Effective Strategies to Reduce A1C Levels and Manage Diabetes
Discover practical strategies to effectively lower your A1C levels and better manage diabetes. This article highlights lifestyle changes including diet, exercise, weight management, and natural supplements like aloe vera, along with the importance of regular testing and medical consultation. Implementing these tips can significantly reduce complications and improve overall health.
Sponsored
Proven Methods to Lower Your A1C Levels
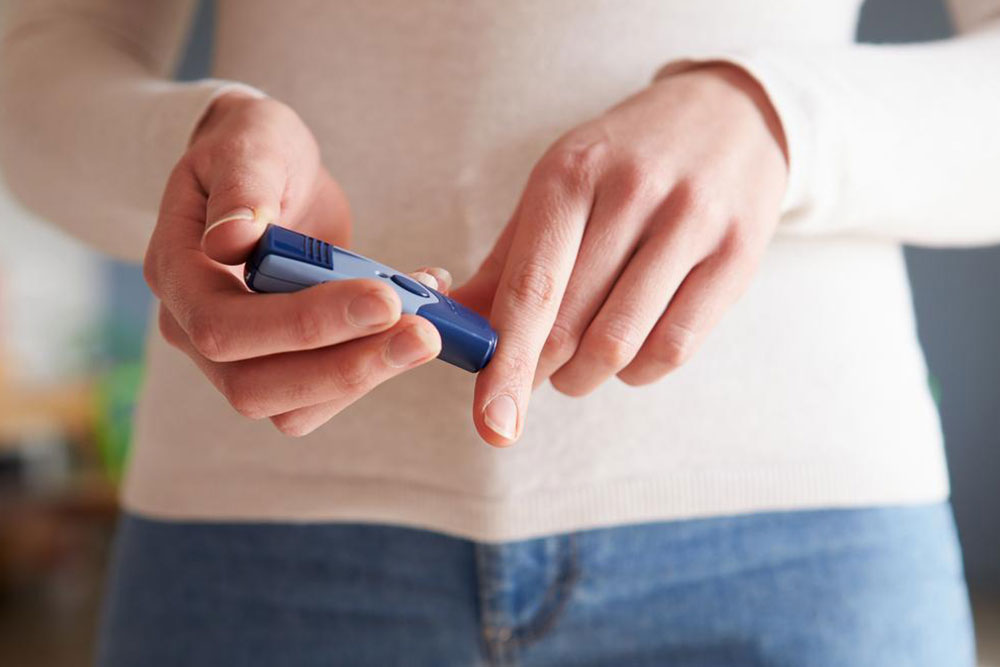
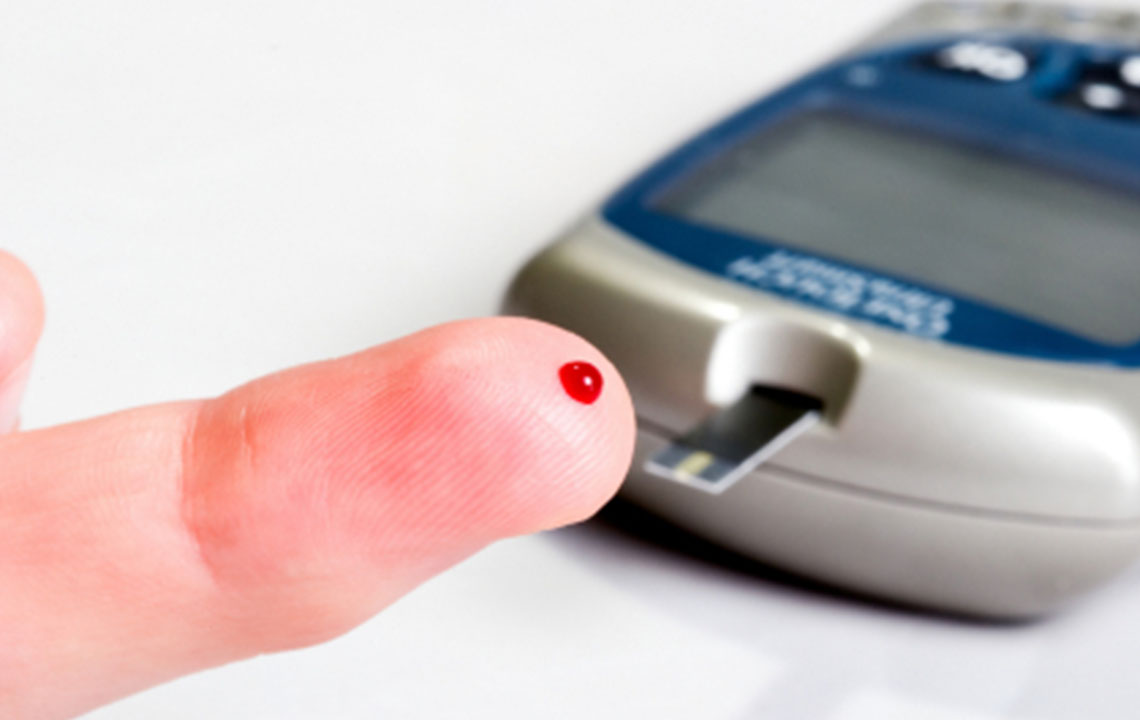
