Main Factors Leading to Persistent Dry Eye Syndrome
Discover the main causes of persistent dry eye syndrome, including aging, hormonal changes, medication effects, and environmental factors. Early detection and professional advice can help manage this uncomfortable condition effectively.
Sponsored
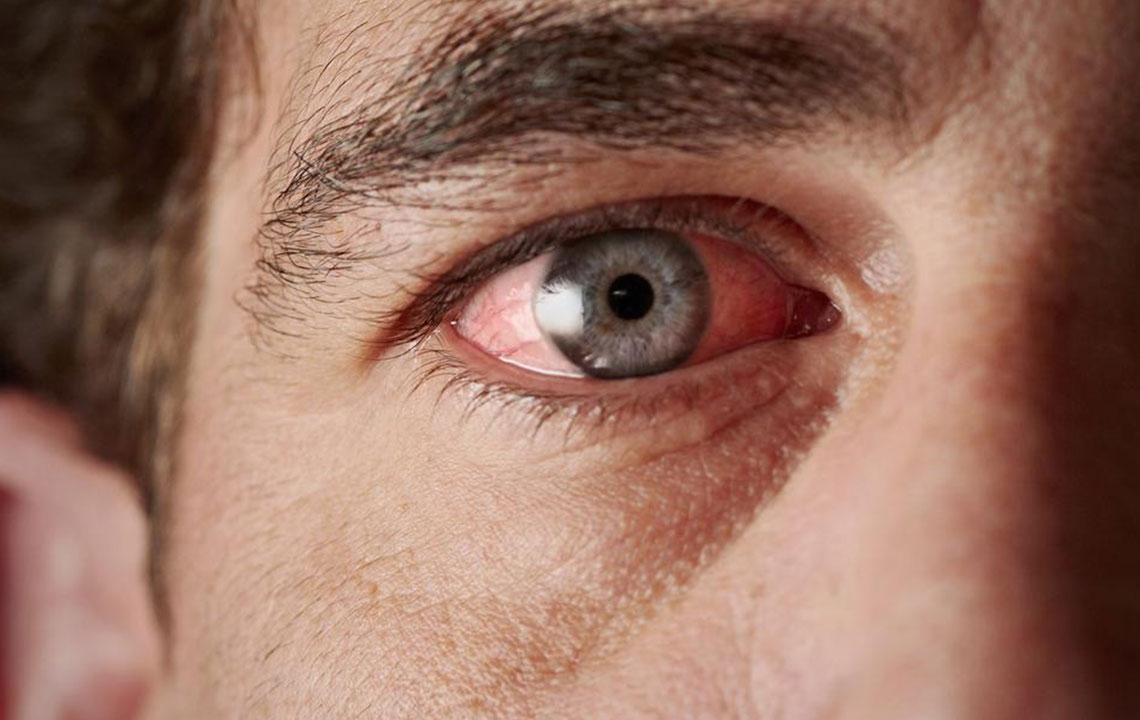
Key Factors Contributing to Persistent Dry Eye Syndrome
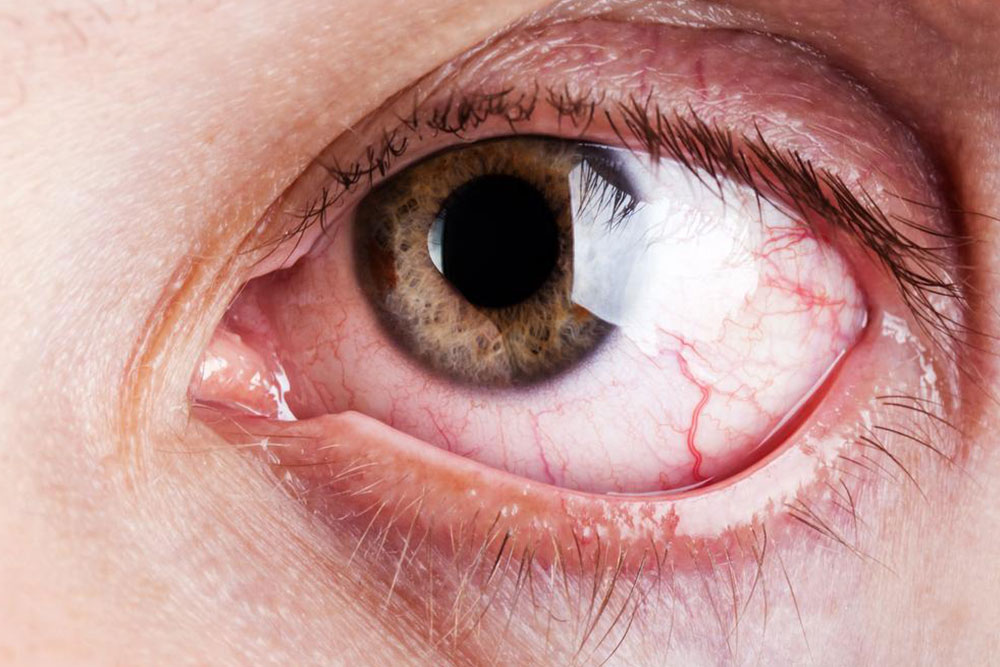
Chronic dry eye syndrome occurs when the eyes do not produce enough tears or the tears lack essential quality, leading to discomfort and potential damage. Also known as dry eye disease, its causes vary widely, making awareness important for early intervention. Recognizing these factors can help in prevention and management.
