Understanding Lung Cancer: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Risk Factors
Learn about lung cancer's symptoms, diagnostic methods, and risk factors. Early detection is vital for effective treatment, so recognizing symptoms like persistent cough, blood in sputum, and chest pain is crucial. Various tests including biopsies, imaging scans, and lab work help confirm diagnosis and determine spread. Key risk factors include smoking, environmental exposure, family history, and prior lung diseases. Stay informed to identify early signs and seek prompt medical attention for better outcomes.
Sponsored

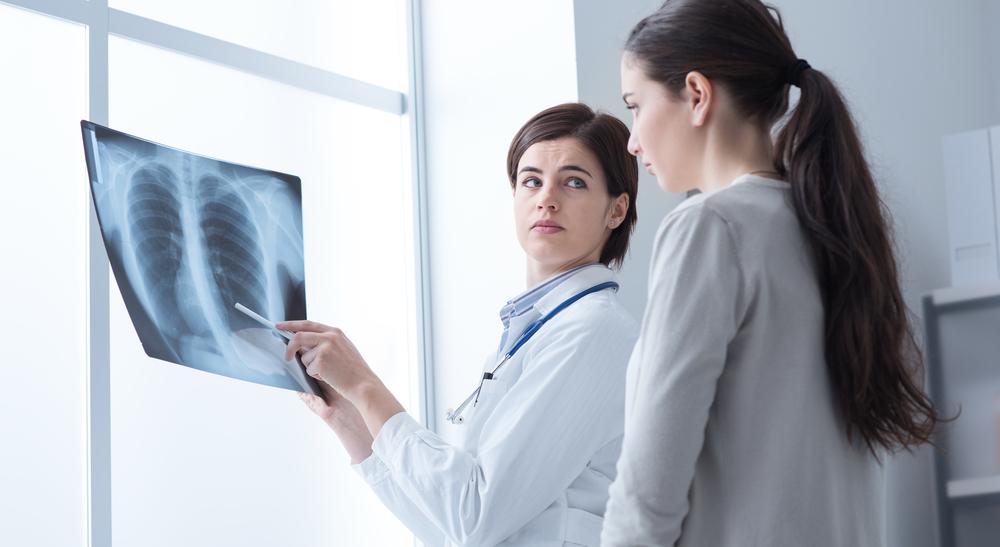
The lungs play a vital role in oxygen intake and carbon dioxide release. Composed of various cell types, mainly epithelial cells, they also contain blood, nerve, structural, and hormone-producing cells. These cells line the airways and produce mucus to safeguard lung tissues. Lung cancer develops when mutations disrupt the normal cell cycle, causing abnormal cell growth. These mutated cells create tumors, which can invade surrounding tissues. Accurate diagnosis involves multiple tests such as biopsies, medical history reviews, lab work, and imaging scans to confirm cancer presence and spread.
Biopsy: A crucial microscopic examination of lung tissue samples to diagnose cancer definitively.
Medical history: Analyzing patient history helps assess risk factors like family history or environmental exposures.
Laboratory tests: Blood tests evaluate overall health, and sputum cytology examines mucus for cancer cells.
Imaging studies: X-rays, CT scans, MRI, PET scans, and bone scans identify tumors and assess spread, guiding treatment options.
