Understanding Blood Glucose Monitoring: Significance, Components, and Best Practices
Learn about the importance of blood glucose monitoring, how to interpret glucose charts, and effective methods to maintain healthy levels. This guide emphasizes the significance of regular tracking for both diabetics and healthy individuals, highlighting lifestyle tips to ensure optimal blood sugar control and prevent health complications.
Sponsored
Blood glucose levels measure the amount of sugar present in your bloodstream at any given moment. This sugar is transported to body cells to generate energy needed for daily activities. The body obtains this glucose from the food we eat, such as carbohydrates and sugars.
Regulation of blood glucose is crucial to prevent levels from becoming too high or too low. The sugar in blood exists as glucose, distinct from common table sugar, sucrose.
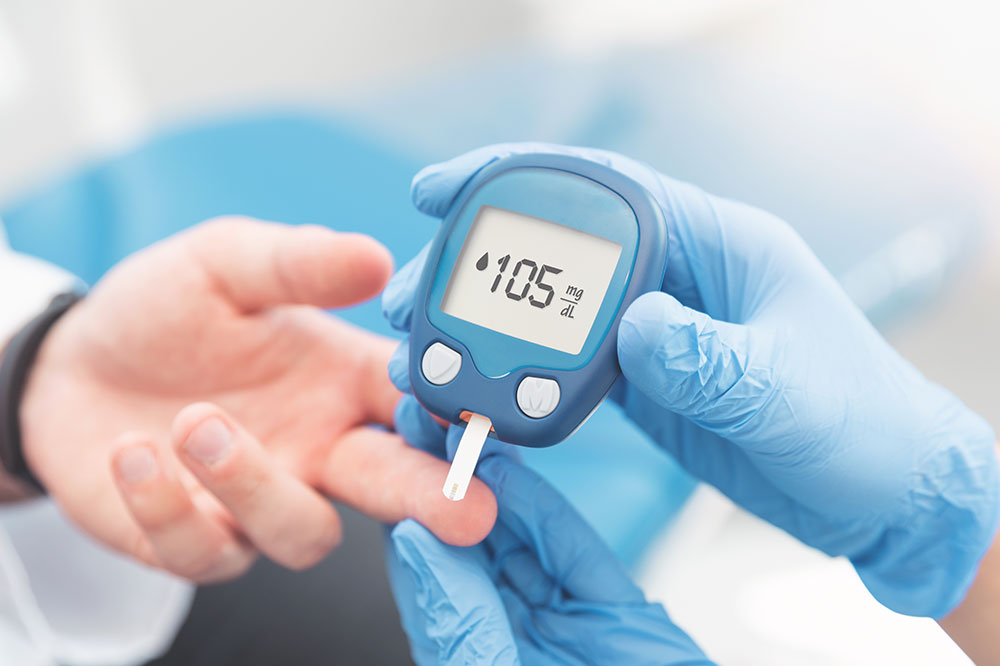
Blood sugar levels fluctuate throughout the day, typically reaching their lowest point early mornings before breakfast, then rising after meals before stabilizing. Healthy fasting levels are usually below 99 mg/dl, but in diabetics, these fluctuations are more pronounced. Maintaining pre-meal levels under 130 mg/dl and post-meal levels below 180 mg/dl is ideal.
What Is a Blood Glucose Chart?
A blood glucose chart tracks your sugar levels over time, helping manage and monitor diabetes. Since blood glucose varies constantly, keeping a regular record can prevent complications affecting kidneys, eyes, and heart. It involves measuring fasting and post-meal sugar levels to guide treatment and lifestyle adjustments.
Monitoring is vital for both healthy individuals and those managing diabetes. Sudden changes may indicate health issues, emphasizing the importance of consistent record-keeping.
Why Monitoring Blood Sugar Is Essential
Just like blood pressure or cholesterol, blood glucose levels reflect overall health. Regular monitoring helps avoid potential damage to vital organs, ensuring the body functions properly. For diabetics, tracking helps maintain safer levels, reducing risks of complications.
Maintaining optimal glucose levels supports healthy kidney, eye, and heart functions. Unchecked fluctuations can lead to serious health problems, so consistent monitoring is key.
