Effective Strategies for Obesity Control and Prevention
Learn about the comprehensive stages of obesity management, accurate diagnosis methods, and essential strategies for prevention. This article emphasizes lifestyle changes like healthy eating and regular exercise to combat obesity and prevent related health issues, supporting long-term well-being.
Sponsored

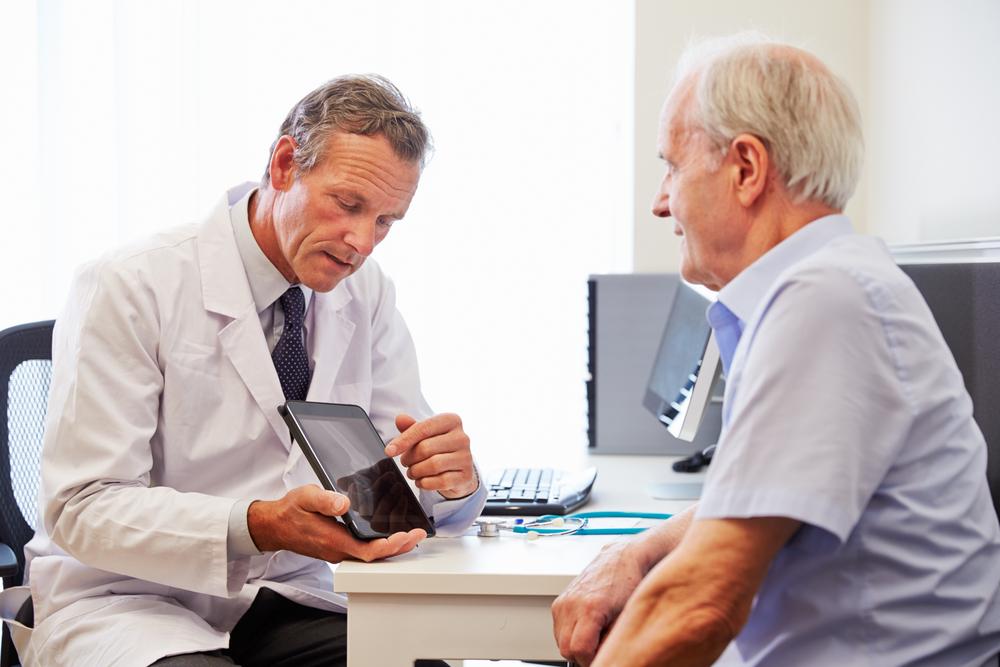
Obesity remains a widespread health concern, affecting nearly one-third of adults nationwide. An adult over 35 with a BMI of 30 or higher is classified as obese. Understanding the different stages of managing obesity, how to diagnose it accurately, and preventive measures is crucial for health maintenance.
Stages of Obesity Management
There are six main steps in managing obesity:
Denial
This initial phase involves ignoring or minimizing weight issues, though objective measures like BMI clearly define obesity.
Decision
Recognizing weight concerns prompts individuals to plan lifestyle changes, such as modifying diet or increasing physical activity.
Action
This active phase involves adopting healthy eating habits, regular exercise, and reducing detrimental behaviors to combat obesity.
Achieving Goals
Reaching weight targets is encouraging and motivates continued effort as progress becomes evident.
Maintenance
Sustaining these habits is vital post-goal to prevent weight regain.
Acceptance
Long-term commitment to healthy living is essential, acknowledging that weight management is an ongoing journey.
Diagnosing Obesity
Obesity diagnosis is straightforward: a BMI exceeding 30 indicates obesity. BMI relates height, weight, and age, supplemented by assessments like skinfold measurements, waist-to-hip ratios, and imaging techniques such as ultrasound and MRI for precise evaluation.
Preventing Obesity
Beyond aesthetic concerns, obesity can lead to chronic illnesses—including diabetes, heart disease, hypertension, and certain cancers. Preventive measures include maintaining a nutritious diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing psychological factors like depression, which may contribute to weight gain. While genetics play a role, adopting a healthy lifestyle significantly reduces obesity risk.
Consistent healthy eating and active living are vital for long-term health and obesity prevention.