Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis: Effective Treatments and Medications
Discover comprehensive strategies for managing rheumatoid arthritis, including medications, physical and occupational therapies, and surgical options. Learn how tailored treatment plans can help control symptoms, prevent joint damage, and enhance daily living. Consulting healthcare professionals is essential for effective management of this autoimmune condition.
Sponsored
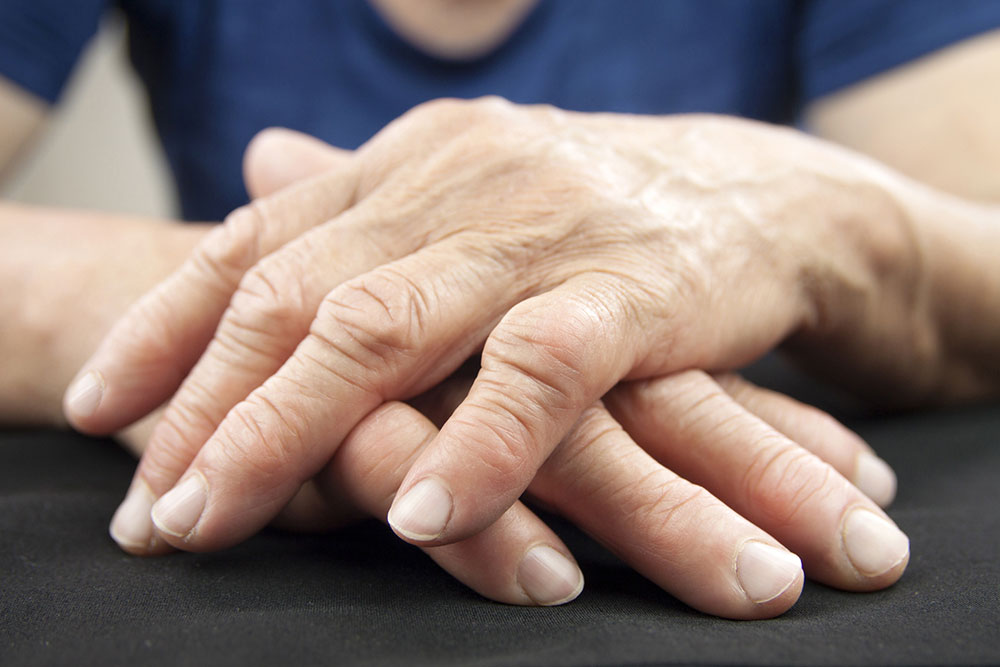
Overview of Rheumatoid Arthritis Management
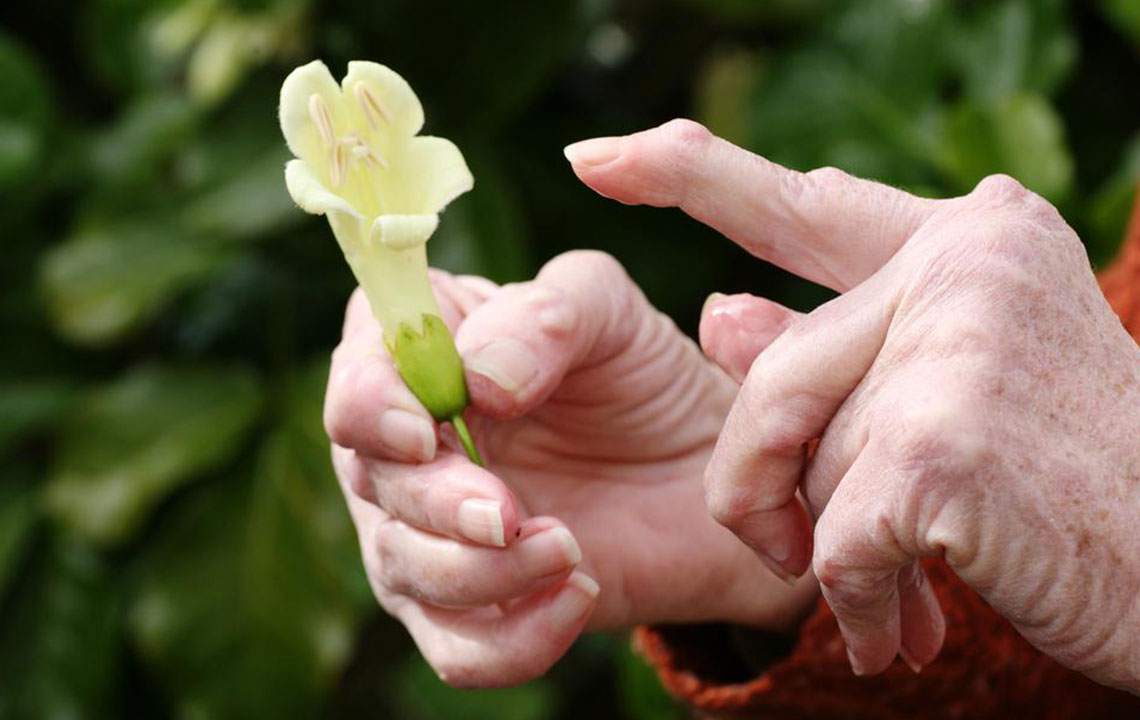
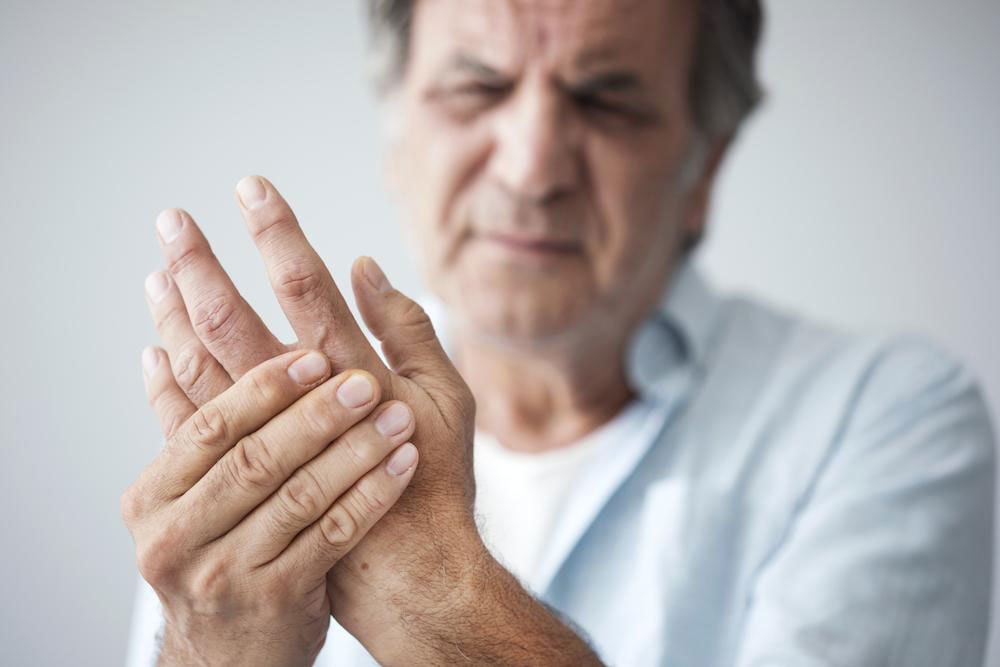
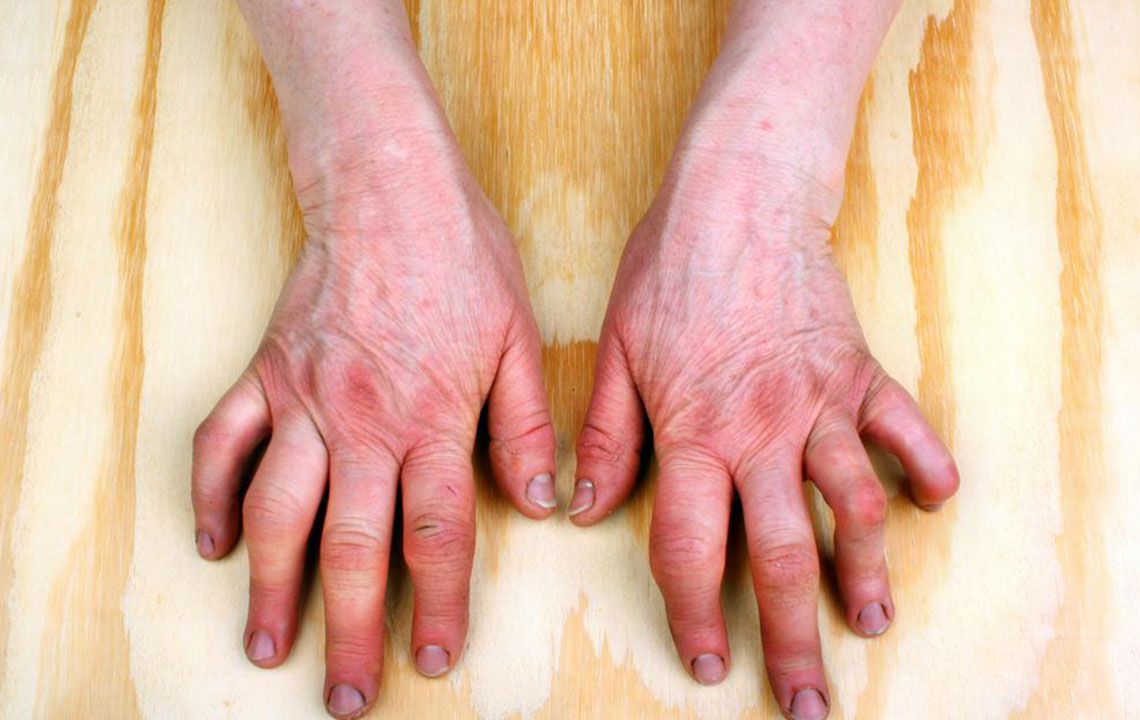
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic autoimmune disorder that causes persistent inflammation, pain, and swelling in the joints and other organs. It occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's tissues. Typically beginning in small joints such as the hands and feet, it can eventually affect multiple areas. While there's no cure, various treatments aim to control symptoms, reduce inflammation, and prevent joint damage.
