Effective Strategies to Reduce Blood Sugar Levels Naturally
Learn practical and natural methods to lower your blood sugar levels effectively. This guide covers the basics of blood sugar, types of diabetes, testing methods, and lifestyle adjustments including diet, exercise, and medication. Proper management helps prevent severe health complications associated with high blood sugar. Stay proactive and consult healthcare professionals to tailor the best plan for your needs.
Sponsored

High blood sugar levels can lead to serious health complications if not managed properly. Maintaining optimal sugar levels is crucial to prevent diseases like diabetes. Before exploring methods to lower blood sugar, it’s important to understand how blood sugar and diabetes work.
The pancreas releases insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar. When insulin production drops or the body's cells resist insulin, blood sugar rises, resulting in diabetes.
Types of Diabetes
There are three primary types: Type 1, Type 2, and gestational diabetes. About 90% of cases are Type 2, caused by insufficient insulin production or insulin resistance. Initially, the pancreas compensates by secreting more insulin, but over time, this becomes inadequate, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
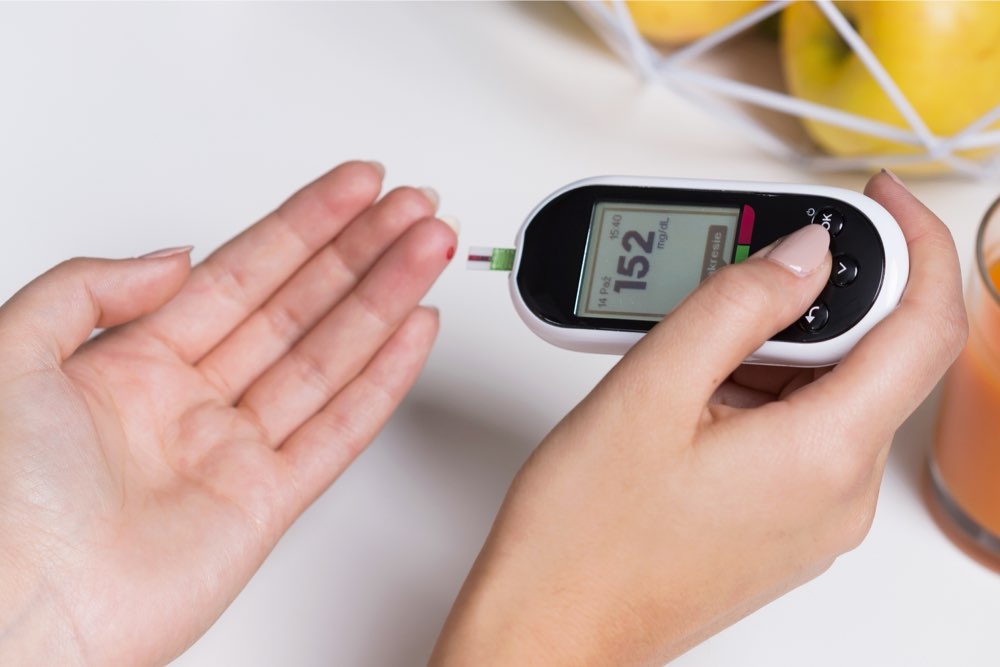
Normal Blood Sugar Range
A fasting blood sugar level between 70-99 mg/dL is considered normal. Two hours after eating, a normal level should be below 140 mg/dL. Levels exceeding 126 mg/dL during fasting or 200 mg/dL randomly indicate possible diabetes.
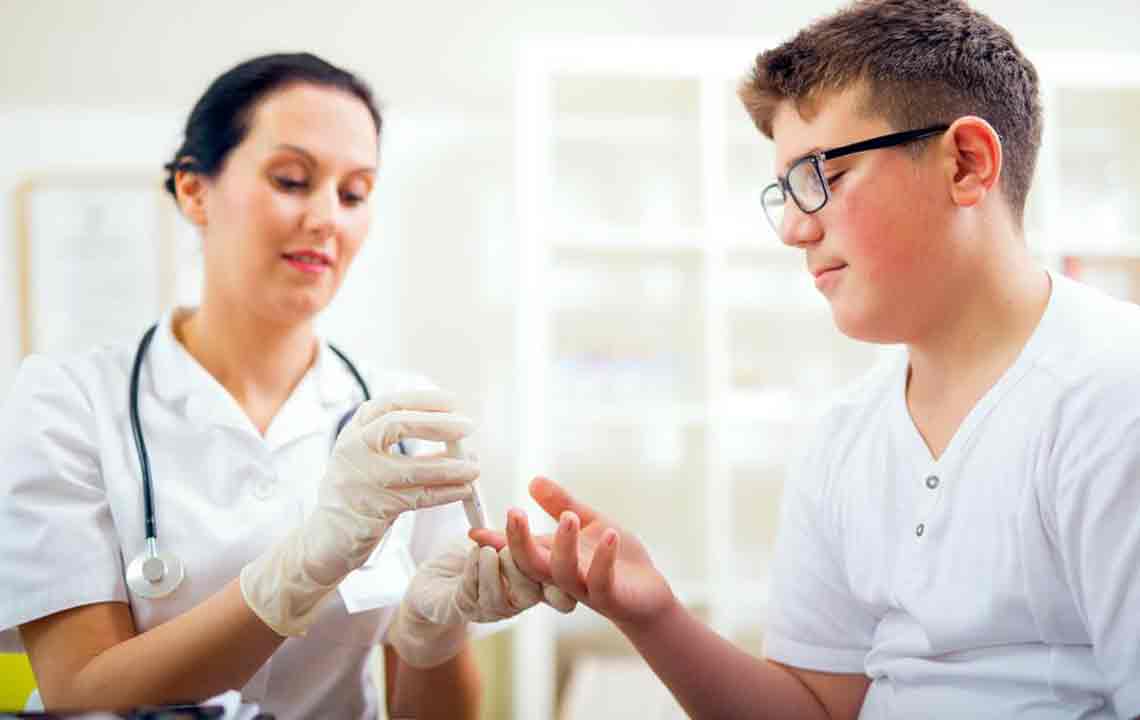
Blood Sugar Testing Methods
Tests like A1C, plasma glucose, and lab analyses help monitor blood sugar. A1C provides an average over 2-3 months, while fasting plasma tests require an overnight fast. Regular testing is key to managing diabetes and preventing complications such as heart disease, kidney issues, and nerve damage.
Ways to Lower Blood Sugar
Achieving better blood sugar control involves consistent effort. Here are effective strategies:
Weight Management – Shedding excess weight can substantially reduce diabetes risk.
Physical Activity – Daily walks of 30-40 minutes enhance insulin sensitivity.
Diet and Lifestyle – Reducing intake of high-carb, sugary, and fatty foods is crucial. Alcohol consumption should also be moderated to prevent blood sugar fluctuations.
Medication – Doctors prescribe medications tailored to individual needs, including options like Metformin, insulin, and other oral drugs that improve insulin effectiveness or production.
Managing blood sugar levels can be challenging, especially in cases of hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia. Hyperglycemia (levels over 240 mg/dL) can be controlled with diet, medication, and exercise, while hypoglycemia causes dizziness and unconsciousness. Keep glucose tablets or carbohydrate-rich foods handy for emergencies. Consulting your healthcare provider regularly is essential for effective management.