Effective Strategies for Controlling Type 2 Diabetes
Learn practical methods to manage type 2 diabetes effectively, including dietary tips, exercise routines, and medication guidance. Discover how lifestyle changes play a crucial role alongside medical treatment for controlling blood sugar levels. Personalized plans created with healthcare providers can improve health outcomes and may reduce dependence on medication over time.
Sponsored
Type 2 diabetes is a lifelong chronic condition that currently has no cure. Managing the disease requires ongoing effort, including lifestyle adjustments and medical interventions. Your healthcare provider might suggest changes in diet, physical activity, and medications to keep blood sugar levels in check.
Key Approaches to Managing Type 2 Diabetes
Successful management involves a balanced diet, regular exercise, and possibly medication, as medication alone isn't sufficient.
Nutrition
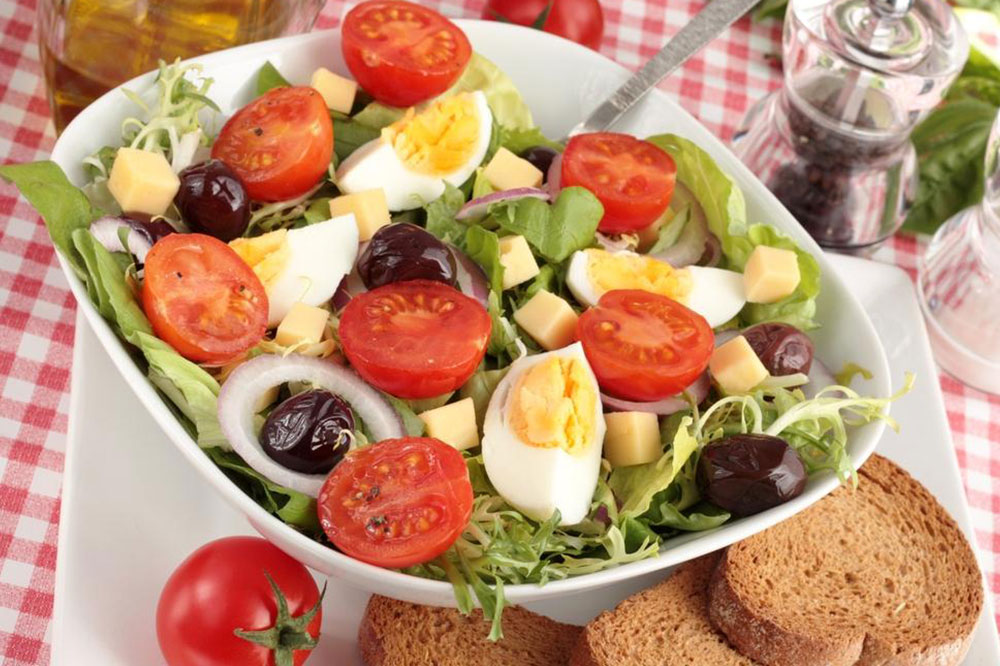
Proper nutrition plays a vital role in controlling blood glucose levels for those with diabetes.Your healthcare provider or a registered dietitian can help design a personalized diet plan that suits your needs. Common features include:
Increase intake of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Consume meats, fatty foods, salty snacks, sweets, and processed items in moderation.
Maintain consistent meal timings.
Physical Activity
Consult with your doctor to identify suitable cardiovascular exercises.A mix of aerobic workouts, resistance training, yoga, and stretching can offer better benefits than focusing on a single activity. For example, try walking, cycling, or jogging combined with strength exercises. You don’t have to do everything daily.
Physical activity helps lower blood sugar levels. If you are on medication, consider eating a light snack before exercising.
Medication
Medication isn’t necessary for everyone with type 2 diabetes. Your doctor may prescribe insulin or other drugs based on your condition.Initial treatments might include medications that enhance insulin use or stimulate production by the pancreas.
Some individuals may require insulin injections, which your doctor will prescribe as needed.
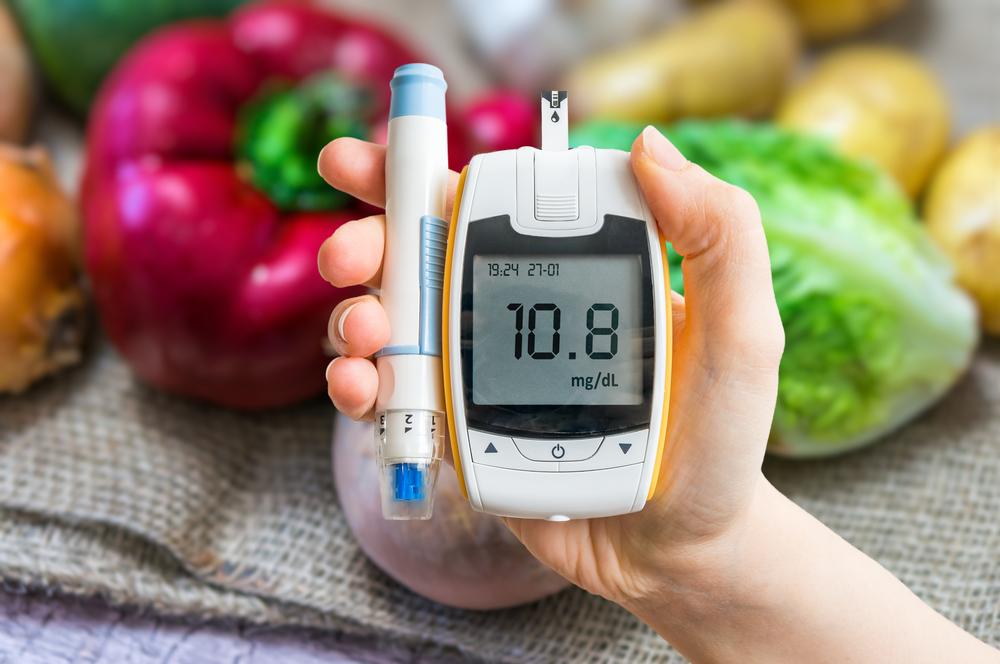
Monitoring blood sugar regularly is crucial in managing the disease effectively. Your doctor can advise on how and when to do this. With proper management, some may eventually reduce or stop medication.