Understanding Rosacea: Types and Effective Management Strategies
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition with four main types, affecting facial areas and sometimes the eyes. Management strategies include medications, laser treatments, and lifestyle modifications to reduce symptoms and flare-ups. Understanding triggers and adopting gentle skincare routines are key to controlling this long-term skin disorder.
Sponsored
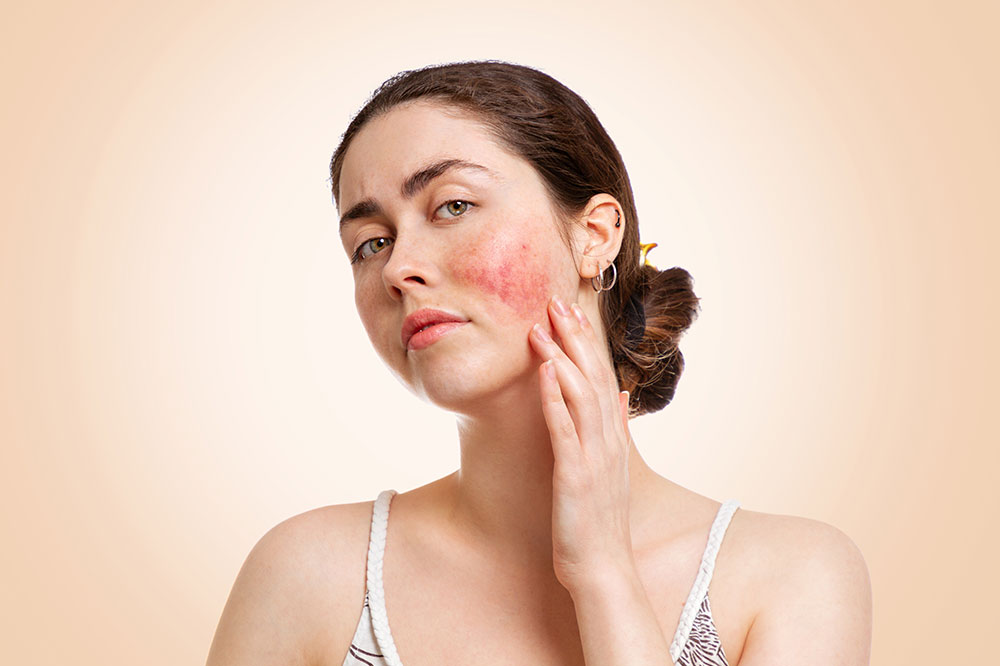

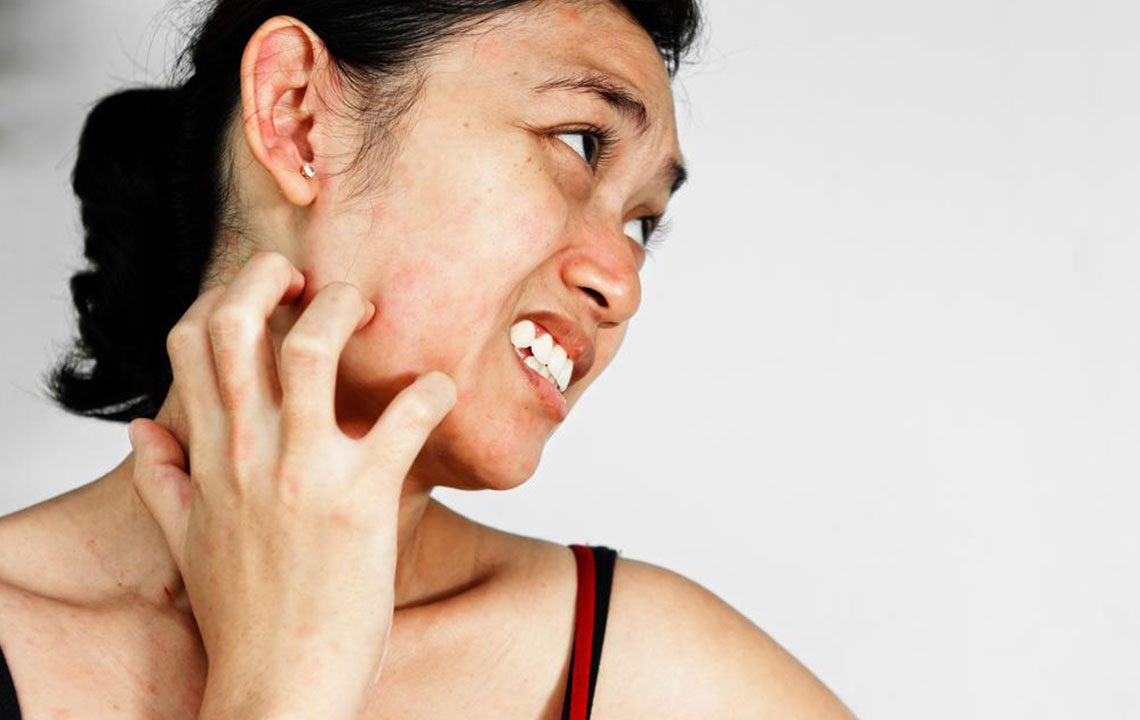
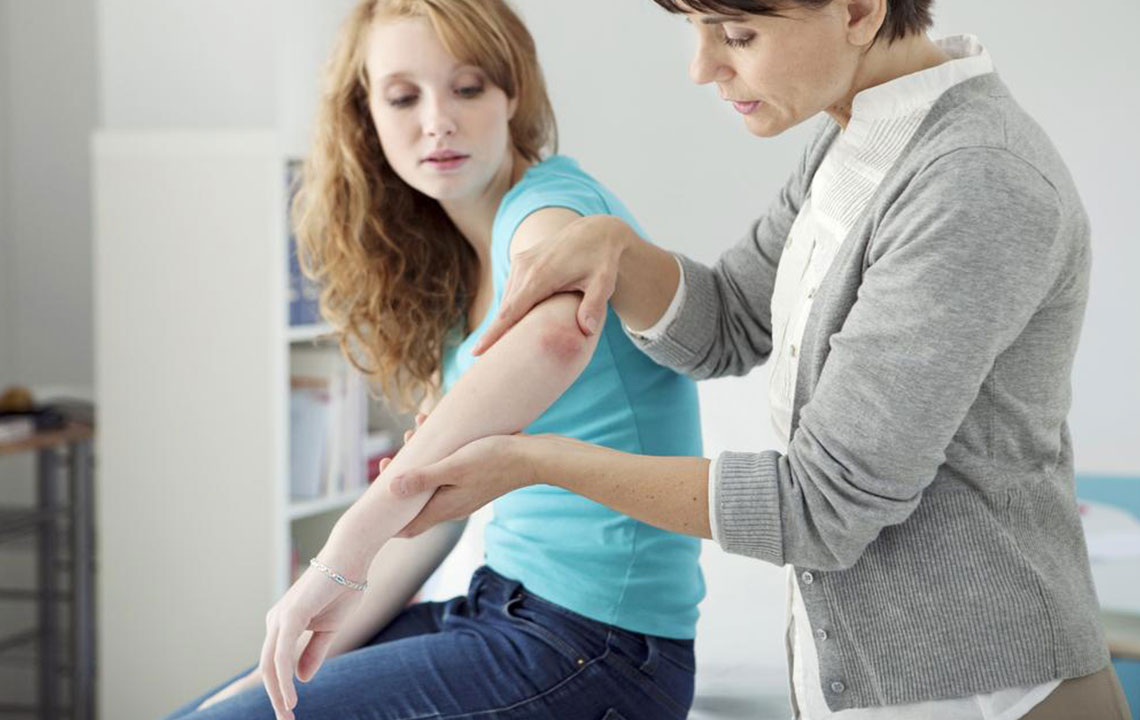
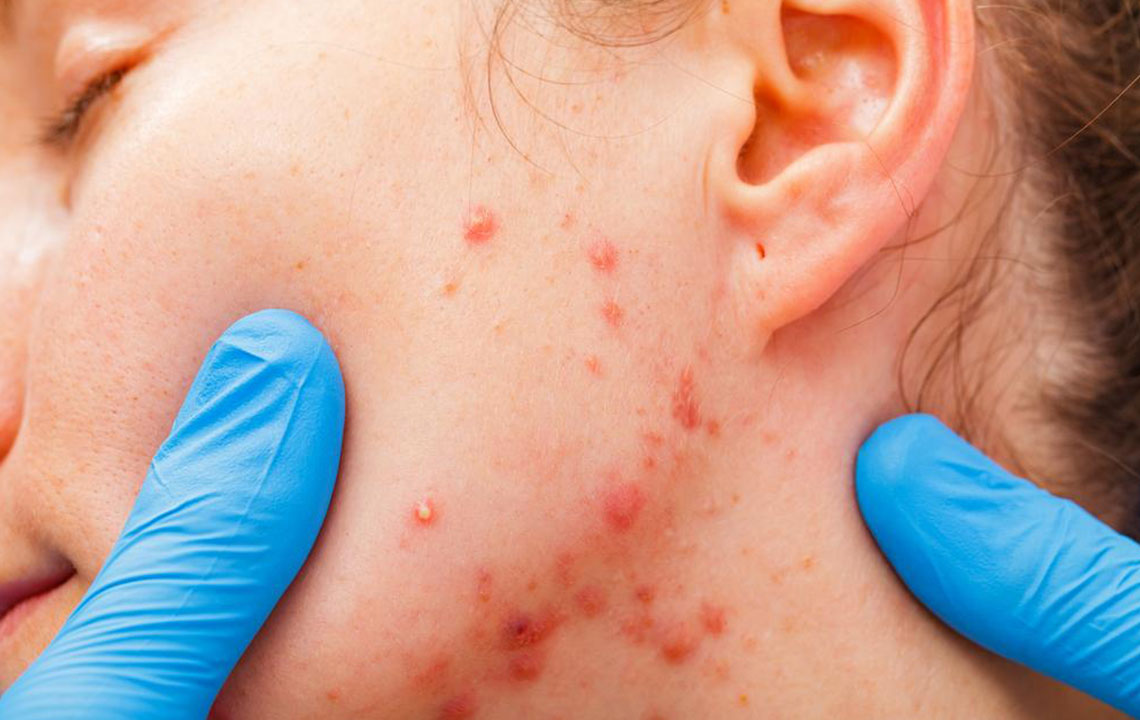
Rosacea is a chronic skin disorder impacting over 16 million individuals, predominantly middle-aged women. Although not deadly, it can cause significant discomfort. Typically affecting the nose, cheeks, and forehead, rosacea