Comprehensive Guide to Managing Genital Psoriasis
Genital psoriasis is a chronic condition affecting the sensitive skin of the genital area, causing discomfort and emotional stress. This comprehensive guide discusses symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and effective management strategies, including topical treatments and lifestyle adjustments. Recognizing triggers and seeking professional care are key to controlling symptoms. Emotional support is equally important for overall well-being. With proper treatment and support, individuals can manage this condition effectively and improve their quality of life.
Sponsored

Genital psoriasis is a persistent skin disorder impacting the genital region, leading to discomfort and emotional strain for sufferers. While psoriasis is typically associated with skin lesions elsewhere, its manifestation in sensitive areas presents unique challenges. This article offers an in-depth overview of genital psoriasis, including symptoms, causes, and effective management options, presented with professionalism and sensitivity.
What Is Genital Psoriasis?
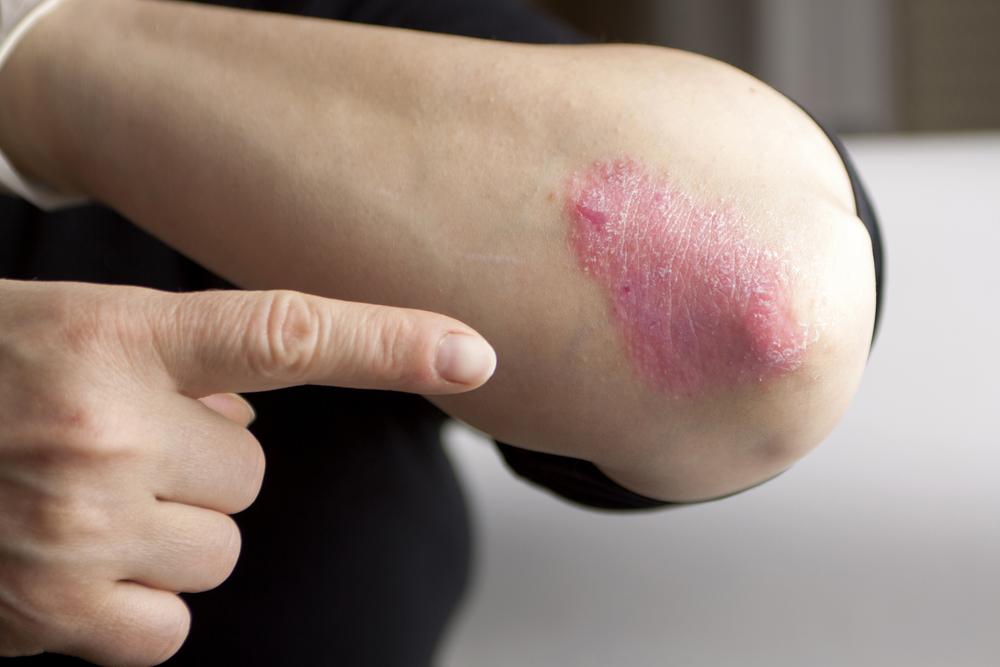
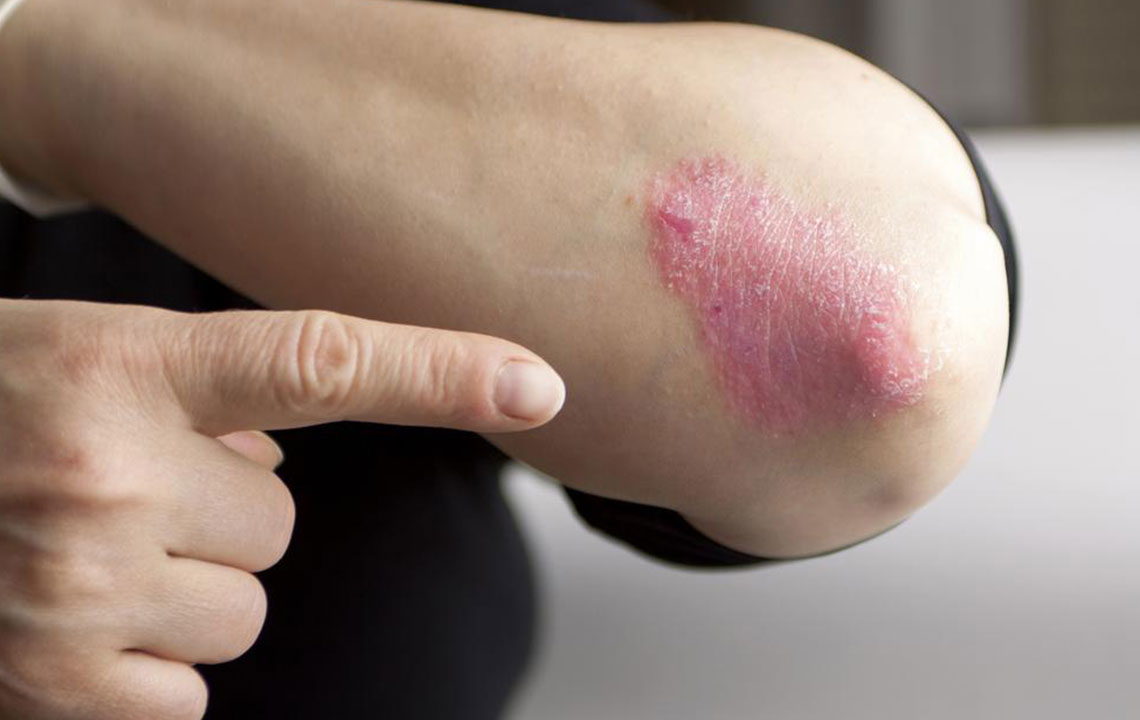
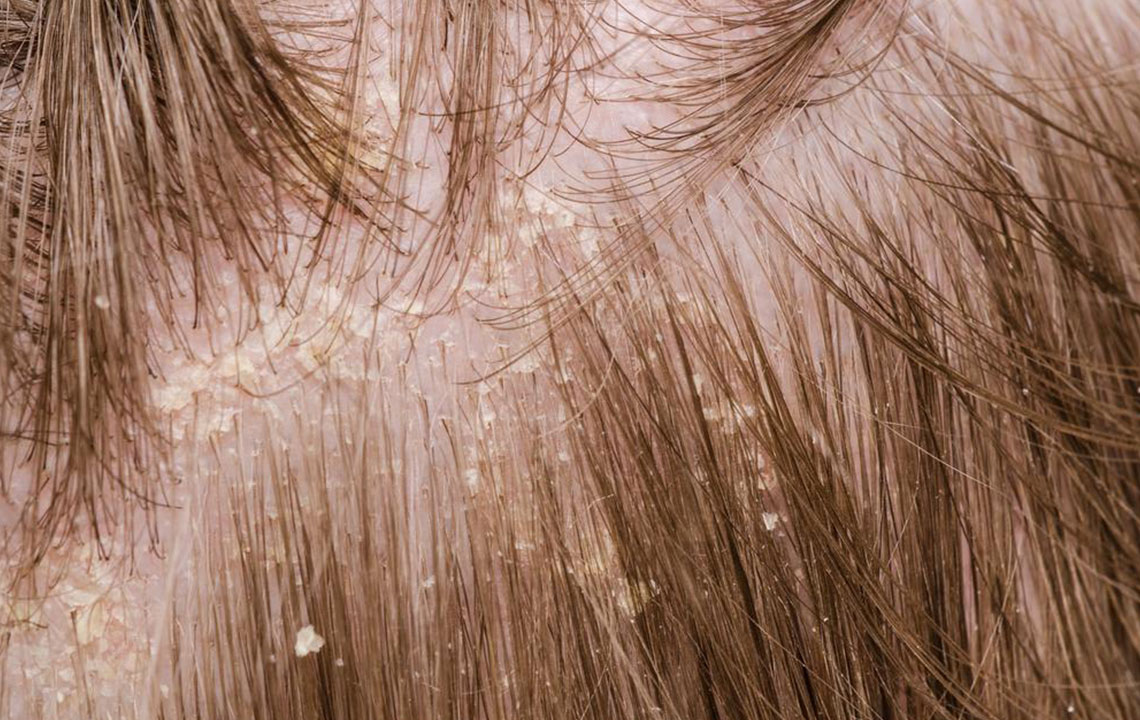
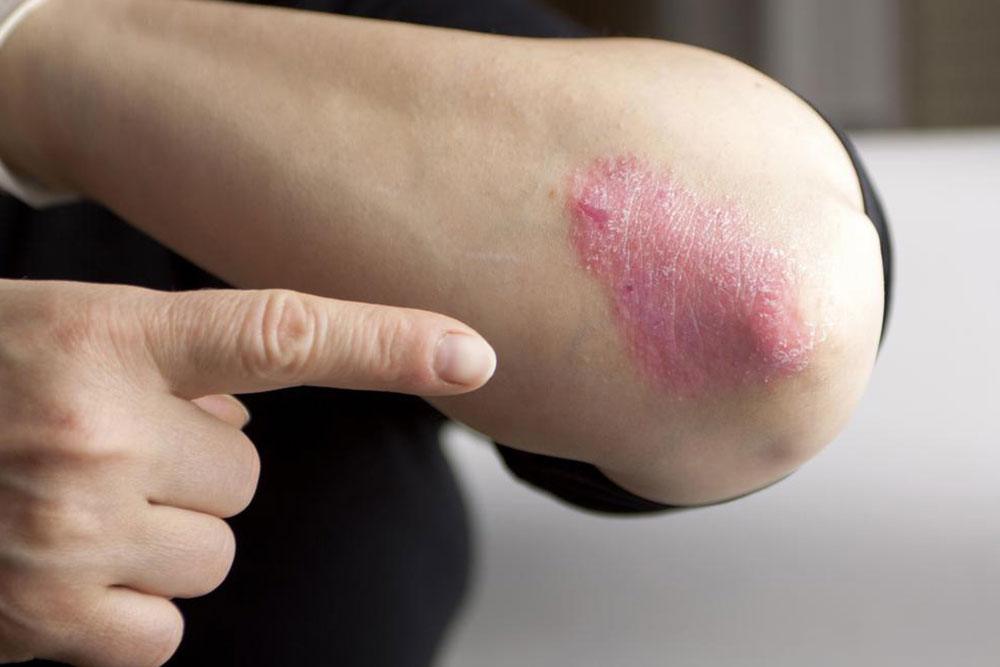
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease characterized by accelerated skin cell production, resulting in red, flaky patches. When it affects the genital area, it is called genital psoriasis. It commonly involves regions such as the groin, inner thighs, and buttocks. Unlike psoriasis on other skin parts, lesions here tend to be smoother and less scaly due to moisture levels in the area.
Symptoms of Genital Psoriasis:
Reddish, smooth patches: These differ from typical psoriasis spots by their less scaly appearance.
Itching and discomfort: The sensitive nature of genital skin makes symptoms particularly distressing.
Burning sensation: Some experience a burning feeling, especially during physical activity or intimacy.
Dryness and cracking: Damaged skin may crack and cause further irritation.
Causes and Exacerbating Factors:
While the precise cause remains unclear, genetic, immune, and environmental factors are involved. Triggers that may worsen psoriasis include:
Stress: Emotional strain can activate or intensify symptoms.
Infections: Conditions like strep throat can trigger outbreaks.
Skin injuries: Cuts or scrapes can lead to flare-ups.
Diagnosis: A healthcare professional typically diagnoses genital psoriasis through physical exam, sometimes supplemented by a biopsy to differentiate from other conditions.