Approaches to Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis
Physical Therapy: Focused on maintaining movement, this therapy employs exercise routines designed by specialists to bolster muscles, bones, and joint health, tailored to the challenges posed by rheumatoid arthritis.
Occupational Therapy: Assists patients in managing daily activities by offering adaptive devices and strategies to ease tasks like dressing, cooking, and bathing amidst symptoms like pain and swelling.
Surgical Options: Considered as a final measure, surgery may be necessary to repair joint damage, correct deformities, and alleviate persistent pain when other treatments prove ineffective.
Medications for Rheumatoid Arthritis
H.P. Acthar®: A hormone-based medication (corticotropin) used to alleviate symptoms but not a cure for rheumatoid arthritis.
CUPRIMINE®: Reserved for severe cases unresponsive to other treatments; not approved for juvenile rheumatoid arthritis due to its potency.
REMICADE®: Contains infliximab, which reduces inflammation by targeting specific substances involved in the process, typically used after other medications fail.
HUMIRA®: Adalimumab blocks tumor necrosis factor, thereby reducing inflammation but may increase infection risk due to immune suppression.
Enbrel®: Etanercept also inhibits tumor necrosis factor, helping to treat rheumatoid arthritis and certain skin conditions like psoriasis in children over age 4.
SIMPONI®: Golimumab, often combined with methotrexate, decreases inflammatory substances but can weaken immunity, raising infection risk.
While home remedies may offer additional relief, professional medical consultation is crucial for personalized treatment. Managing rheumatoid arthritis effectively involves a combination of therapies, medications, and lifestyle adjustments. Though permanent remission is unlikely, proper management can significantly improve quality of life. Always seek medical advice before starting any new treatment or remedies.