manifests as small, red bumps filled with pus that flare up periodically. The condition cycles through active and remission phases.
Classification and Causes
The American Academy of Dermatology categorizes rosacea into four primary types:
Erythematotelangiectatic rosacea (ETR): Marked by facial redness, flushing, and visible dilated blood vessels. It may also cause skin sensitivity, swelling, dryness, and rough patches.
Papulopustular rosacea: Characterized by redness, swelling, and acne-like lesions, often accompanied by oily and sensitive skin, broken blood vessels, and inflammation.
Phymatous rosacea: A rare form mainly affecting men, leading to thickened, bumpy skin with large pores, especially on the nose, cheeks, chin, and forehead. It can also cause skin thickening on other face areas and enlarged pores.
Ocular rosacea: Symptoms focus on the eye area, including redness, dryness, itching, watery eyes, vision issues, cyst formation, broken blood vessels around the eyelids, and burning sensations.
The exact cause remains unknown, but genetic predisposition, facial blood vessel abnormalities, and fair skin are common factors. Triggers such as weather extremes, strenuous activity, stress, alcohol, spicy foods, and hot drinks can worsen symptoms. Management includes lifestyle adjustments and medications. Topical treatments and oral antibiotics help reduce inflammation and redness. Laser therapy targets visible blood vessels, minimizing redness. Gentle skincare, avoiding irritants like alcohol and menthol, and monitoring diet are also essential. Identifying and avoiding triggers can significantly improve quality of life for those affected.