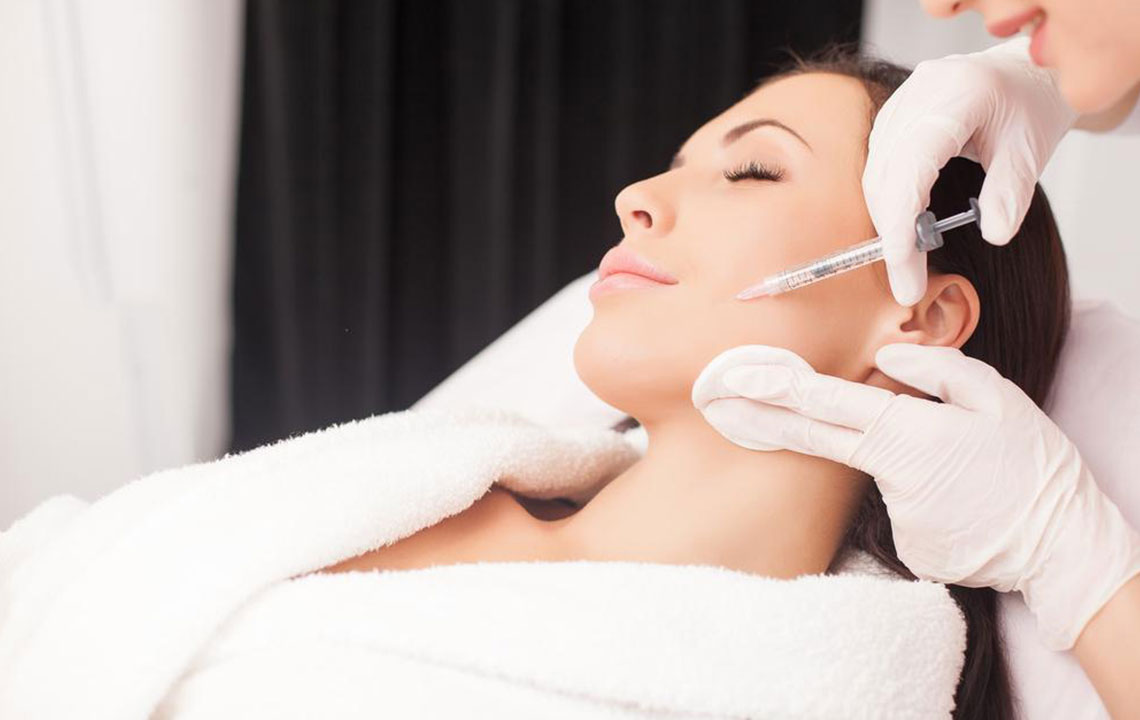
Top 10 Medical Applications of Botox Treatments
Discover the versatile medical applications of Botox beyond cosmetics, including treatment for migraines, muscle spasms, excessive sweating, and eye conditions. Proper administration by qualified professionals is essential for optimal results and safety. This article highlights the top 10 medical uses and important considerations when choosing a provider.