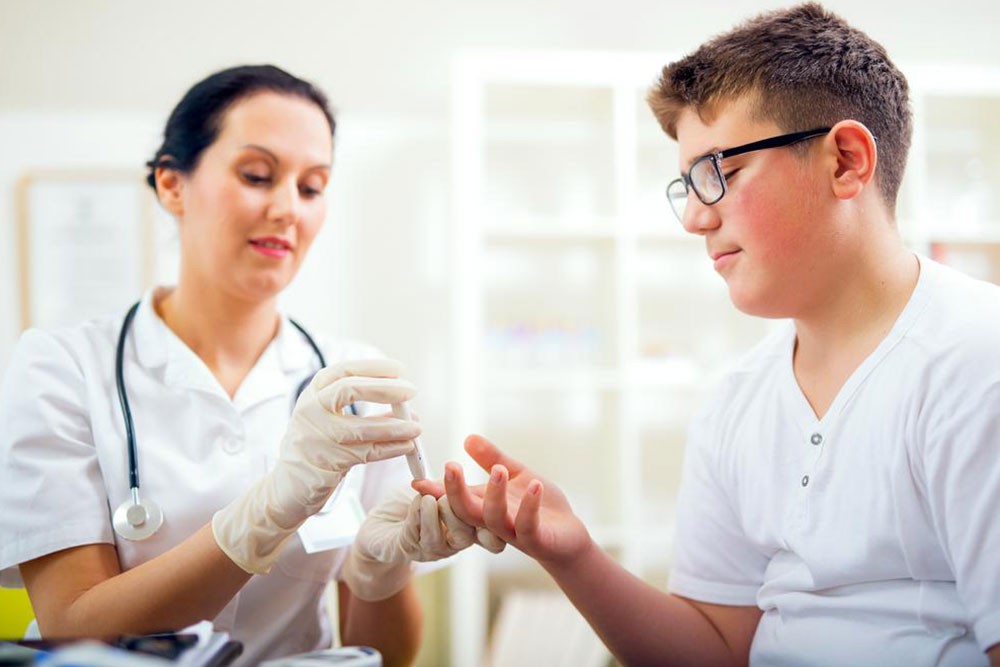
Diabetes is a persistent illness that, if not addressed promptly, can lead to serious health issues. Early stages of diabetes often show no symptoms, making regular blood sugar tests essential. If you have a family history or risk factors for type 2 diabetes, proactive testing can prevent complications. The A1C test measures your average blood glucose over two to three months and is a vital tool for those diagnosed with diabetes. Managing A1C levels through lifestyle adjustments can significantly reduce health risks.