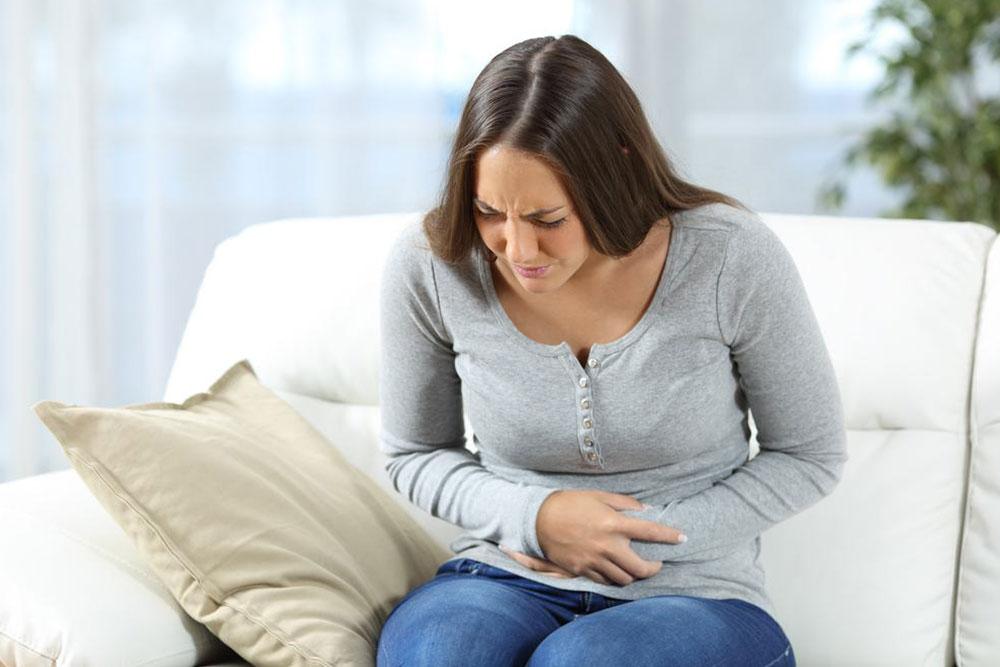
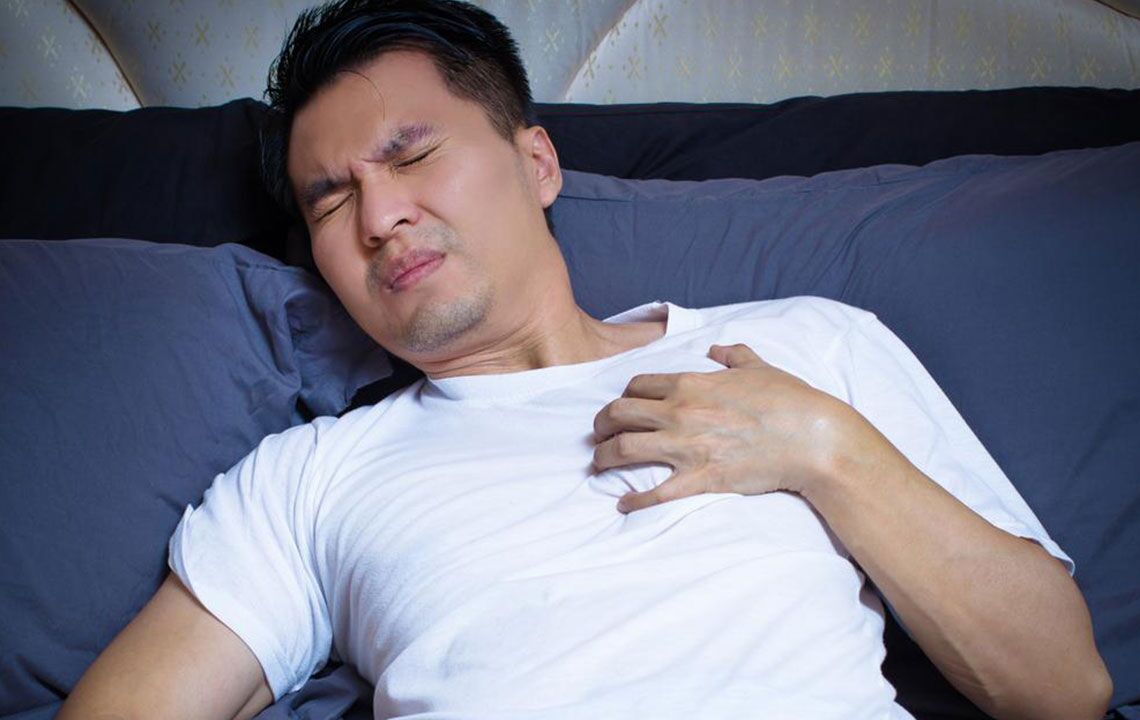
Early signs of lung cancer are often subtle or absent until advanced stages. Symptoms may include persistent cough, blood in sputum, chest pain, hoarseness, breathlessness, fatigue, recurring infections, and wheezing. When metastasis occurs, symptoms such as back pain, headaches, weakness, jaundice, or neurological issues may emerge. Risk factors include smoking, exposure to certain occupational hazards like asbestos and metals, air pollution, family history, previous lung illnesses, and radiation exposure.