Understanding Blood Clots: Causes and Preventive Strategies
Explore the causes of blood clots, including lifestyle factors and health conditions, along with effective prevention and treatment strategies. Learn how staying active, maintaining a healthy weight, and proper hydration can reduce your risk of dangerous clots. Medical guidance is essential for managing blood clot risks and ensuring optimal health outcomes.
Sponsored

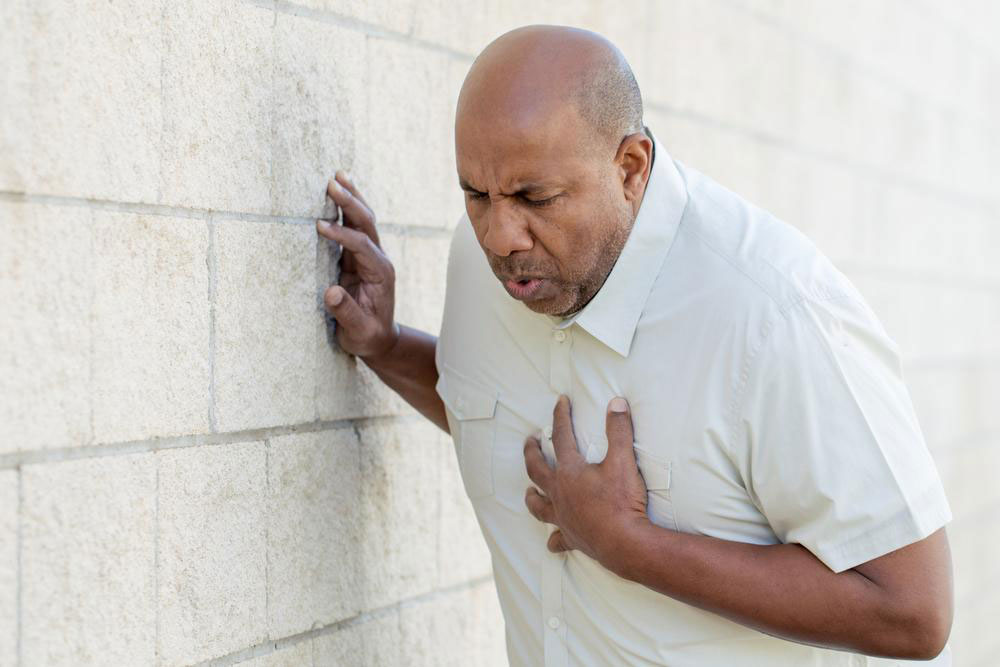
Blood clots vary in danger; some are harmless, while others pose serious health risks. An internal clot that remains stationary and dissolves might go unnoticed, but if it moves toward vital organs like the heart, lungs, or brain, it can trigger life-threatening conditions. Additionally, failure of the blood to clot after an injury can lead to dangerous bleeding. Discover more about blood clots here.
But what leads to the formation of internal blood clots?
Common Causes
Factors contributing to blood clot formation include:
Surgical Procedures: Surgeries, especially those involving arteries and veins repair or heart operations, can increase clot risk.
