Comprehensive Guide to Managing Diabetes Effectively
This comprehensive guide covers effective strategies for managing diabetes, including medication, diet, exercise, and alternative therapies. It emphasizes the importance of professional guidance and lifestyle changes to maintain healthy blood sugar levels and prevent complications. Collaborate with healthcare providers to develop a personalized plan that suits your needs and promotes overall well-being.
Sponsored
Understanding Different Approaches to Diabetes Management
Learn about various strategies for controlling diabetes
Globally, over 100 million individuals live with diabetes or prediabetes, including approximately 30 million in the United States. Diabetes can develop at any age, whether you are 20 or 60. Regular blood sugar testing is crucial, especially for those at risk. Managing diabetes requires professional guidance to develop an individualized treatment plan, often involving a multidisciplinary team including nutritionists, endocrinologists, eye specialists, and podiatrists. Effective management aims to maintain stable blood glucose levels through medication, diet, and exercise.
Patients often require a team of healthcare providers for comprehensive care. This team works together to tailor treatments, which may include medications, insulin therapy, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring. Adherence to prescribed medications, maintaining a healthy diet, and consistent physical activity are vital in controlling blood sugar. Monitoring your intake and timing meals accurately prevents swings in blood glucose, ensuring better overall management.
Insulin Therapy
Individuals with type 1 diabetes lack insulin production by the pancreas and need insulin through injections or pumps. There are five main types of insulin: rapid-acting, short-acting, intermediate-acting, long-acting, and ultra-long-acting, which are chosen based on individual needs and doctor recommendations.
Oral Medications
Various pills are available to manage blood sugar levels, each working through different mechanisms. These medications are prescribed based on individual health profiles and help improve insulin sensitivity or reduce glucose production.
Diet and Meal Planning
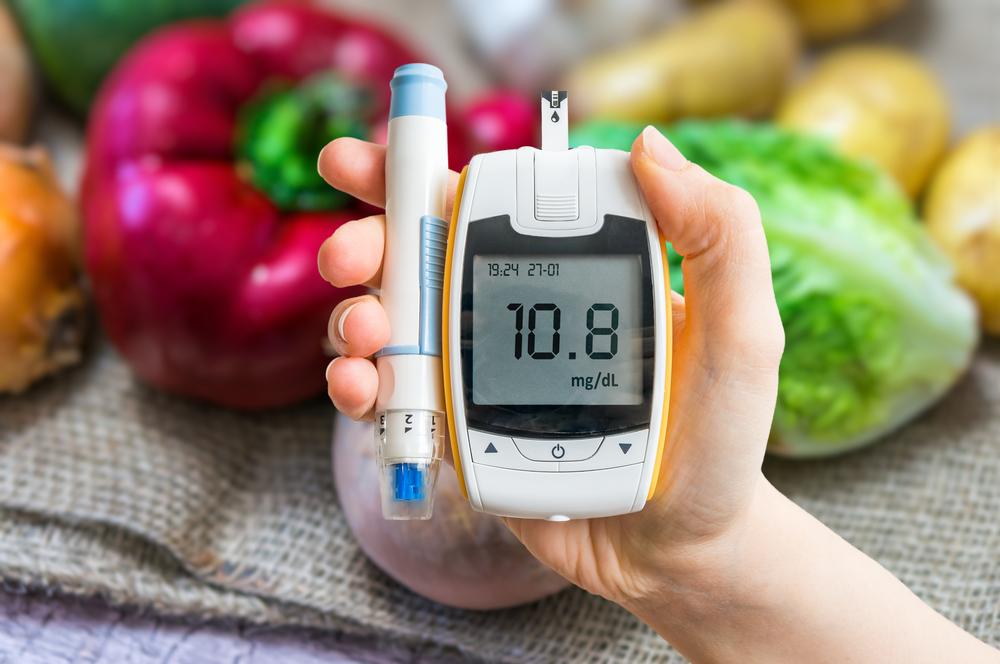
Eating a balanced, nutritious diet is essential. Collaborate with a healthcare provider or dietitian to create a meal schedule that maintains optimal blood sugar levels. Consuming three small meals daily along with healthy snacks can help stabilize glucose. A diet rich in proteins, healthy fats, and controlled carbohydrate intake, avoiding trans fats and limiting saturated fats to under 7%, supports optimal management.
Physical Activity
Regular exercise, including walking and strength training, enhances insulin sensitivity and aids blood sugar control. Always consult your doctor before starting any new exercise regime. Physical activity also reduces cardiovascular risks and promotes healthy circulation.
Complementary and Alternative Treatments
Supplements such as vitamins C, E, B6, B12, and magnesium may support diabetes management, but only after medical advice. Integrating alternative therapies like biofeedback, yoga, meditation, and hypnotherapy can help reduce stress, which positively impacts blood sugar stability.
Herbal Remedies
Certain herbs—such as garlic, holy basil, fenugreek, ginseng, and hawthorn—may assist in managing blood glucose. Always discuss herbal usage with your healthcare provider to ensure safety and compatibility with prescribed treatments. While promising, more research is needed to establish their efficacy conclusively.
Controlling diabetes involves lifestyle modifications and adhering to medical advice. Though not always life-threatening, unmanaged diabetes can damage organs and tissues. Empower yourself with proper knowledge and treatment strategies to lead a healthy, balanced life.