Effective Strategies to Overcome Opioid Dependency
Discover proven methods to combat opioid dependency, including medication-assisted treatments like Methadone, Buprenorphine, and Naltrexone. Learn how these therapies help reduce cravings, withdrawal symptoms, and prevent relapse, supported by medical supervision for a successful recovery journey.
Sponsored
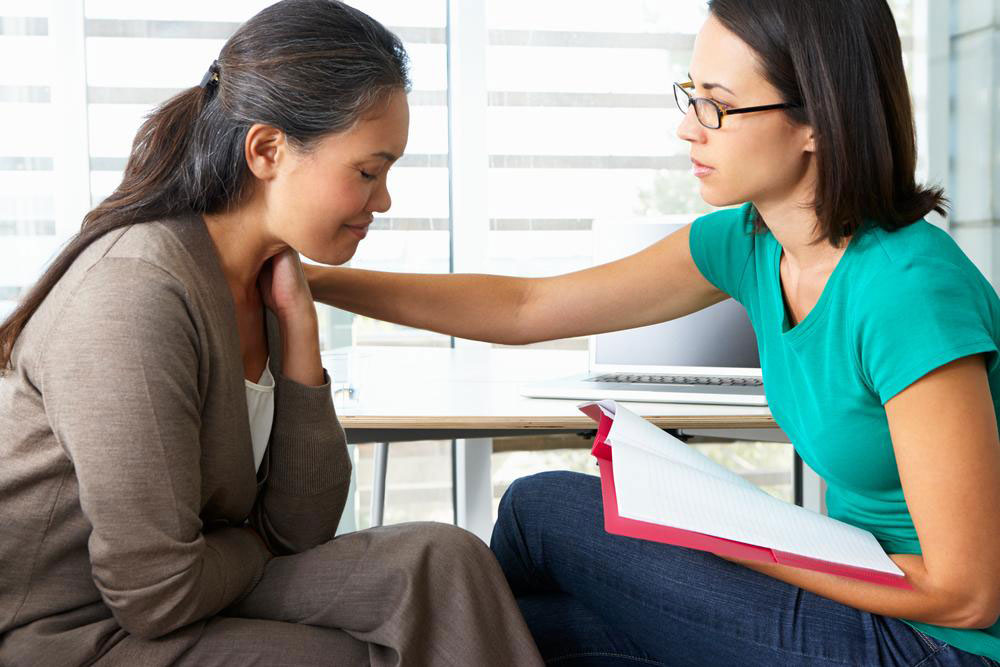

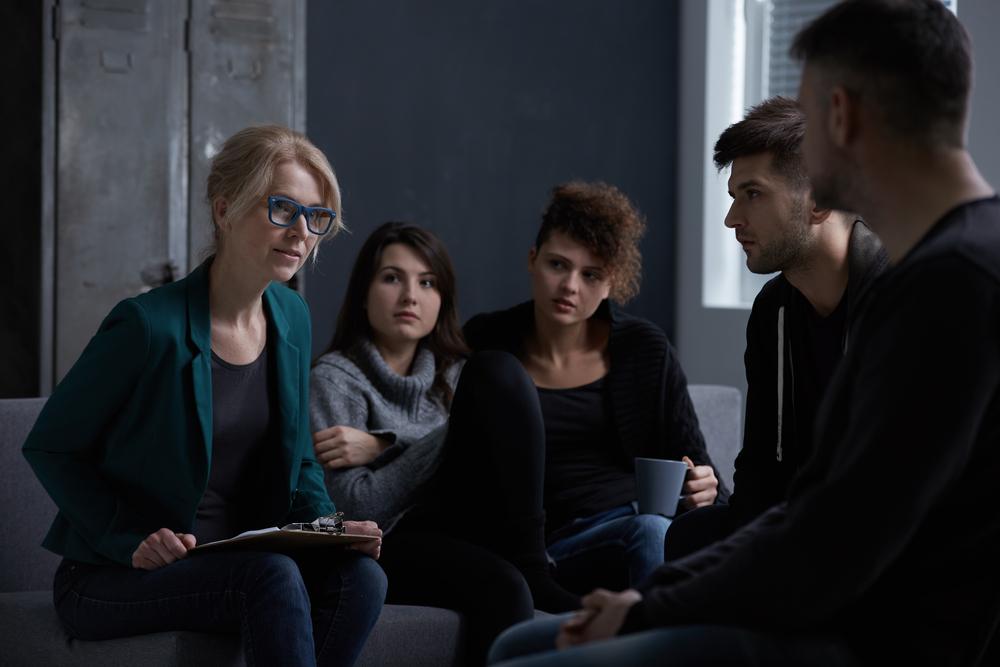
Disruptions to the body's normal functions can lead to significant discomfort, especially when caused by chronic pain. Conditions resulting from surgery, injuries, or physical ailments often require pain management. To cope with moderate to severe pain, healthcare providers frequently prescribe opioids, powerful pain relief medications. However, long-term use can lead to tolerance and dependence, risking addiction. Opioid addiction can cause serious life challenges, but it is treatable. Recovery options include inpatient rehab programs and medication-assisted treatments tailored to help individuals regain control over their lives.
Medications play a vital role in managing opioid addiction. These include:
Methadone - An FDA-approved medication that effectively reduces withdrawal symptoms and cravings by targeting opioid receptors in the brain. It has been successfully used for over four decades to assist recovery without producing a euphoric effect.
Buprenorphine - A partial opioid agonist that binds to the same receptors but activates them less intensely. It helps lessen cravings and withdrawal, making it easier for individuals to recover without feeling high, provided proper dosing is followed.
Naltrexone - An opioid blocker that prevents the receptors from being activated by other opioids. Unlike the other medications, it does not ease withdrawal or cravings but is effective in preventing relapse by blocking rewarding effects of opioids.
It's crucial to seek medical advice before starting any medication-assisted treatment, as self-medication can be risky. Different approaches work for different individuals, and professional guidance ensures safe and effective recovery.