Effective Strategies for Managing Scabies Skin Rash
Discover effective treatments for scabies skin rash, including topical and oral medications, to alleviate symptoms and prevent spread. Early diagnosis and proper treatment are essential for cure and relief from itching and discomfort.
Sponsored
Strategies for Managing Scabies Skin Rash
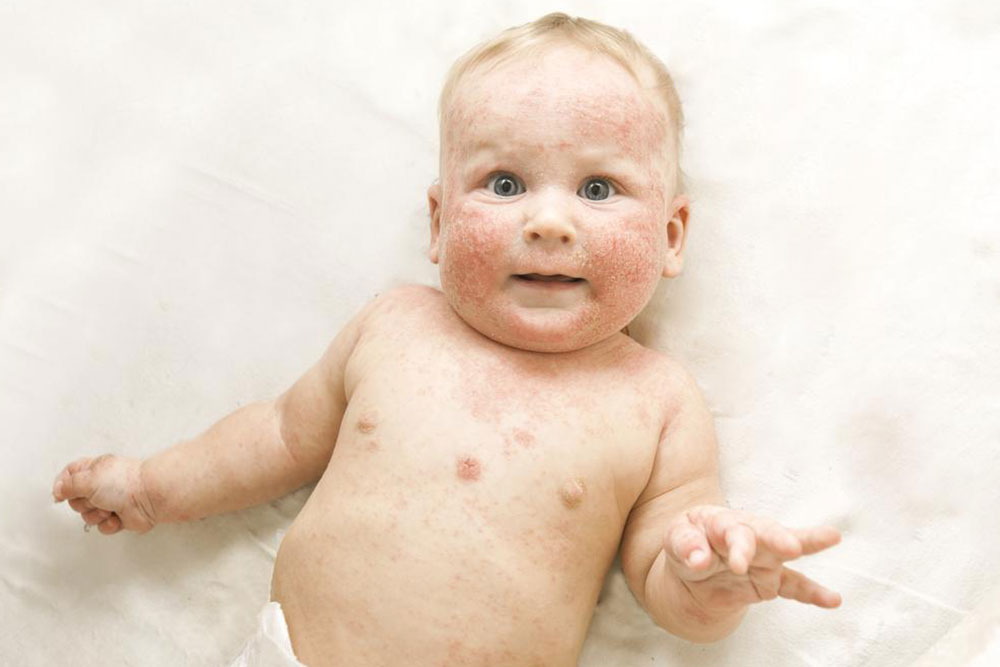
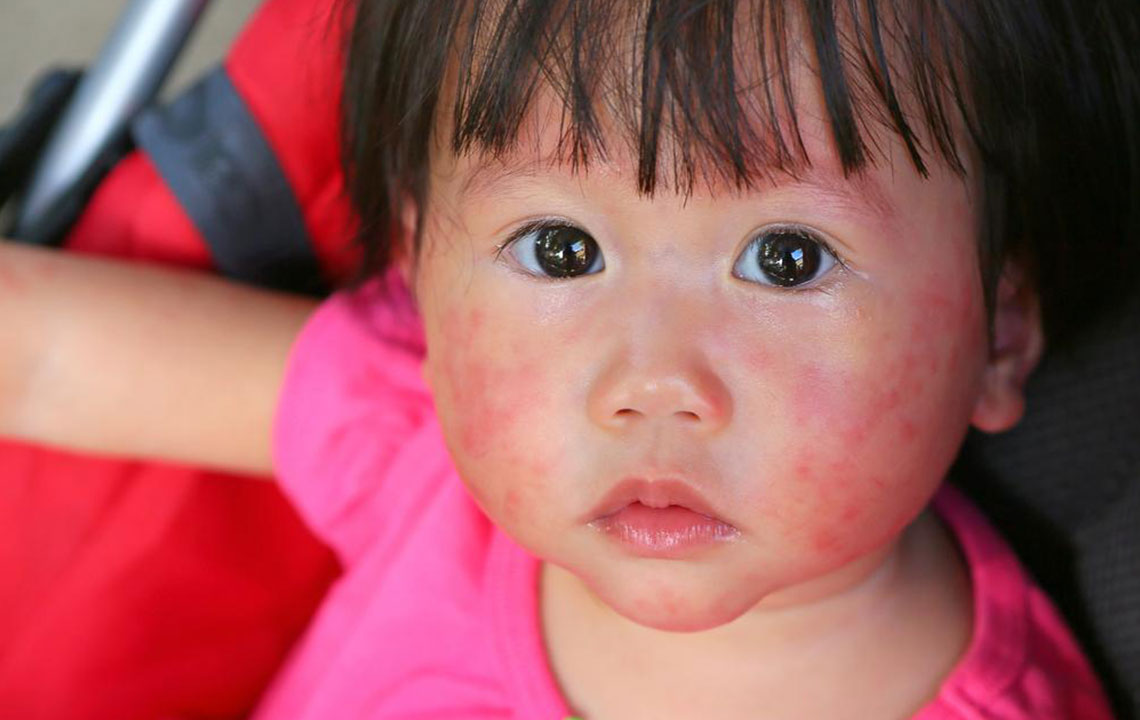
Scabies is an infectious skin condition presenting as redness and intense itching, caused by the mite Sarcoptes scabiei. These microscopic mites burrow into the skin, laying eggs, making the condition highly contagious. If left untreated, mites can survive on the skin for several months.
Fortunately, multiple treatment options are available to alleviate symptoms. Most therapies involve prescribed medications that eliminate both mites and their eggs. Because of its highly contagious nature, healthcare providers often recommend treating all close contacts simultaneously.
