Key Indicators of Diabetes You Need to Recognize
This article highlights key symptoms and causes of diabetes, emphasizing early detection and lifestyle strategies for prevention. Understanding the disease's signs like frequent urination, excessive thirst, and fatigue can help individuals seek timely medical advice and manage their health effectively.
Sponsored

Diabetes has become a prevalent health concern, affecting individuals across all ages, from celebrities like Justin Bieber to iconic actors such as Al Pacino.
Understanding what the disease entails and recognizing its warning signs is essential for early detection and management.
What is diabetes?
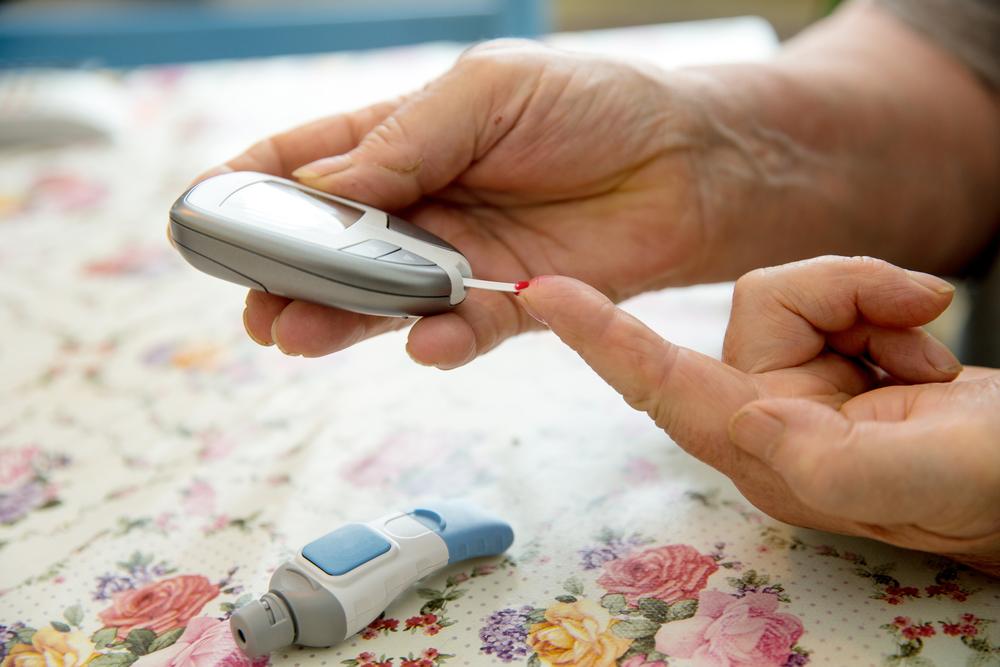
Diabetes is a condition characterized by elevated glucose levels in the blood.
Fasting blood sugar levels in the morning are typically the lowest. For non-diabetics, normal fasting levels range from 3.9 to 5.5 mmol/L, whereas diabetics usually have levels between 4.4 to 7.2 mmol/L.
Blood sugar spikes occur after eating. The typical post-meal blood sugar for non-diabetics is between 6.5 to 7.8 mmol/L, while for diabetics, it can reach around 10.0 mmol/L.
Recognizing the signs of diabetes:
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Excessive thirst
- Fatigue and exhaustion
- Unexpected weight loss
- Itching or discomfort in the genital area
What causes diabetes?
To understand its root causes, it's important to grasp insulin's role in blood sugar regulation.
Insulin, produced by the pancreas, helps break down sugar for energy storage. If insulin is lacking or ineffective, sugar accumulates in the bloodstream, leading to diabetes.
Insulin acts as a key that enables glucose to enter cells. Without it, sugar builds up outside the cells, causing them to be starved for energy. The failure or absence of insulin results in various types of diabetes:
Prediabetes: A mild stage where blood sugar levels are elevated but not high enough to qualify as diabetes. Early intervention can prevent progression.
Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune response destroys insulin-producing cells, leading to insulin deficiency. Treatment involves insulin injections or medications.
Type 2 Diabetes: The most common form, characterized by insulin resistance where the body produces insulin but cannot effectively use it. Management includes lifestyle changes like diet and exercise.
Gestational Diabetes: Occurs during pregnancy, requiring regular monitoring and insulin regulation.
Don't worry if diagnosed; maintaining a positive outlook and healthy habits—balanced diet, regular exercise, avoiding sugary drinks—can significantly reduce your risk of developing diabetes.