Comprehensive Guide to Garden Irrigation: Types, Installation, and Maintenance Tips
This comprehensive guide covers various irrigation system types, installation strategies, and maintenance tips to keep your garden green and healthy. Learn about surface, drip, center pivot, and manual irrigation, along with expert advice on efficient setup and repairs to optimize water use and garden health.
Sponsored
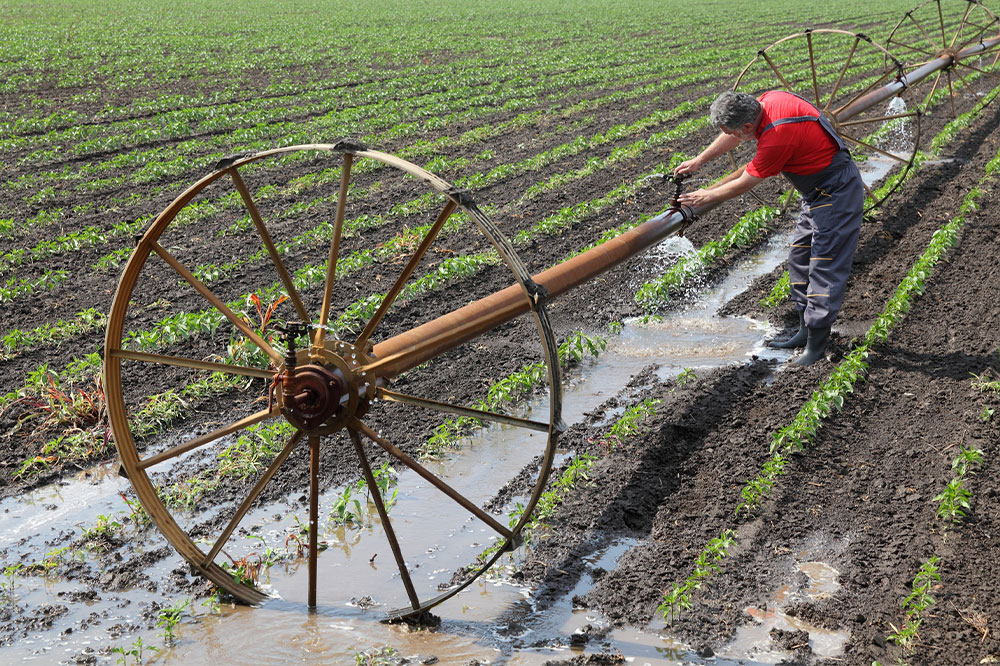

Maintaining a lush garden or vibrant lawn requires consistent watering of the soil. While rainfall is natural, many prefer controlled irrigation methods to ensure optimal growth. Irrigation involves the regulated supply of water for agricultural, landscaping, or lawn purposes. Here, we explore various irrigation systems, along with installation and maintenance guidance to keep them functioning efficiently.
Understanding Different Irrigation Methods
Various irrigation options are suited for different terrains and needs. Here are some of the most commonly used systems:
Surface Irrigation
This method distributes water over the land using gravity through canals, basins, or furrows. It is ideal for certain crops and landscaping setups, such as fruit trees or row crops with furrow systems.
Localized (Drip and Micro-sprinkler) Irrigation
This approach delivers water directly to plant roots via piping systems. It includes:
Drip irrigation: Water is released near roots, minimizing waste through evaporation or runoff.
Micro-sprinklers: Water is dispersed through small overhead sprinklers close to plants or trees.
Bubbler Irrigation
This technique floods small soil basins around individual trees to hydrate roots efficiently.
Center Pivot Systems
Used predominantly on flat terrains, this setup involves a rotating sprinkler arm mounted on wheeled towers, covering large areas.
Lateral Move Irrigation
This method uses pipelines and wheeled sprinkler systems that slowly transfer water across fields. It is cost-effective but may demand frequent manual adjustments.
Sub-surface (Sub-irrigation)
Ideal for regions with high water tables, it involves raising underground water levels via pumping stations, canals, or drainage systems.
Manual Watering
The simplest and most affordable option, using tools like watering cans. It requires physical effort and suits delicate plants or small gardens.
Installation Tips for Irrigation Systems
To ensure effective setup, consider the following:
Strategic Planning
Divide your garden into zones and position sprinkler heads to optimize water use and coverage.
Prepping the Site
Remove and temporarily set aside the sod before digging trenches. Replace it afterward for a seamless lawn appearance.
Proper Pipe Placement
Use polyethylene pipes, avoiding roots, and aim for around 10 inches deep. Avoid splicing underground pipes; hire professionals for precise installation.
Careful Digging
Hand-dig near utilities to prevent damage. For installing pipes under sidewalks, opt for horizontal boring machines.
Cutting Pipes Safely
Use a poly pipe cutter instead of a saw for clean cuts, preventing clogging from shavings.
Securing Main Lines
Reinforce with double clamps to withstand water pressure and prevent leaks.
Efficient Fittings
Use self-tapping or saddle fittings for faster, easier underground connections.
Smart Control Systems
Invest in automated controllers that adjust watering based on weather data, avoiding overwatering and conserving resources.
Maintaining your irrigation system involves regular cleaning of pipes to prevent blockages and safeguarding components from rust and cold damage. Repair tasks like replacing sprinkler heads or fixing leaks are common. For complex issues, consult professional irrigation repair services to ensure proper troubleshooting and fixes.