Understanding Hemoglobin A1c: Essential Facts You Should Know
This article provides a comprehensive overview of the Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) test, explaining its purpose, how it works, result interpretation, and its role in diabetes management. It highlights the importance of regular testing and personalized treatment goals to prevent complications and improve health outcomes.
Sponsored
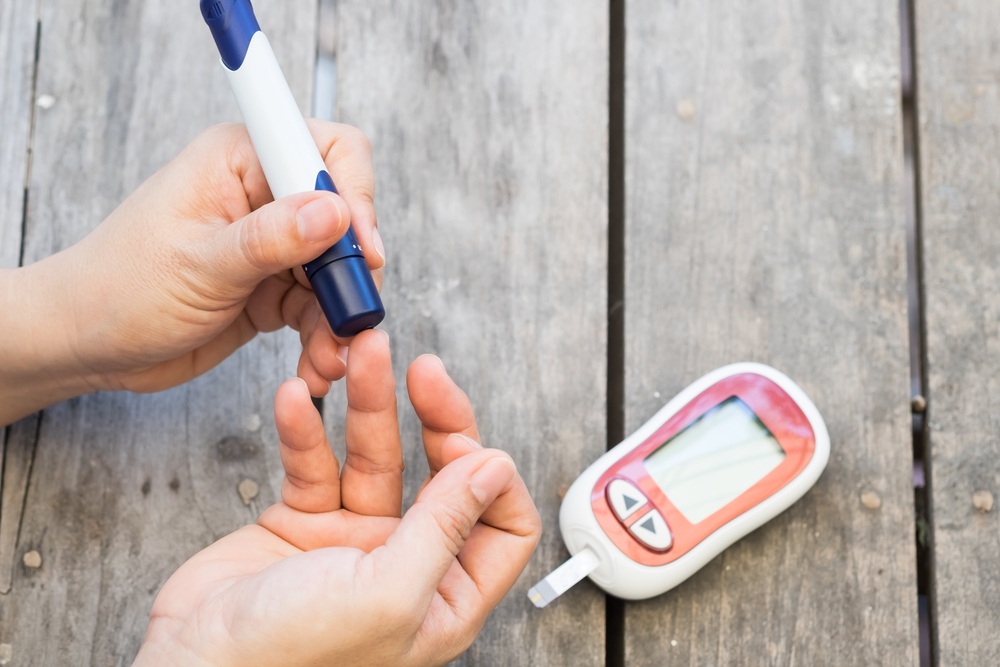
The Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) test assesses average blood sugar levels over the previous 2-3 months, aiding in diabetes diagnosis and management. This simple blood test, conducted via a finger prick and requiring no fasting, measures the percentage of glycated hemoglobin, reflecting glucose exposure. Elevated HbA1c indicates higher risk or presence of diabetes. Results are expressed as percentages, with higher levels signaling increased risk. The test helps monitor disease progression and treatment effectiveness. A healthy HbA1c level is typically below 5.7%, while levels between 5.7% and 6.5% suggest prediabetes, and above 6.5% confirm diabetes. Treatment targets vary based on age, health status, and individual conditions. Regular testing, usually biannual or more frequent for insulin users, supports optimal blood sugar control. The HbA1c test is an invaluable tool for establishing a personalized diabetes management plan, reducing complications, and maintaining overall health.