Sponsored
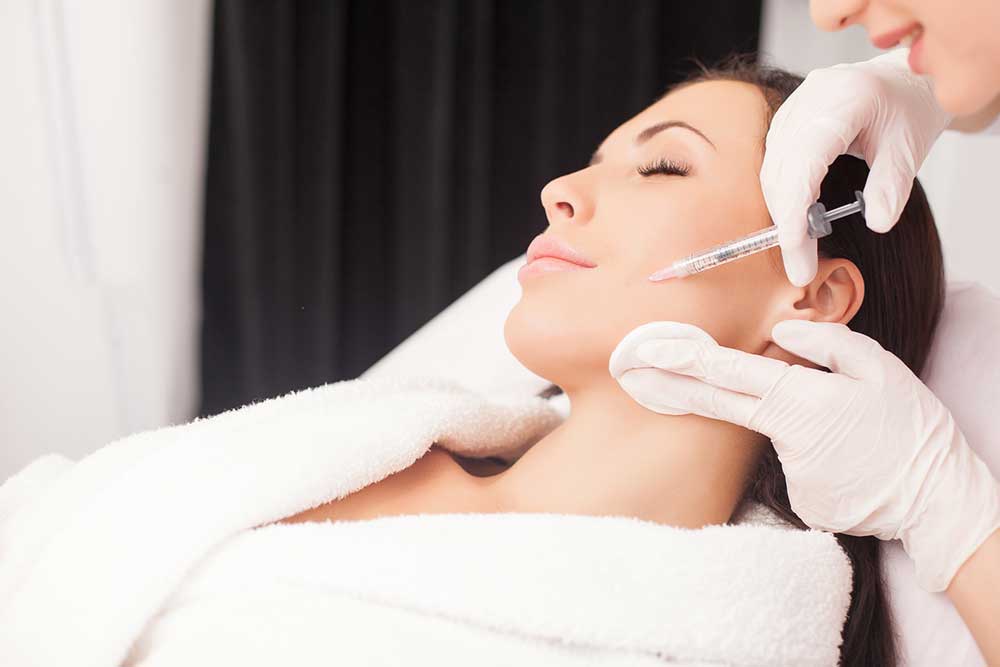

Top 10 Medical Uses of Botox
Botulinum toxin, commonly known as Botox, is derived from the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. Naturally occurring in soil, lakes, and forests, this toxin is also present in the intestines of various animals, including mammals and aquatic life. While widely recognized for its cosmetic benefits in reducing wrinkles, Botox has expanded its medical applications. Currently, it is approved to treat over 20 medical conditions. Here are the top 10 medical uses you should know about:
Blepharospasm
Also called eyelid spasms, this condition involves involuntary twitching of the eyelids. Botox works by temporarily blocking nerve signals to the muscles, alleviating the spasm and drooping.
Blepharospasm results in uncontrollable eye twitching and drooping, impairing communication with the brain’s basal ganglia. Botox interrupts nerve transmissions at the neuromuscular junction, providing relief from these symptoms.
Crossed Eyes (Strabismus)
Originally FDA-approved for strabismus, Botox relaxes overactive eye muscles, correcting eye alignment. Often preferred for its minimally invasive approach, it serves as an effective long-term solution for both congenital and trauma-related crossed eyes.
Excess Salivation (Hypersalivation)
Overproduction of saliva, caused by health issues or medication side effects, can be managed with Botox. Administered by ENT specialists, injections target salivary glands, reducing nerve signals that stimulate saliva release.
Severe Sweating (Hyperhidrosis)
For excessive sweating on the face, scalp, armpits, palms, or feet, Botox has proven highly effective. Studies show sweating reduction by up to 80%, helping prevent skin infections due to moisture buildup.
Chronic Headache Relief
FDA-approved for migraine management, Botox relaxes muscles in the temple, neck, and forehead, easing headache severity and frequency. It is particularly beneficial for those with persistent migraines involving scalp and neck discomfort.
Spasmodic Dysphonia
A neurological disorder causing strained, shaky voice, this condition benefits from Botox by softening abnormal muscle spasms around the vocal cords.
Bell’s Palsy
Temporary facial paralysis characterized by drooping, Bell's palsy can be alleviated by Botox to relax paralyzed muscles, promoting improved facial symmetry and recovery.
Thyroid Eye Disease
In autoimmune disorders like Graves' disease, Botox relaxes eyelid muscles, reducing bulging and retraction, improving eyelid function and appearance.
Neck Spasms
Causes include trauma and neurological conditions; Botox injections near the neck may reduce spasms and associated discomfort.
Irregular Heartbeat
Research explores the potential of Botox to prevent abnormal heart rhythms during cardiac surgeries.
Choosing an experienced provider is crucial. Seek a board-certified plastic surgeon or dermatologist with extensive practice in both cosmetic and therapeutic Botox procedures. Proper injection placement ensures safety and effectiveness, minimizing side effects like eyelid drooping.