Understanding Joint Discomfort: Types, Causes, and Remedies
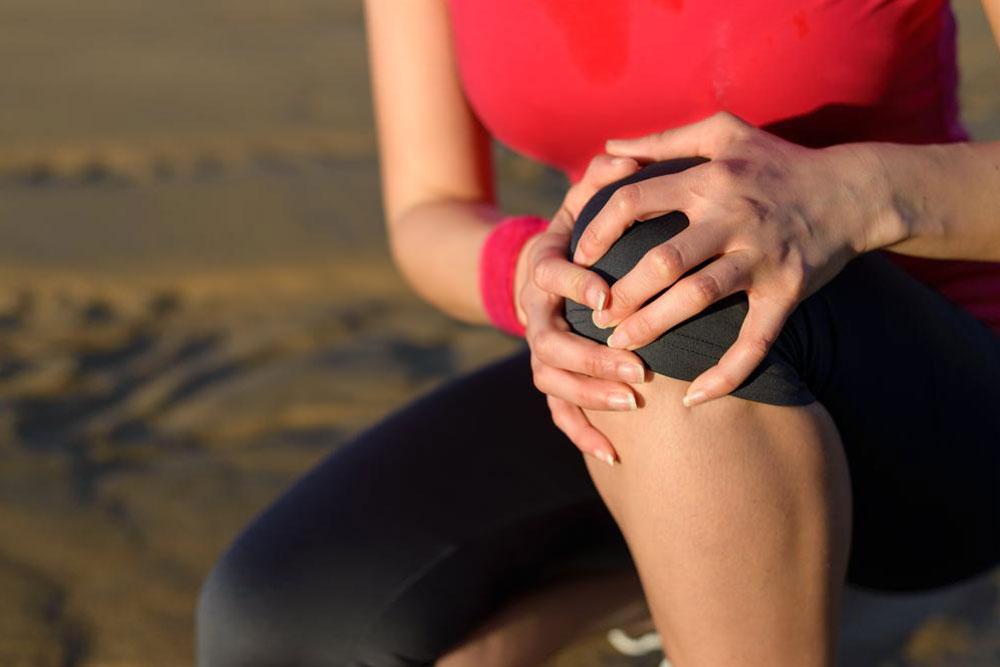
Joint pain, or arthritis, affects many and can result from injury, genetic factors, infections, or immune issues. Management includes medications, lifestyle adjustments, and sometimes surgery. Maintaining a healthy diet and regular exercise can help alleviate symptoms and prevent further damage. Early medical intervention is crucial for effective treatment.
Sponsored
Joint discomfort, also known as arthritis or inflammation, can impact one or multiple joints across the body. There are nearly 200 variants of joint conditions, but the most prevalent include:
Inflammatory arthritis
Degenerative or mechanical arthritis
Soft tissue musculoskeletal pain
Back pain
Connective tissue disorders
Infectious arthritis
Metabolic arthritis
While symptoms typically develop gradually, in some cases, they can appear suddenly. Arthritis mostly affects individuals over 65 years; however, children, teenagers, and younger adults can also be affected.
Women experience joint issues more frequently than men, and overweight individuals are at higher risk.
Causes of joint woes: Specific causes vary with arthritis type but generally include:
Injuries leading to wear and tear
Metabolic issues causing gout or pseudogout
Genetic predispositions such as osteoarthritis
Infections
Immune dysfunction
The reduction of cartilage—flexible tissues in joints—often contributes to joint pain. Cartilage absorbs shocks during movement. Its degeneration, often due to aging, injuries, or infections, leads to conditions like osteoarthritis. Autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis happen when the immune system attacks joint tissues, harming cartilage and bone, resulting in pain.
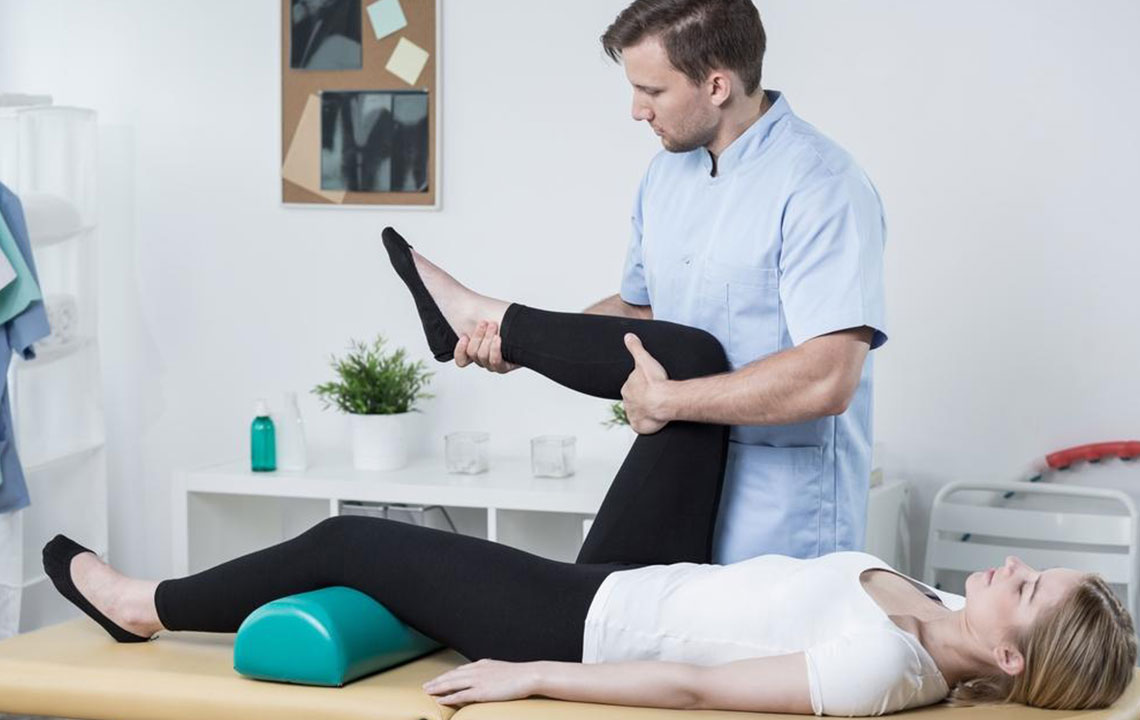
Effective management involves medications, lifestyle adjustments, and sometimes surgery to control pain, slow joint damage, and restore function. Treatment options include:
Medications
Non-drug therapies
Physical and occupational therapy
Support aids like splints
Weight reduction
Surgical procedures such as joint replacements
Medications are tailored to arthritis type:
Analgesics to relieve pain
Topical creams with ingredients like capsaicin
Biologic agents targeting immune responses
Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
Nutritional and self-care strategies: A balanced diet rich in fish, nuts, fruits, vegetables, beans, olive oil, and whole grains supports joint health. Self-management includes tracking symptoms, managing fatigue, exercising regularly, resting adequately, maintaining healthy sleep, and avoiding inflammatory foods. These practices empower individuals to better control their condition, reducing symptoms and preventing progression.
Consult healthcare professionals promptly for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plans based on symptom analysis and medical history.