Effective Strategies for Managing Diabetes and Leading a Healthy Life
Learn effective strategies to manage diabetes through lifestyle changes, medication, and diet. Understanding the different types and symptoms helps in early detection and personalized treatment. Incorporate healthy foods like fatty fish, leafy greens, and nuts, along with regular exercise, to improve quality of life. Medical options such as insulin therapy, medications, and surgical procedures are available for comprehensive management. Early intervention and lifestyle modifications are essential for preventing complications and maintaining health with diabetes.
Sponsored

Strategies for Managing Diabetes and Maintaining Well-being
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder where the body cannot properly regulate blood glucose levels. Normally, insulin facilitates the transfer of sugar from the bloodstream into cells to produce energy. In diabetes, either the body produces insufficient insulin or becomes resistant to it, leading to elevated blood sugar. Prolonged high glucose levels can harm vital organs such as eyes, kidneys, and nerves, and increase risks of heart disease and strokes. Effective management is vital for improving quality of life.
Types of diabetes
Type 1 diabetes:
This autoimmune condition occurs when the immune system attacks insulin-producing pancreatic cells. The cause remains unclear, but genetics and viral factors may contribute. Patients require daily insulin injections or pumps to stay healthy.
Type 2 diabetes: Unlike type 1, the body still produces insulin, but cells become resistant, causing sugar buildup in the blood. It’s the most common type, strongly associated with obesity and sedentary lifestyles.
Prediabetes: Blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not enough to diagnose diabetes, with levels between 100-125 mg/dL.
Normal blood sugar is between 70-99 mg/dL. Levels above 126 mg/dL indicate diabetes, while prediabetes ranges from 100-125 mg/dL.
Gestational diabetes: Occurs during pregnancy when hormonal changes reduce insulin sensitivity. Usually resolves after childbirth but requires monitoring, especially if risk factors exist.
Understanding the different types helps tailor management plans. Consulting a healthcare professional is essential to develop personalized strategies based on symptoms and diagnosis.
Common symptoms include increased thirst, hunger, weight loss, fatigue, blurry vision, frequent urination, and slow-healing sores. Men may face reduced libido and erectile issues, while women might suffer recurrent UTIs, yeast infections, or dry skin.
Symptoms specific to diabetes types:
Type 1: Increased thirst and hunger, unintended weight loss, fatigue, blurry vision, frequent urination, mood swings.
Type 2: Similar symptoms, often with recurring infections and slow healing.
Gestational: Often asymptomatic; diagnosed through glucose tolerance tests; some women experience increased thirst.
Causes vary with type: autoimmune destruction of pancreas cells in type 1; genetic predisposition combined with lifestyle factors for type 2; hormonal and weight-related factors during pregnancy in gestational diabetes.
Risk factors include genetic history, obesity, sedentary behavior, age, and existing conditions like high cholesterol or blood pressure. Women with overweight or previous gestational diabetes are more vulnerable.
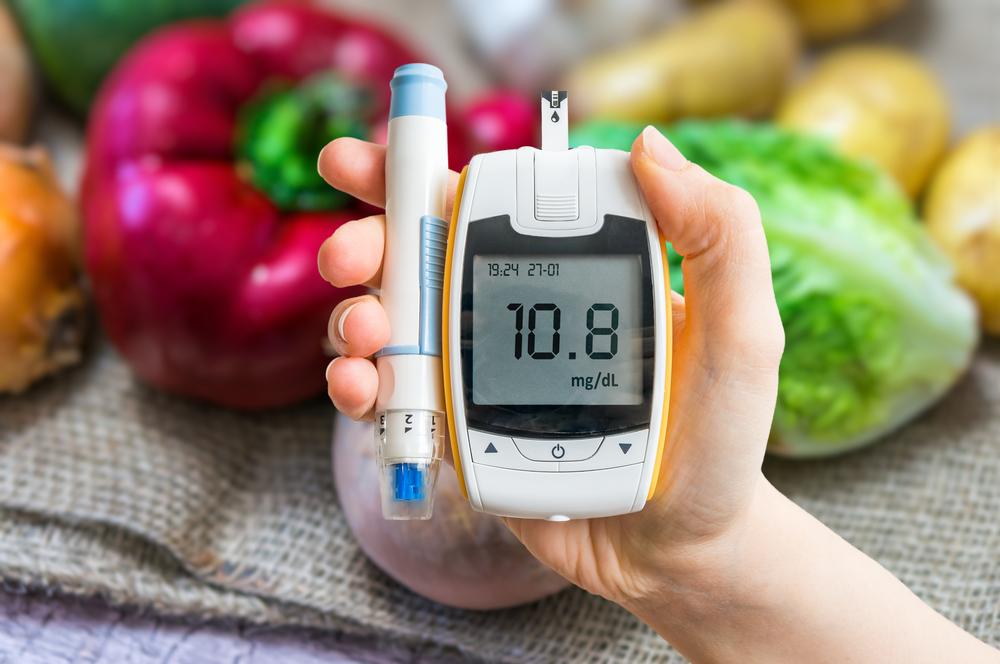
Treatment approaches focus on controlling blood sugar through medication, lifestyle changes, and sometimes surgical options. Monitoring blood glucose regularly is crucial for effective management.
Medication options: Insulin therapy is essential for type 1 and sometimes for type 2. Different insulin forms—long-acting, rapid-acting, premixed—are available. Insulin cannot be taken orally; it’s injected via syringes, pens, or pumps, including tubeless devices.
Oral medications may stimulate insulin production or reduce glucose release from the liver, often combined with insulin for type 2 management. In some cases, pancreas transplants or bariatric surgery are considered, especially for obese patients with type 2 diabetes.
Lifestyle modifications and natural remedies: Following a balanced diet rich in lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains reduces sugar spikes. Avoid sugary, fried, or processed foods, and limit alcohol intake. Regular physical activity—around 45 minutes, 5 days a week—helps regulate blood sugar and achieve weight loss. Managing weight is particularly effective in reversing or controlling type 2 diabetes.
Foods beneficial for managing diabetes include fatty fish like salmon, leafy greens, eggs, chia seeds, turmeric, Greek yogurt, nuts, and broccoli. These foods help reduce inflammation, improve cholesterol, and support overall metabolic health.
While type 1 diabetes largely stems from uncontrollable factors, adopting a healthy lifestyle can prevent or delay type 2 diabetes. Early detection and lifestyle changes are key to maintaining a healthy, balanced life with diabetes.