Understanding and Managing Scalp Psoriasis
Scalp psoriasis is an autoimmune disorder causing thick, scaly patches on the scalp, often mistaken for dandruff. Key signs include silvery scales, dryness, and itching. Differentiating it from dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis is essential for proper treatment. Managing scalp psoriasis involves gentle care, stress reduction, and medical consultation to prevent flare-ups and maintain scalp health.
Sponsored

Scalp psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition characterized by an overactive immune response that accelerates skin cell growth. This leads to thickened, discolored patches on the scalp, accompanied by itching and irritation. Recognizing the symptoms early is crucial for effective management. If you notice signs such as plaques, dry scales, or discomfort, consult a healthcare professional for appropriate treatment. Proper care and lifestyle adjustments can help alleviate symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
What are the visual cues of scalp psoriasis?
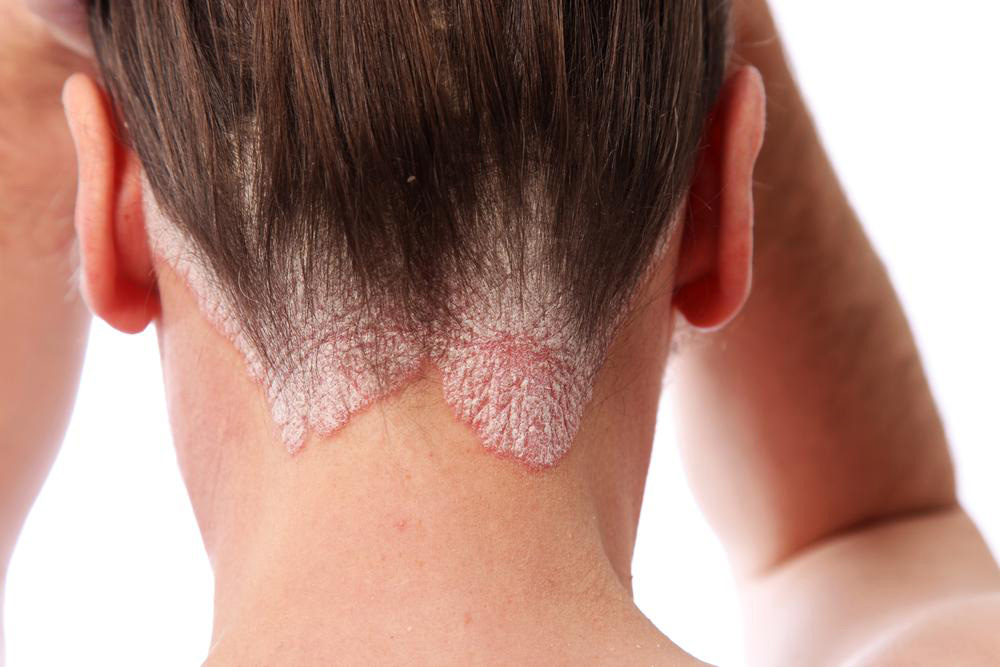
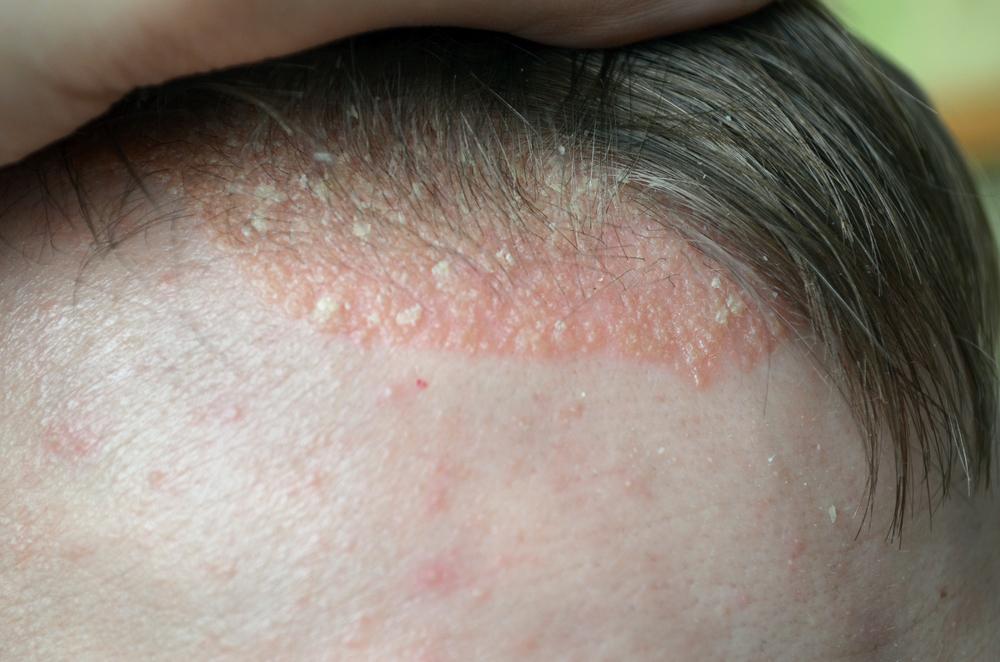
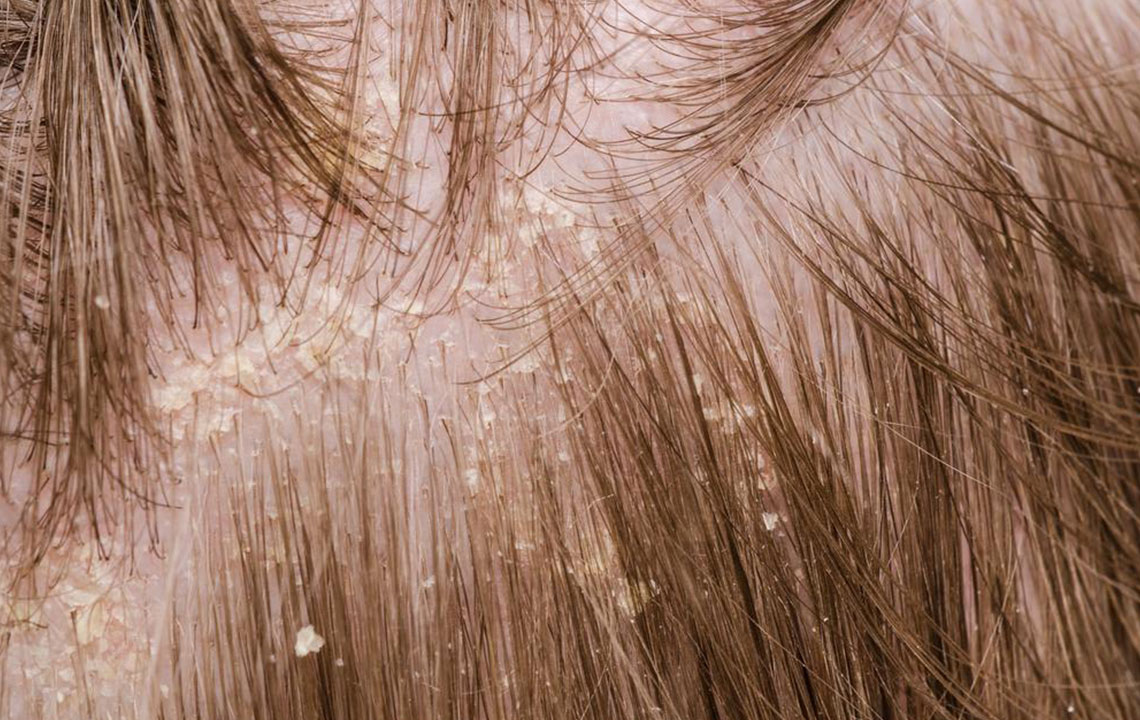
Silver-white scales appearing on the scalp.
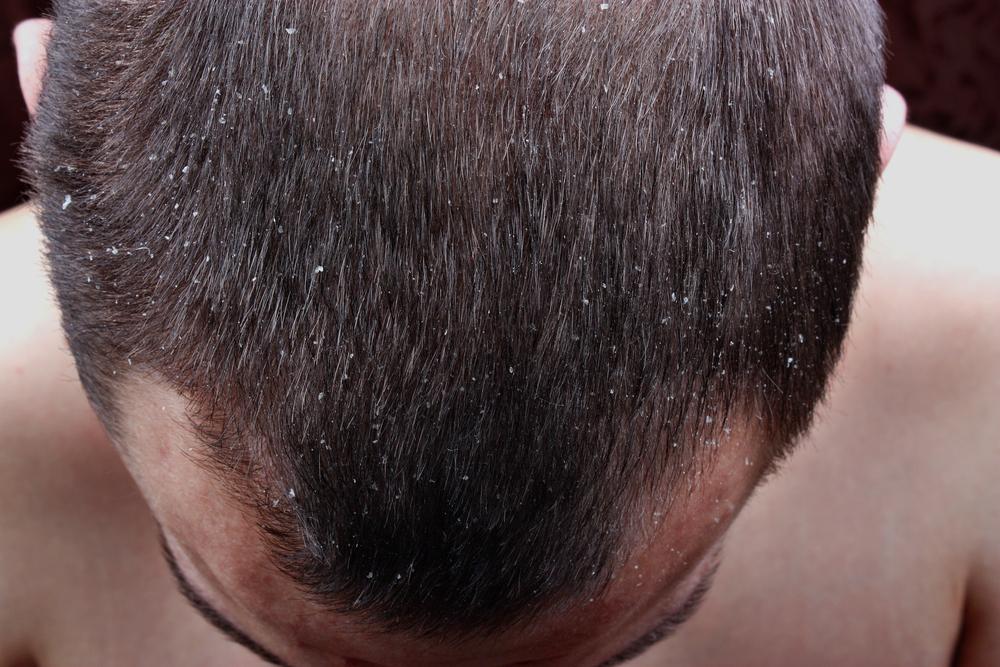
Dry, flaky skin resembling dandruff.
Persistent itching, burning, or scalp discomfort.
