Effective Strategies to Manage Chronic Heart Failure
Discover comprehensive management options for chronic heart failure, including medications, surgeries, and lifestyle changes aimed at improving life quality and controlling symptoms. Learn how to effectively manage this ongoing condition through tailored treatment strategies.
Sponsored

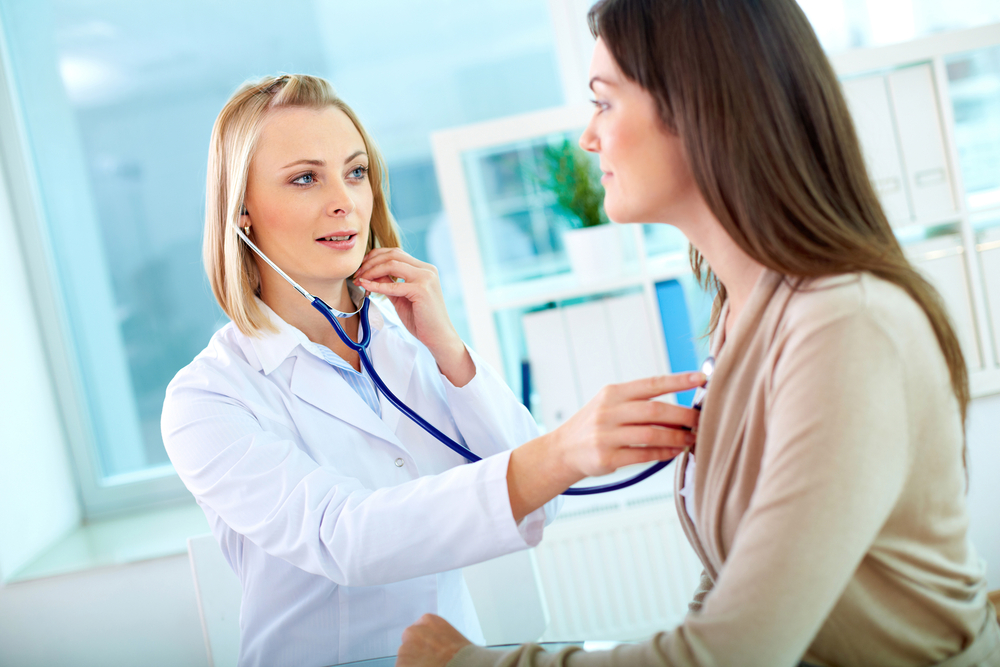
Chronic heart failure has no definitive cure, but several management approaches can help control its progression. Understanding what causes this condition is essential. It develops gradually when the heart muscles weaken, impairing the heart’s ability to pump blood efficiently. Factors such as high blood pressure, cardiac diseases, diabetes, obesity, and smoking contribute to its development.
Managing Chronic Heart Failure
This condition necessitates ongoing treatment and lifestyle adjustments to improve quality of life.
Various treatment options are available, including medications, surgical procedures, and lifestyle modifications.
Medications:
Use of pharmaceutical drugs to alleviate symptoms and improve heart function.
ACE inhibitors help in lowering blood pressure by dilating blood vessels, reducing the heart's workload.
Beta blockers slow heart rate, giving the heart time to rest and function more effectively, potentially enhancing overall heart health.
Diuretics assist in removing excess fluid through urination, relieving symptoms related to fluid retention.
Surgical Interventions:
Surgical procedures may be recommended based on individual cases.
Coronary artery bypass surgery restores blood flow by bypassing blocked arteries.
Valve repair or replacement addresses faulty valves contributing to heart failure.
Pacemakers are implanted devices that help regulate heartbeat and improve cardiac function.
Lifestyle Modifications:
Making essential lifestyle changes is vital for effective heart failure management.
Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise reduces strain on the heart. Monitoring weight is crucial, as sudden increases may indicate fluid buildup.
A heart-healthy diet low in sodium and saturated fats, rich in fiber, fruits, and vegetables, supports cardiac health.
Regular moderate exercise, sufficient rest, and stress management contribute to overall well-being. Quitting smoking, avoiding alcohol, and managing fluid intake are also important.