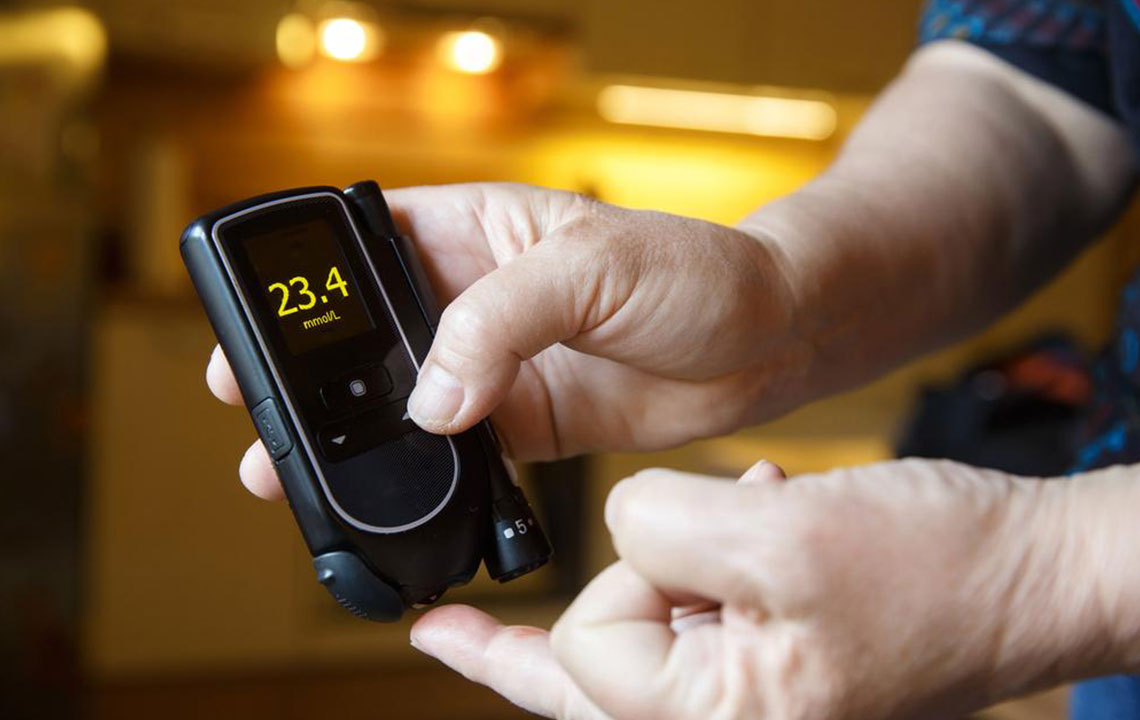
The A1C test is a blood examination that indicates how well blood sugar is controlled over time. Higher A1C percentages suggest a greater risk of diabetes-related complications. This test is popular because it does not require fasting and provides a long-term picture of blood glucose levels.
This test reveals the average blood sugar over two to three months. An A1C above 6.5% typically indicates diabetes. To manage or lower A1C levels, consider adopting these lifestyle strategies: staying physically active, controlling carbohydrate portions, maintaining a balanced diet rich in vegetables, fruits, and healthy fats, managing weight, following your medical plan, quitting smoking, and considering natural supplements such as aloe vera, which has shown promising results in reducing blood sugar levels.
Engage in regular physical activity like walking, cycling, or sports, even for brief periods post-meal, to help control blood sugar.
Eat in moderation with balanced portions of vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, and healthy fats to aid in blood sugar management.
Choose carbohydrate sources wisely, limiting intake to 45-60 grams per main meal and 15-30 grams per snack.
Aim to lose at least 5-10% of excess body weight to lower the risk of high blood sugar levels.
Work with your healthcare provider to develop a personalized diabetes management plan that includes medication, target blood glucose levels, and monitoring schedules.
Cease smoking to reduce cardiovascular risks and improve overall health.
Explore natural supplements like aloe vera, which research suggests can help lower A1C levels safely and cost-effectively.






