Effective Strategies for Managing Blood Glucose and Preventing Diabetes Complications
This article explores effective strategies for blood sugar management and diabetes control. It covers medication options, dietary habits, lifestyle changes, and key precautions for maintaining healthy blood glucose levels. Practical tips include choosing low-glycemic foods, engaging in regular exercise, and managing stress. Understanding the differences between type 1 and type 2 diabetes helps tailor appropriate treatment approaches. Adopting these practices can help prevent complications, improve quality of life, and achieve long-term health stability for individuals with diabetes.
Sponsored

Maintaining stable blood sugar levels is essential for individuals with diabetes. Elevated blood glucose, or hyperglycemia, can lead to serious health issues such as heart, kidney, eye, and nerve problems. About 13% of adults worldwide live with diabetes. Here are proven methods to keep blood sugar in check:
Medication Options
GlucoTrust - An FDA-approved, all-natural supplement suitable for both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
INVOKANA® - Helps regulate blood glucose and diminishes the risk of kidney damage in type 2 diabetes.
Additional Treatments
Kerendia® - A daily tablet designed for type 2 diabetics to reduce kidney and cardiovascular risks.
Insulin therapy remains vital for those with type 1 diabetes and some with type 2. Using modern devices like the Dexcom G6 Continuous Glucose Monitor enhances control without finger pricks.
Things to Avoid
Stay away from foods raising blood sugar, such as fried foods, processed snacks, sugary drinks, and refined carbs like white rice and sweets. Limit processed meats high in salt and oil. Avoid exercising on an empty or full stomach and never skip prescribed medications. Managing stress is equally crucial, as cortisol and glucagon hormones can spike blood sugar levels, complicating control efforts.
Optimal Diet and Lifestyle Adjustments
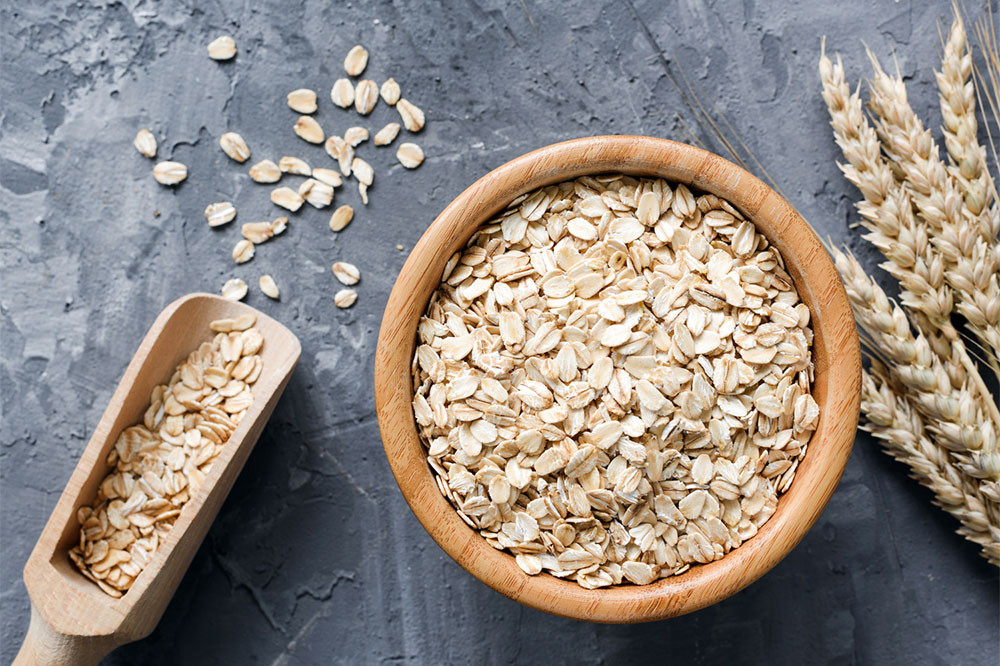
Choosing low-glycemic foods like oats, Greek yogurt, lentils, and beans is beneficial. Focus on fiber-rich options such as brown rice, quinoa, vegetables, and fruits to promote stable blood sugar. Incorporate balanced meals with adequate proteins and healthy fats.
Regular physical activity helps lower blood glucose by burning sugar for energy and improves insulin sensitivity. Meditation or relaxation techniques aid in reducing stress-related hormonal spikes. Adequate sleep further supports blood sugar regulation.
Two primary types of diabetes include:
Type 1 diabetes: A condition where the pancreas produces little to no insulin, requiring daily insulin injections.
Type 2 diabetes: The more common form, characterized by the body’s inefficient use of insulin, often manageable with lifestyle changes and medication.