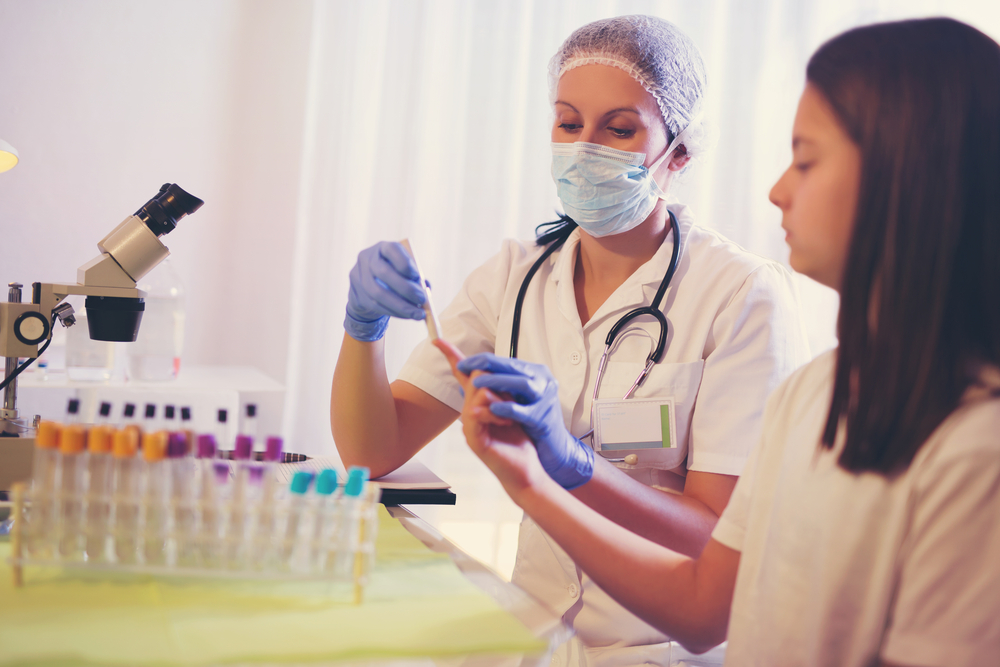
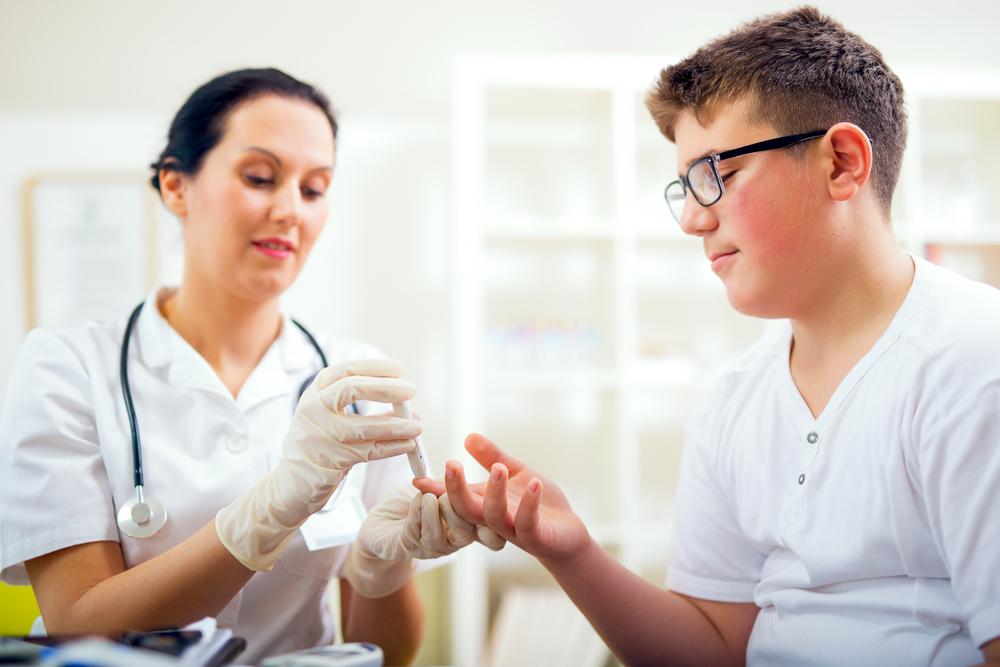
Using Blood Glucose Monitoring Devices
Various devices are available to measure blood sugar levels; however, consulting your healthcare provider before use is essential. Proper operation instructions should be obtained at purchase. For diabetics, recording fasting levels and post-meal readings creates a comprehensive glucose profile. Comparing these with target ranges guides dietary and lifestyle decisions.
Normal blood sugar levels are less than 100 mg/dl fasting and below 140 mg/dl after meals. Achieving and maintaining these levels involves a balanced diet, regular exercise, adequate sleep, and avoiding habits like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. Stress management also plays a vital role in keeping levels stable.