The earliest signs often show along the hairline or the back of the head, but can also appear on the ears, forehead, or neck. Plaques may be dry, raised, and flaky, varying from person to person. Symptoms can be mild to severe, and triggers like stress or infections can worsen the condition. On lighter skin, psoriasis manifests as pink or red patches with silvery scales, while on darker skin, it appears as darker patches with gray scales. It may be mistaken for dandruff or seborrheic dermatitis, but key differences exist.
Differences Between Scalp Psoriasis, Dandruff, and Seborrheic Dermatitis
Unlike dandruff, psoriasis shows thick, dry, and raised plaques with clear borders.
Seborrheic dermatitis often causes greasy, yellowish scales and typically remains limited to the scalp, whereas psoriasis can extend beyond the hairline and affect other skin areas.
Psoriasis may also cause nail changes like pitting, which are not seen with dandruff or seborrheic dermatitis.
Tips for Managing Scalp Psoriasis
Refrain from scratching to prevent aggravating the condition or causing hair loss.
Seek medical advice promptly when symptoms appear to start treatment early.
Be gentle when washing or applying treatments; avoid harsh scrubbing or rubbing.
Remove loose scales carefully without picking to minimize hair damage.
Regularly clean hairbrushes and combs to prevent infections.
Reduce stress through relaxation, exercise, or hobbies, as stress can trigger flare-ups.