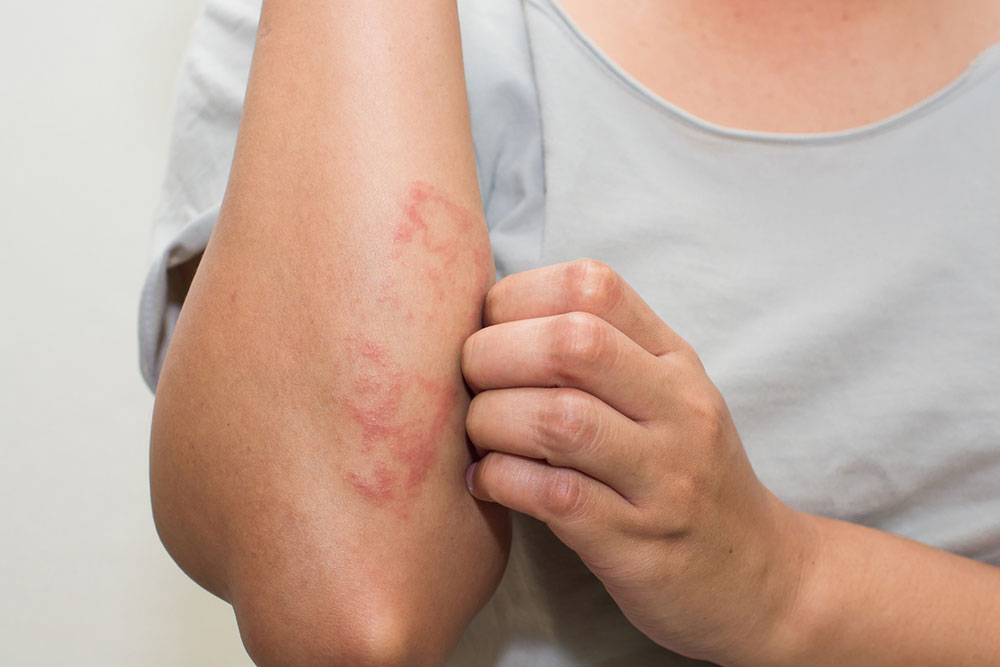
Signs and Symptoms of Scabies
Typical symptoms include:
Intense itching, especially during nighttime
Appearance of blisters or scales
Rash resembling pimples
Sores from scratching
In initial stages, scabies can look similar to other skin issues like insect bites or acne. It's advisable to take photos of the rash before consulting a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis.
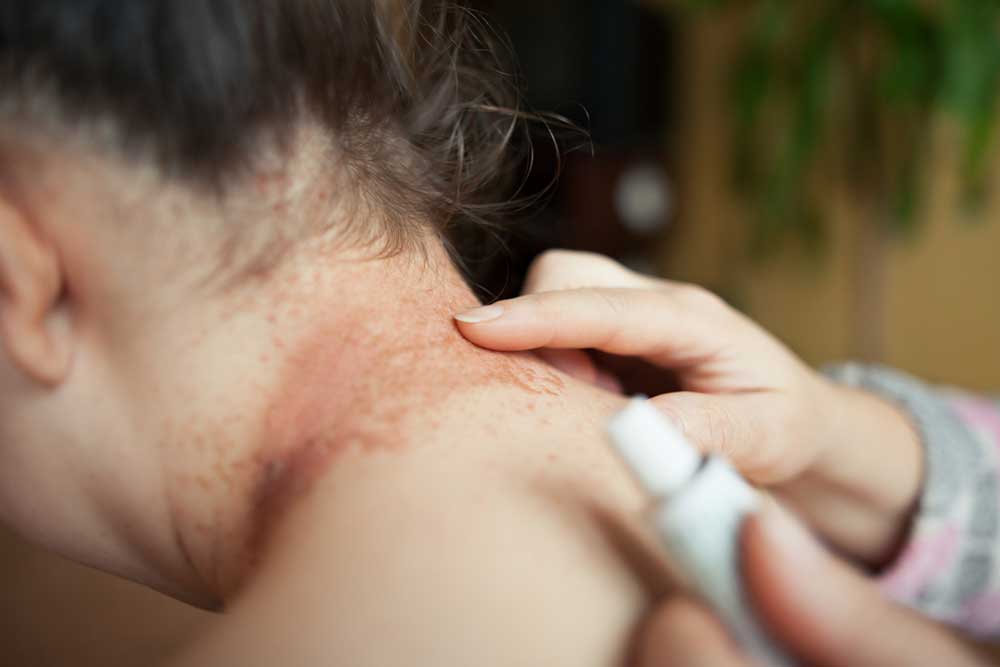
Common Treatments for Scabies Rash
Topical treatments are primarily used, including ointments, lotions, and creams directly applied to the skin.
These medications are most effective when applied at night when mites are most active.
Application typically involves covering the entire body, excluding the face. The medication is rinsed off the following morning. Often, a repeat application is recommended after seven days.
Oral medications are also an option. Some frequently prescribed medications include permethrin cream, crotamiton cream, lindane lotion, sulfur ointment, and benzoate lotion.
Your doctor might also suggest additional medicines to manage symptoms, such as:
Antibiotics for secondary bacterial infections
Steroid creams to reduce inflammation and swelling
Antihistamines like pramoxine lotion to control itching
Oral treatments are typically reserved for cases where topical treatments fail, or in widespread or crusted scabies.
Initial improvement may not be noticeable within the first week; however, itching usually diminishes significantly by the second week. Complete symptom relief generally occurs within four weeks.
If no improvement is observed after four weeks, consult your healthcare provider with photos and symptom details for further evaluation and tailored treatment options.