Treatment and Management:
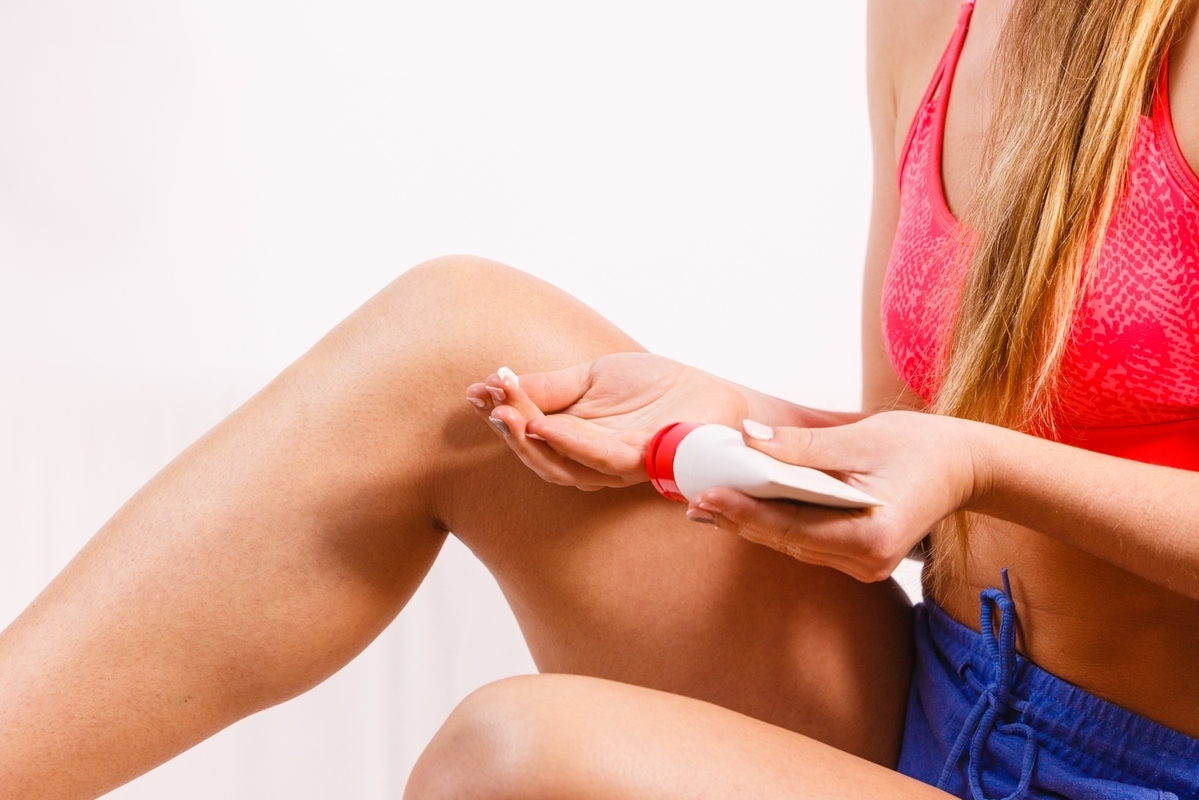
Topical medications: Corticosteroids and medicated creams help reduce inflammation and itching.
Moisturizers: Regular application of fragrance-free moisturizers keeps skin hydrated.
Trigger avoidance: Lifestyle adjustments like stress management and gentle skin care minimize flare-ups.
Phototherapy: Controlled ultraviolet light exposure can be beneficial for some patients.
Healthy habits: A balanced diet and regular exercise support overall skin health.
Emotional and Psychological Support:
Living with genital psoriasis can impact mental health and relationships. Seeking support from healthcare providers, counselors, or support groups is vital to cope and maintain quality of life.
Effective management of genital psoriasis involves awareness, appropriate treatment, and emotional support. With proper care and open communication, individuals can lead fulfilling lives despite this condition.