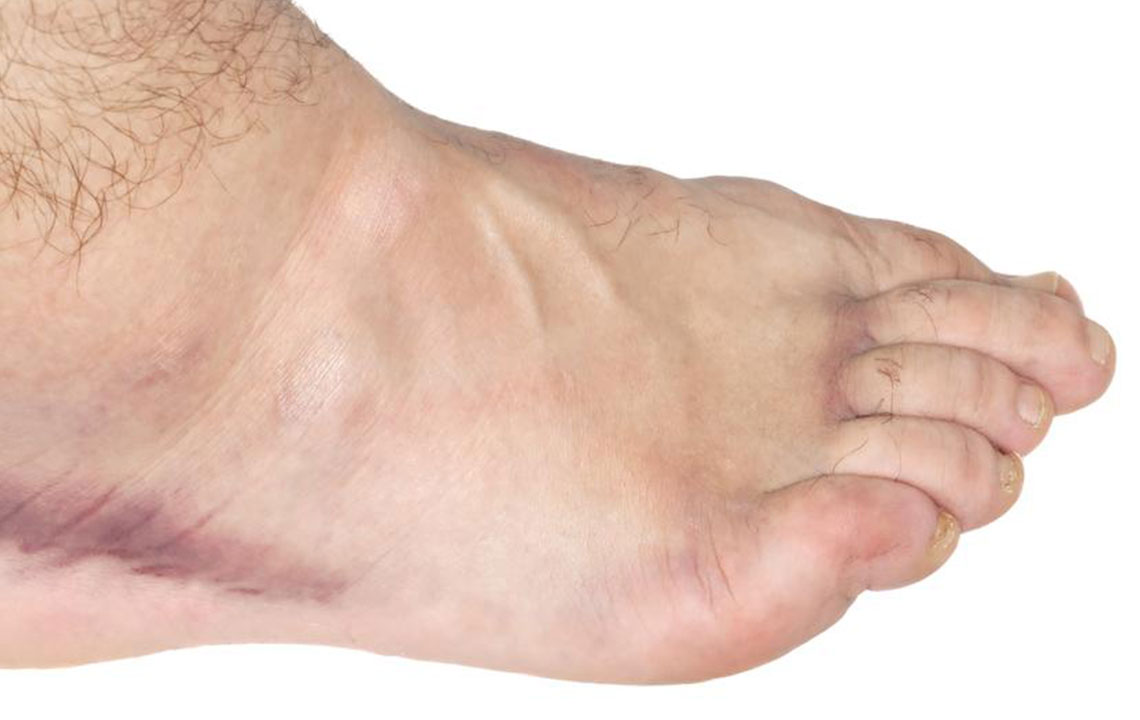
Prolonged Immobility: Extended bed rest, long flights, or staying still for long periods, especially in seniors over 65, can cause blood pooling in the legs, leading to deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism.
Atherosclerosis: Excess cholesterol can develop into arterial plaque, which can rupture and lead to clot formation, potentially resulting in a heart attack.
Atrial Fibrillation: This irregular heartbeat disrupts normal blood flow, causing pooling and clot formation, which can travel to the brain and cause strokes.
Diabetes: This condition makes blood more prone to clotting, and nearly 80% of diabetic patients face a higher risk of clot-related complications, including death.
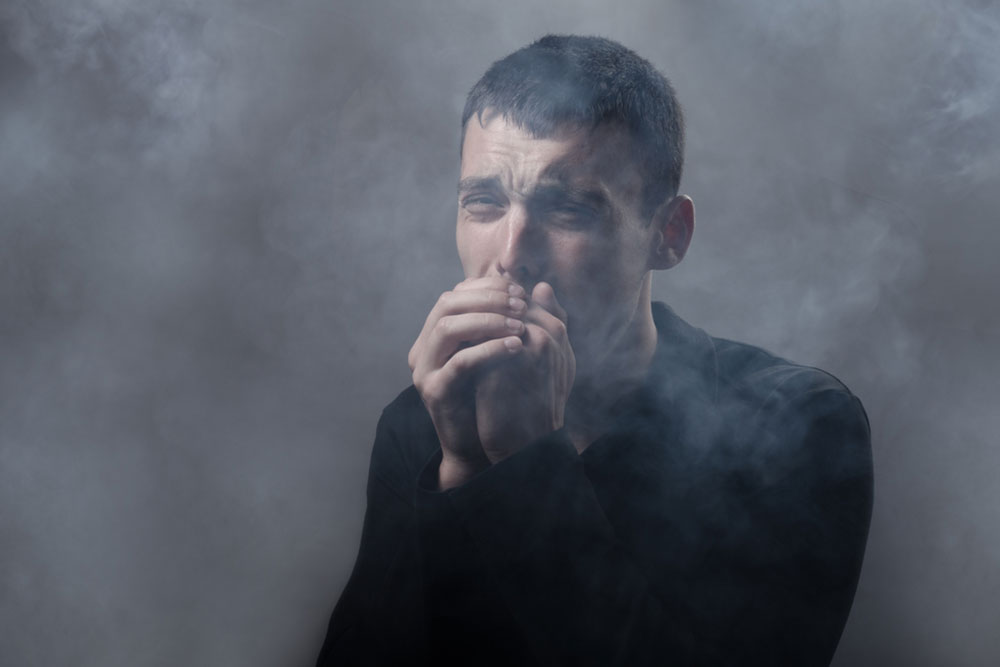
Smoking: Long-term smoking damages blood vessel linings, increasing clot formation risks.
