Understanding the Main Types of Blood Sugar Tests for Better Health
Learn about the four main types of blood glucose tests, including fasting, random, oral, and hemoglobin A1c. Understanding these tests helps in early detection and management of blood sugar-related conditions. Regular testing, coupled with healthy lifestyle choices, is crucial for preventing complications like diabetes, cardiovascular issues, and vision problems. Know which test suits your health needs and work with your healthcare provider for optimal well-being.
Sponsored

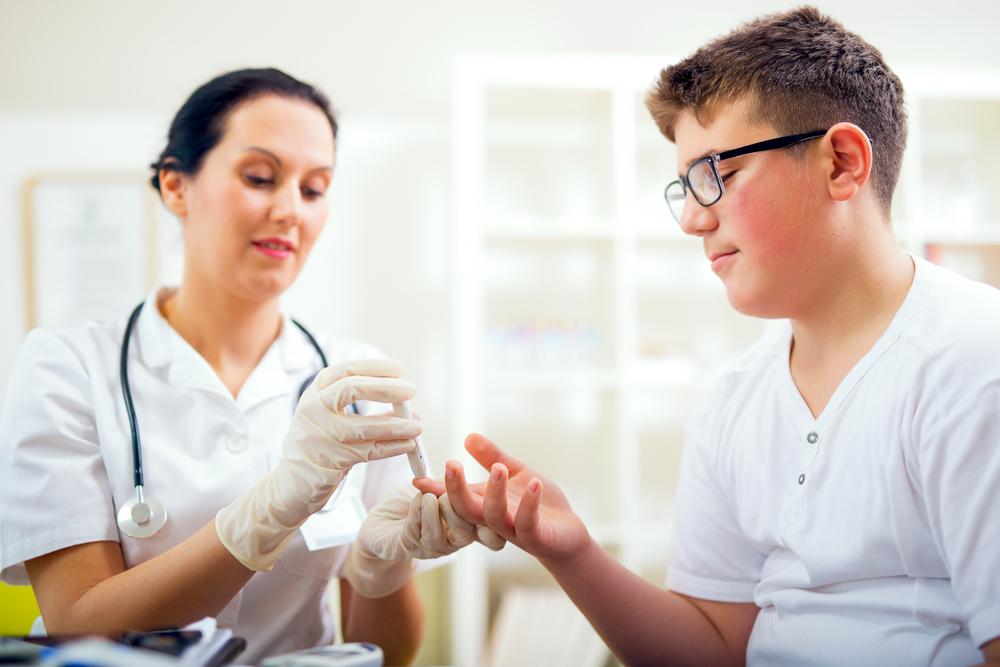
Blood sugar testing is essential for assessing the amount of glucose in your bloodstream. This process helps regulate blood sugar levels controlled by insulin, a hormone from the pancreas that converts glucose into energy. When insulin production is insufficient, it can lead to diabetes, an autoimmune condition. Elevated blood sugar levels, if unmanaged, increase risks of cardiovascular issues, vision loss, poor wound healing, and high stress on organs. Regular testing is vital not only for diabetics but also for healthy individuals to maintain overall wellness.
Performing blood glucose tests can guide lifestyle changes, influence diet plans, and help adjust medications under medical supervision. Preoperative testing is also crucial to evaluate body glucose levels before major surgeries. Depending on your health condition, your healthcare provider may recommend various testing methods, including fasting, random, oral, or hemoglobin A1c tests, detailed below.
Each type of blood test provides different insights. Understanding these can help you communicate better with your healthcare provider and maintain optimal health.
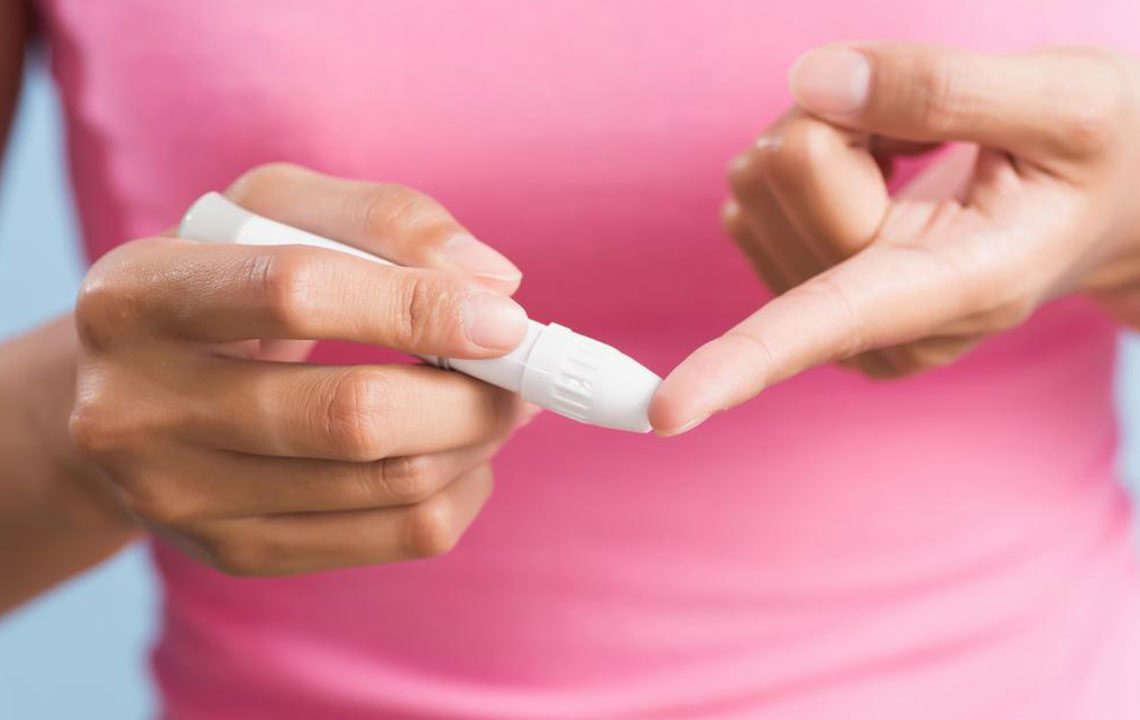
Fasting Blood Glucose Test – Requires abstaining from food for at least eight hours before blood draw, typically in the morning. It detects early signs of diabetes or prediabetes. Normal levels are below 100mg/dL. Levels between 100-125mg/dL suggest prediabetes, requiring further testing. Readings above 126mg/dL suggest diabetes, prompting confirmatory testing.
Random Blood Glucose Test – Can be performed anytime without fasting. It measures blood sugar at a specific moment, providing insight into how blood glucose fluctuates throughout the day. Significant variations may indicate diabetes risk.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test – Often used for gestational diabetes detection. The individual drinks a sugary solution, with blood samples taken before and after, usually within 1-2 hours. Fasting for eight hours is required before the initial test.
Hemoglobin A1c Test – Reflects average blood glucose over 2-3 months by measuring hemoglobin’s glucose attachment. Below 5.7% is normal, 5.7-6.4% indicates prediabetes, and above 6.5% confirms diabetes. Regular testing helps monitor the condition, particularly in diagnosed diabetics, for better management.
Overall, blood sugar testing combined with lifestyle modifications—such as avoiding smoking and excessive drinking, and embracing exercise—are key to maintaining healthy blood sugar levels and overall health.