Understanding Type 2 Diabetes: Causes, Symptoms, and Management
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic condition affecting glucose metabolism due to insulin resistance or deficiency. It develops gradually, with symptoms like thirst, fatigue, and frequent urination. Managing the disease involves diet, exercise, medications, and regular monitoring. Proper management can prevent serious complications such as kidney, eye, and heart problems. Early diagnosis and lifestyle adjustments are crucial for effective control and a better quality of life for those affected.
Sponsored

What Is Type 2 Diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a persistent condition where the body struggles to process glucose effectively. Glucose, a form of sugar, relies on insulin to enter cells for energy. In this form of diabetes, either insufficient insulin is produced, or the body’s cells become resistant to it. Although treatments can help manage the disease, there’s no current cure.
Causes
The pancreas, an organ producing insulin, faces increased demand when the body doesn’t respond properly to insulin. Over time, pancreatic cells may become damaged, potentially halting insulin production.
When insulin function is compromised or production declines, blood sugar levels rise, depriving cells of fuel. The exact cause of insulin imbalance remains unclear, but factors linked to type 2 diabetes include:
Genetics
Obesity
Inactive lifestyle
Signs & Symptoms
Symptoms of type 2 diabetes develop gradually, making awareness crucial for early intervention.
Excessive thirst
Increased hunger
Fatigue
Unintentional weight loss
Dry mouth
Frequent urination
Blurred vision
Itchy skin
Advanced Symptoms
Slow wound healing
Dark patches on skin
Nerve issues
Yeast infections
Pain in feet
Management Strategies
Consume a balanced diet rich in fiber, fruits, and vegetables; limit processed foods and meats.
Engage in regular physical activity as advised by your healthcare provider.
Take prescribed medications, including pills or insulin.
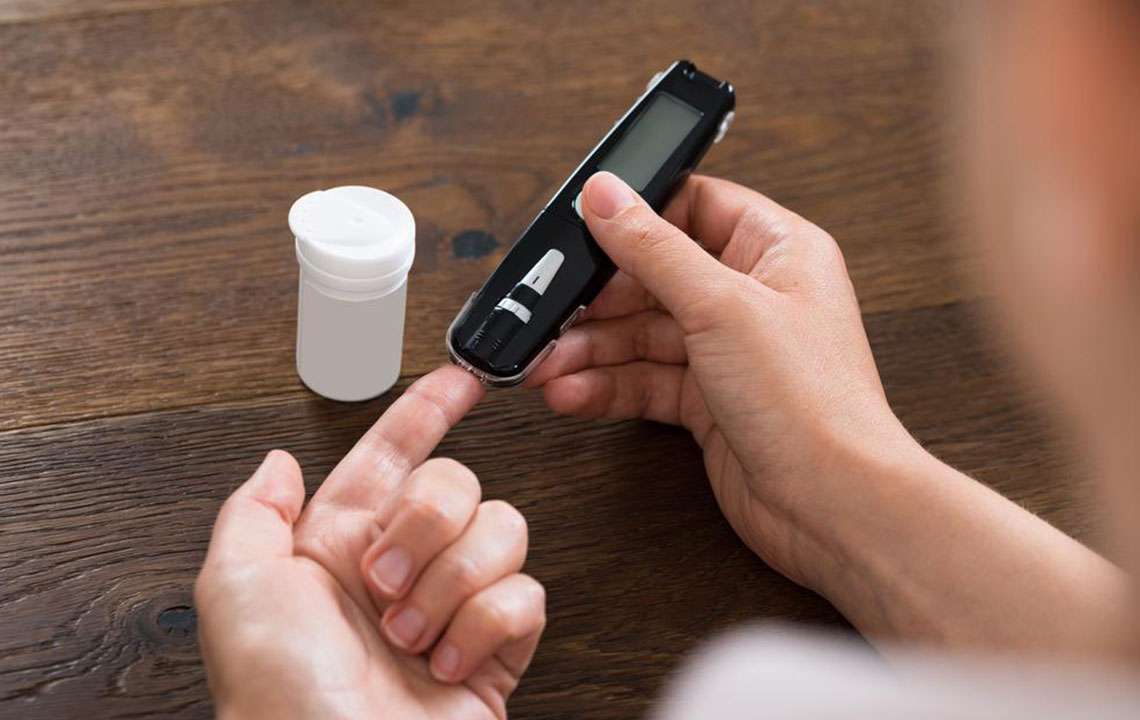
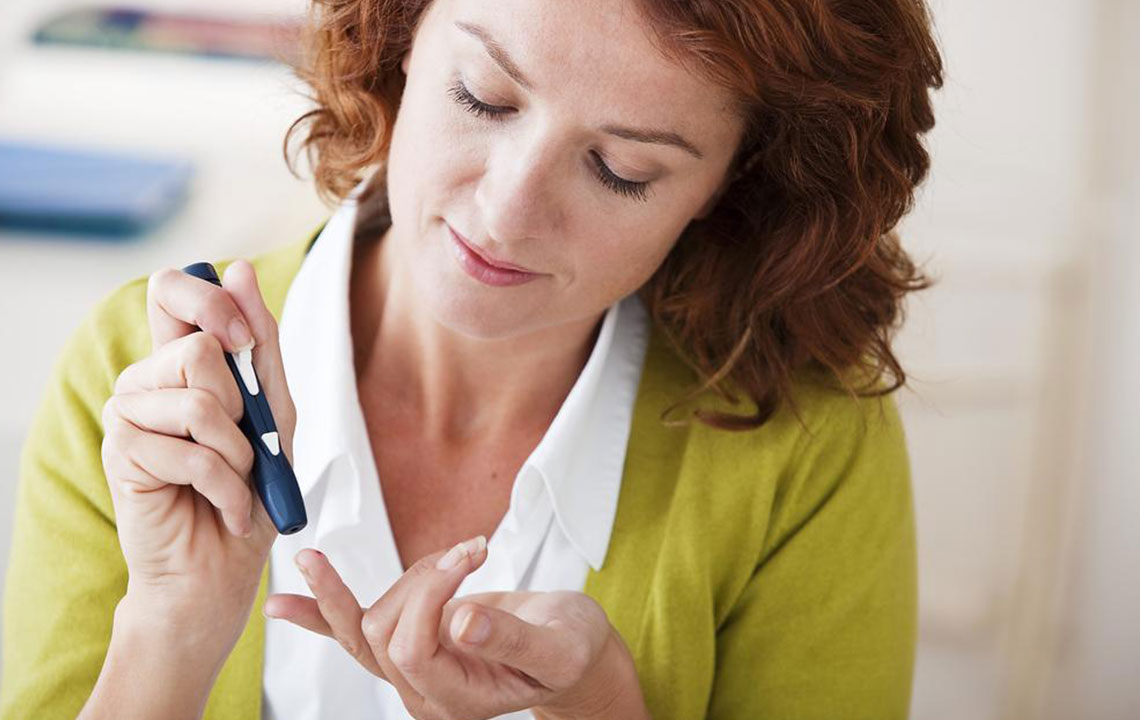
Monitor blood glucose levels regularly.
Proper control of type 2 diabetes is essential to prevent complications affecting kidneys, eyes, and heart. Pregnant individuals with diabetes should exercise extra caution. With appropriate lifestyle changes, medication, and diet, you can reduce health risks. If insulin therapy is prescribed, do not discontinue it without medical consultation.