Understanding Normal Blood Pressure by Age Group
Learn about healthy blood pressure levels across different age groups, the significance of maintaining balanced readings, and tips for prevention of hypertension-related health issues. Accurate monitoring and lifestyle changes are key to cardiovascular health.
Sponsored

The circulatory system transports blood throughout the body, delivering essential oxygen and nutrients. Blood pressure measures the force exerted by circulating blood against vessel walls. Keeping blood pressure within healthy limits is crucial for proper organ function.
Blood provides oxygen, hormones, and antibodies, ensuring overall health. The heart acts as a pump, creating the pressure necessary for blood movement. Blood pressure varies at different points, peaking near the heart and decreasing in smaller arteries. Elastic artery walls help maintain steady flow.
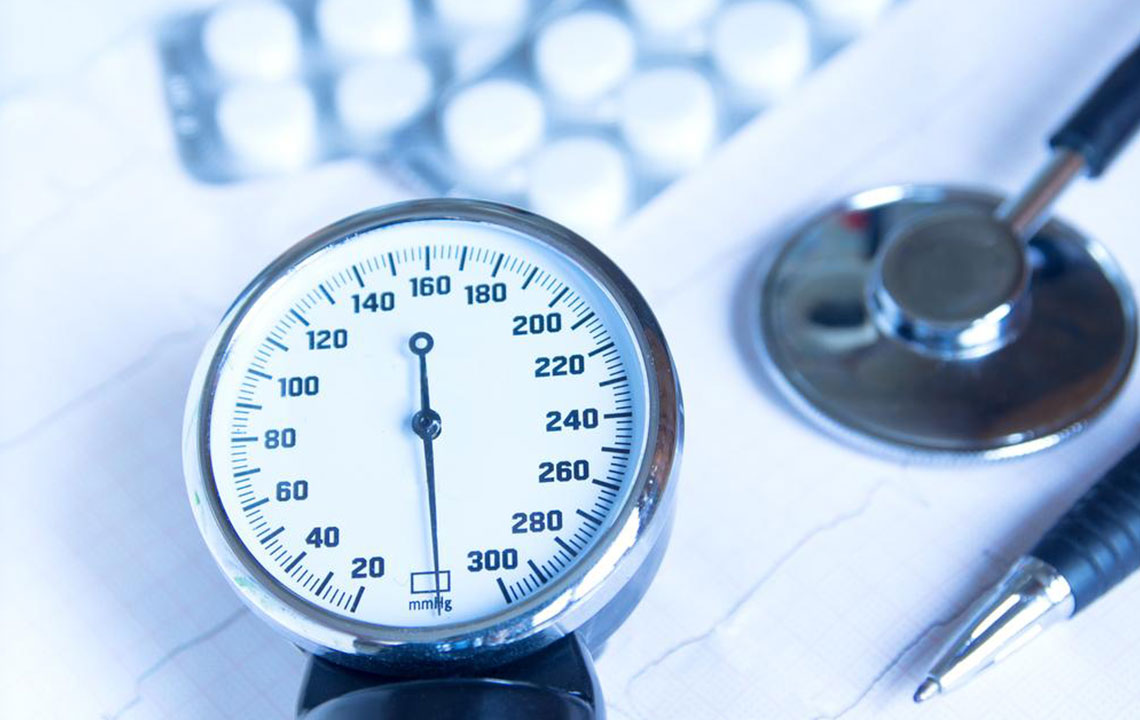
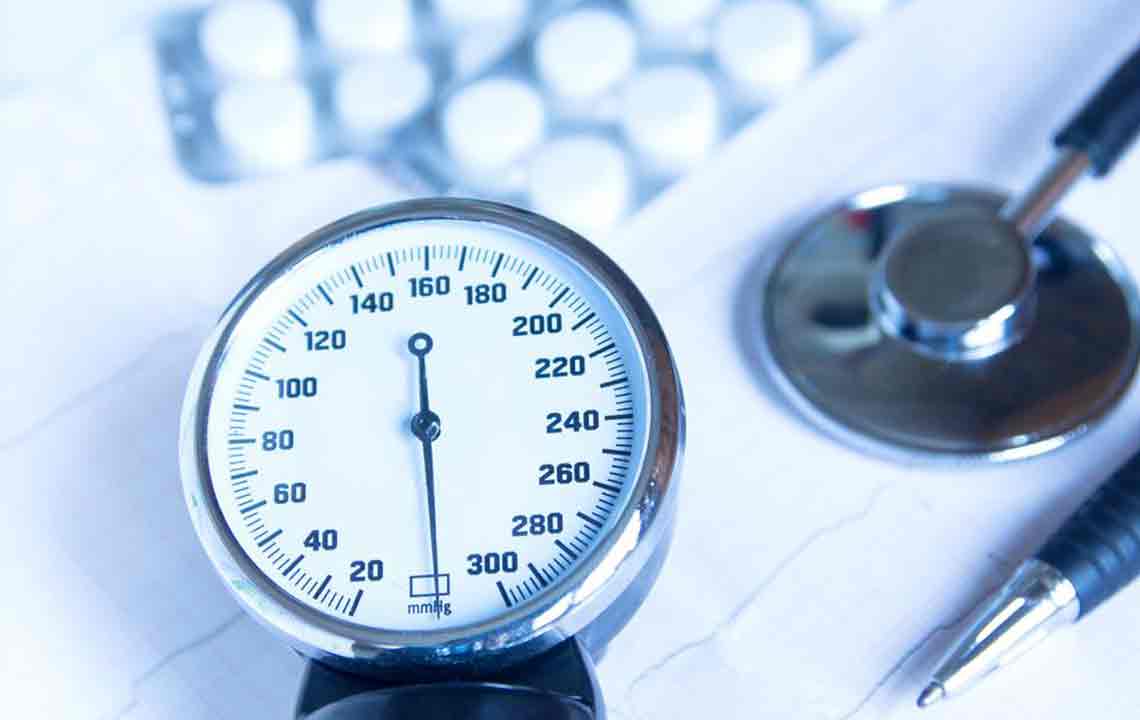
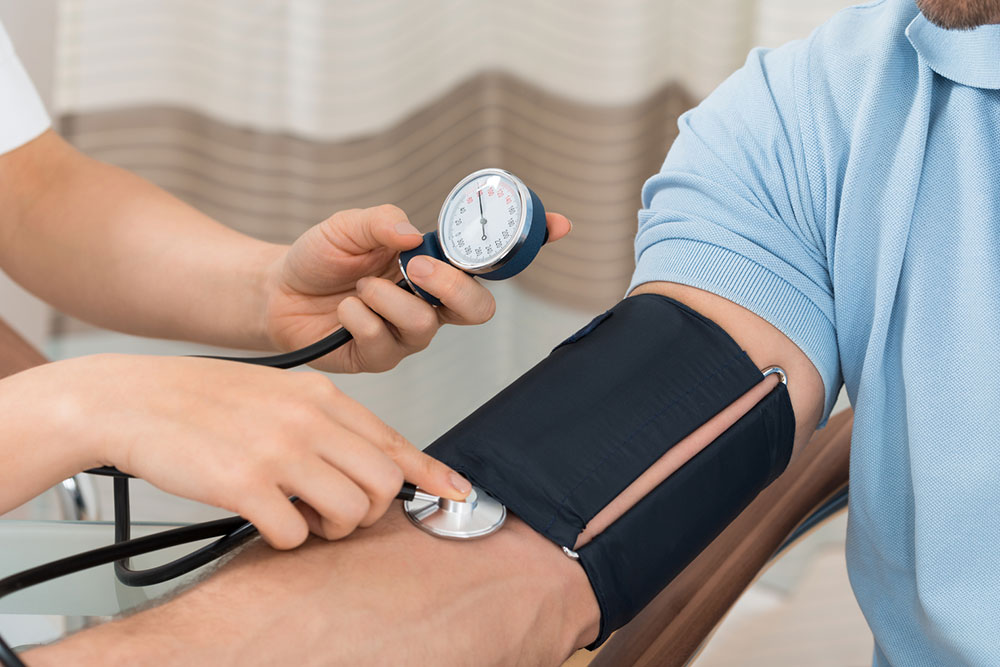
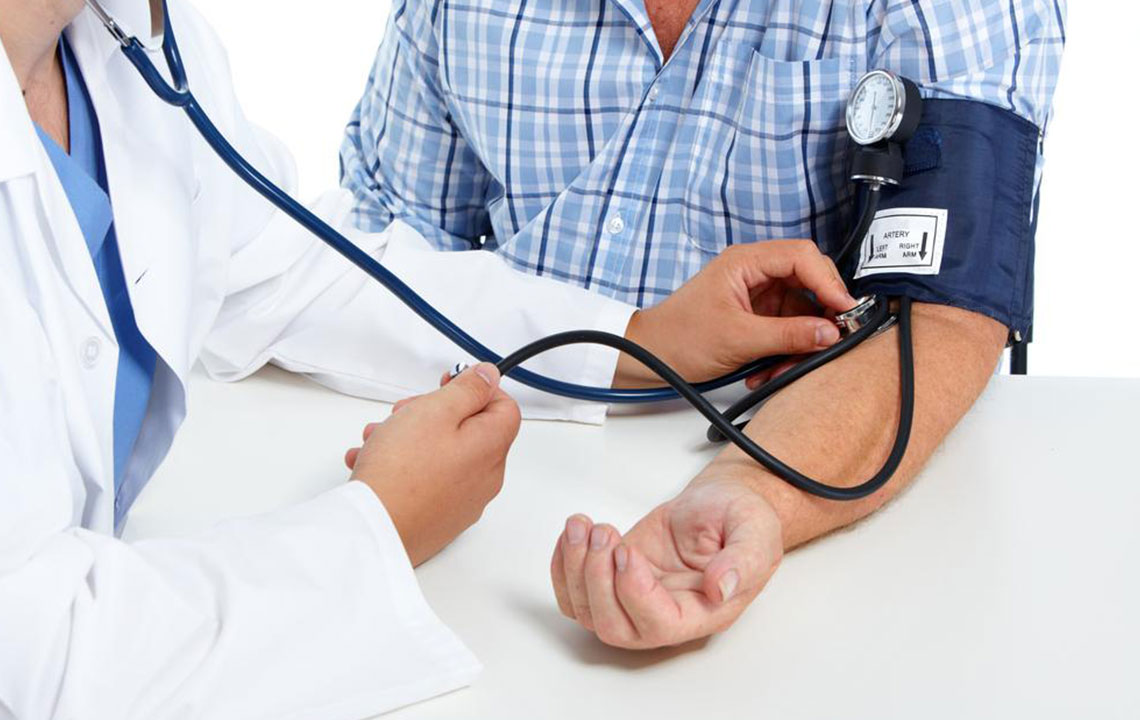
A sphygmomanometer records blood pressure in mmHg. Healthcare professionals reference blood pressure charts to evaluate normal ranges for different ages.
According to guidelines, a systolic reading of 120 mmHg and diastolic of 80 mmHg are considered normal. Readings above 130/80 may indicate hypertension. Blood pressure categories include low (70/40 to 90/60), normal (90/60 to 120/80), prehypertension (120/80 to 140/90), and high (above 140/90). Age influences these thresholds, and lifestyle modifications are vital for managing elevated levels.
Healthy arteries are essential in maintaining balanced blood pressure. Narrowed arteries can lead to abnormal readings, increasing health risks. Regular monitoring and healthy habits are important for cardiovascular wellness.