Obesity: Excess weight impairs circulation and raises vein pressure, especially when combined with inactivity and diabetes.
Pregnancy: Pregnancy naturally increases clotting factors; women with C-sections have a higher risk of clots.
Approaches to Treatment and Prevention
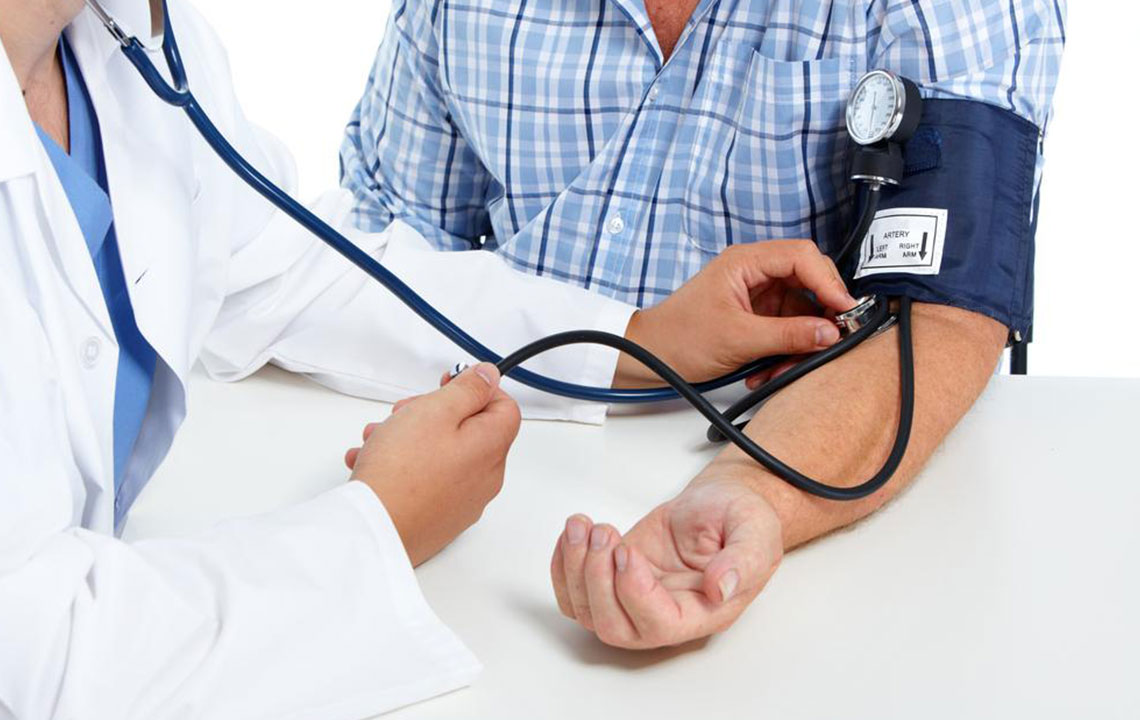
Management of blood clots depends on severity and underlying causes. Always seek medical advice, but some OTC measures and lifestyle modifications can aid in prevention.
Wearing compression stockings helps improve blood flow in the legs. Regular walking, as advised by a healthcare professional, supports circulation. Avoid prolonged sitting; stand and move periodically. Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight through proper diet and exercise reduces clot risk. Hydration is essential, as adequate water intake prevents blood thickening.