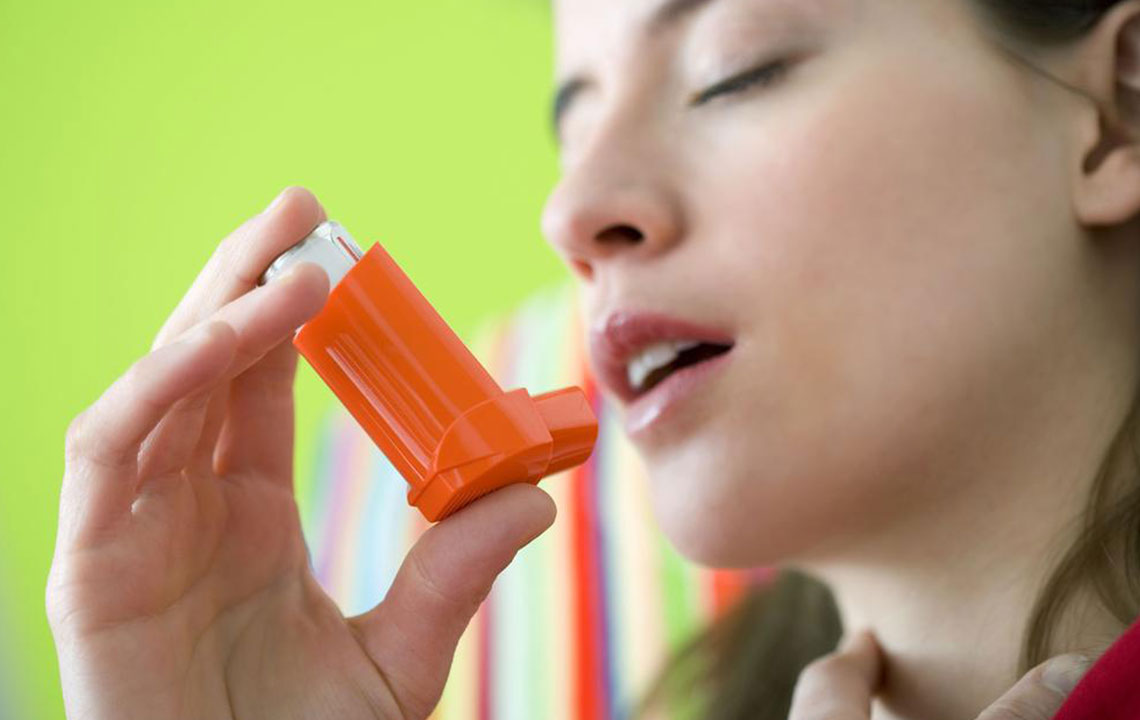
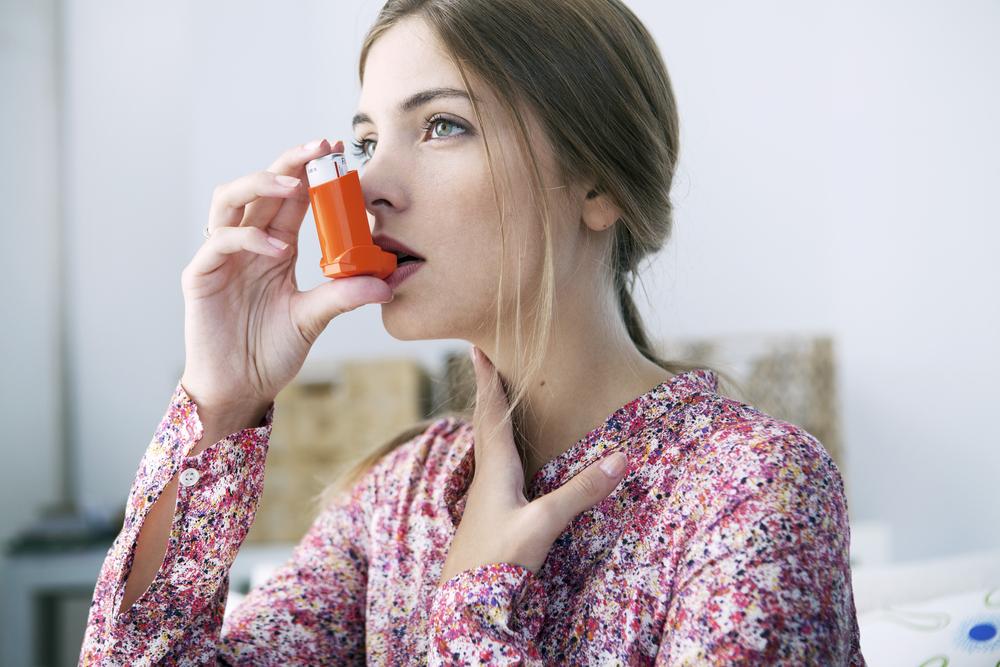
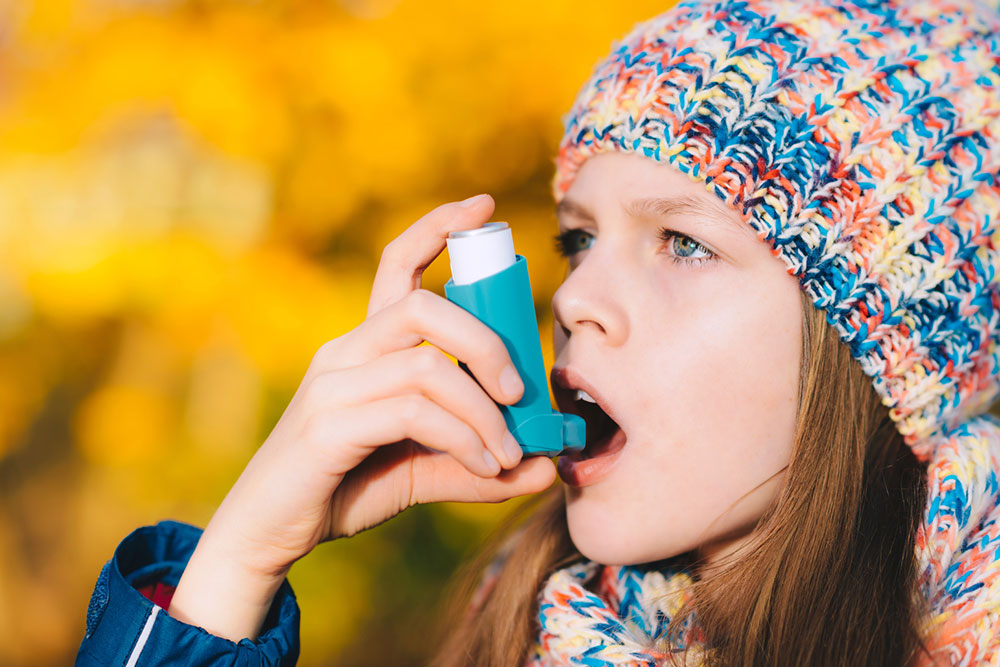
Effective asthma management involves medications such as bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteroids, and leukotriene modifiers tailored to individual severity. Patients should avoid triggers and recognize early symptoms to prevent attacks. Combination inhalers provide an integrated treatment option for ongoing control. Regular medical consultation ensures optimal care and minimizes complications.
Sponsored

Although a complete cure for asthma has not yet been discovered, various medications can help control the condition, minimize symptoms, and prevent severe attacks. Some individuals may experience outgrowth of asthma over time. Those with persistent or episodic asthma can rely on medication to keep symptoms in check.
Patients should identify and avoid asthma triggers and recognize early signs of an attack. Healthcare providers tailor treatment plans based on the severity and type of asthma, with common medications including bronchodilators, corticosteroids, leukotriene modifiers, and mast cell stabilizers.
Bronchodilator Medications
Short-acting beta-agonists (e.g., Albuterol):
Used for quick relief during asthma attacks, administered via inhaler to relax airway muscles.
Long-acting beta-agonists (e.g., Salmeterol, Formoterol):
Taken daily via inhaler for maintenance purposes.
Beta-agonists work by binding to beta receptors on airway muscles, causing relaxation and airway expansion.
Inhaled Corticosteroids
Examples include Flovent, Beclovent, Pulmicort.
Primarily used for regular maintenance, especially for frequent symptoms, inhaled corticosteroids reduce airway inflammation and help prevent wheezing episodes. They mimic cortisol to mitigate inflammation.
Leukotriene Modifiers
Brands like Singulair, Accolate, Zyflo.
Help decrease allergic inflammation, keeping airways open.
Mast Cell Stabilizers
Cromolyn sodium.
Decrease allergic-related airway inflammation.
Oral Steroids
Prednisone.
Used for severe asthma flare-ups, may be given intravenously. These drugs carry side effects like weight gain, ulcers, abnormal hair growth, sleep issues, and dizziness. Patients on steroids longer than 10 days should gradually reduce dosage to prevent withdrawal.
Combination Therapy
Inhalers combining corticosteroids with long-acting beta-agonists offer a comprehensive approach to controlling persistent asthma.