Primary causes of dry eye syndrome
Several factors can lead to this condition, including:
Natural aging reduces tear production, causing dryness and irritation.
Hormonal fluctuations, especially in women during pregnancy, menopause, or due to contraceptive use, increase vulnerability to dry eyes.
Medications such as decongestants, antihistamines, antidepressants, and blood pressure treatments can decrease tear production.
Pre-existing health conditions like diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, or thyroid disorders often contribute to dry eye development.
Other factors include eyelid inflammation, abnormalities in eyelid positioning, or surface issues affecting eye moisture. Environmental factors like windy, dry climates can also exacerbate symptoms.
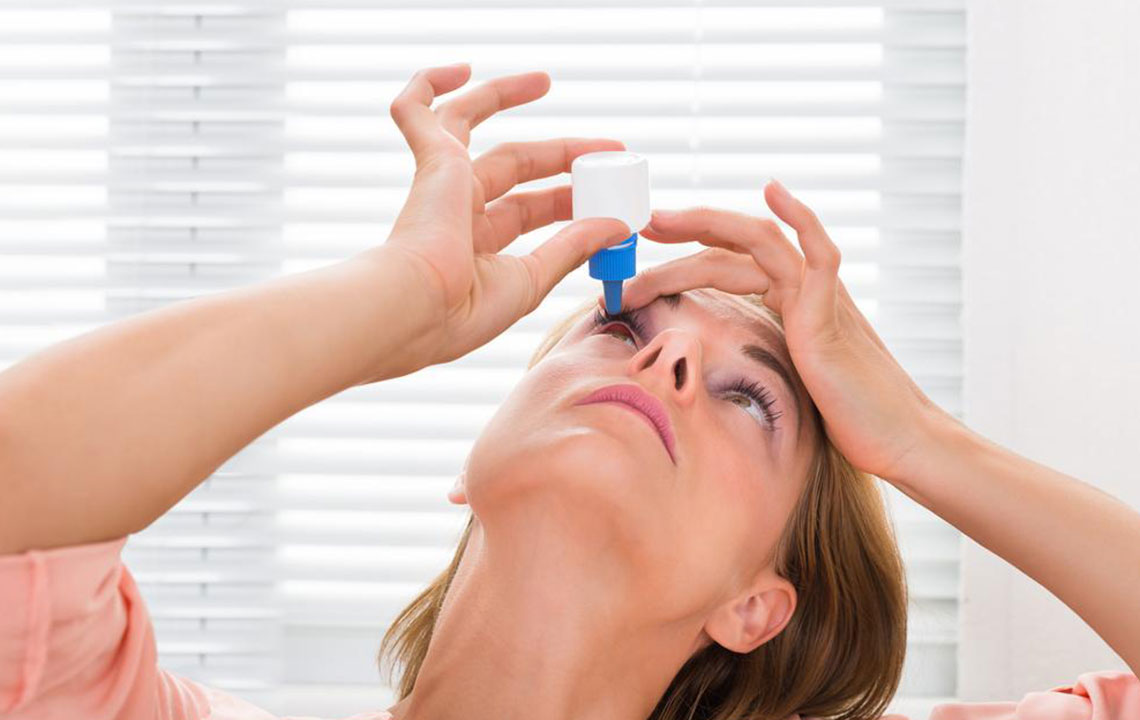
To minimize risks, it’s best to avoid preventable causes of dry eyes and consult a healthcare professional if symptoms arise.