Proven Strategies to Reduce Your A1C Levels
Learn practical, proven strategies to effectively lower your A1C levels and improve diabetes management. This guide covers lifestyle changes such as exercise, balanced diets, regular monitoring, and personalized plans to achieve better blood sugar control and overall health.
Sponsored

Effective methods to lower your A1C
The A1C blood test measures average blood sugar over approximately three months, focusing on the relationship between glucose and hemoglobin, a component of red blood cells (RBCs) responsible for oxygen transport. Since RBCs typically last about three months, this test helps assess diabetes management. A result below 5.7% is normal; 5.7% to 6.4% indicates prediabetes. An A1C level of 6.5% or higher signifies diabetes, with a target of 7% or lower for those diagnosed. Lowering A1C is essential for diabetes control.
To effectively manage blood sugar and reduce A1C, consider these lifestyle adjustments:
Regular Exercise
Engaging in physical activity is vital for diabetics to build stamina. Aim for about 30 minutes of moderate exercise, five days a week. Activities can be simple and enjoyable, such as brisk walking, playing outdoor sports, or cycling. Total weekly activity should reach around 150 minutes. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting new physical routines.
Balanced Nutrition
Focus on consuming vegetables low in starch, moderate fruits, lean proteins, and healthy carbs. Opt for smaller portions to keep blood sugar stable, and avoid processed foods, sugary drinks, and sodas. A registered dietitian can help tailor a meal plan suited to your needs, ensuring carbohydrate intake is monitored for better A1C control.
Eating Schedule
Maintain consistent meal times to prevent blood sugar fluctuations. Skipping meals or overeating can cause significant changes in blood glucose levels. Keeping a food diary helps identify patterns and habits that influence your A1C.
Adherence to Treatment Plan
Diabetes management is highly individual. Work with your doctor to develop a personalized plan that includes medication, emergency protocols, blood sugar monitoring schedules, and goals. Regular consultation ensures effective control and timely adjustments.
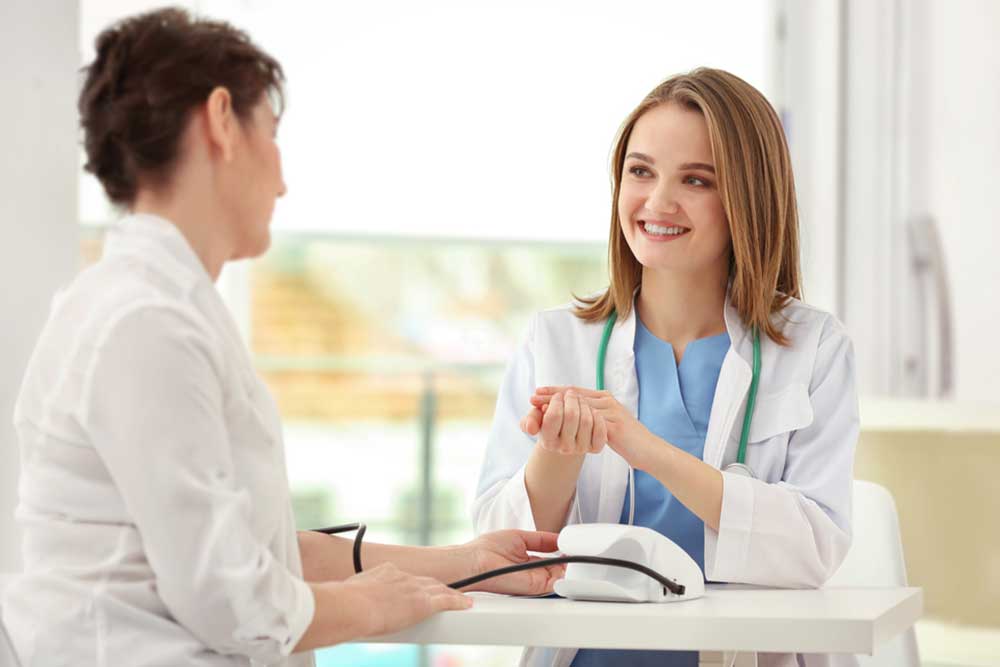
Monitoring Blood Sugar
Regularly check your blood glucose levels as advised by your healthcare provider. Monitoring is critical for understanding your control and making necessary lifestyle or medication adjustments to keep your A1C within target range.
Recommended foods that support lowering A1C include:
Fatty Fish
Rich in protein and healthy fats, fish helps manage weight and reduce inflammation. Avoid frying; opt for grilled or baked options for maximum benefit.
Spinach
High in Vitamin K and Magnesium, spinach can be eaten raw or briefly blanched for optimal nutrient retention, aiding in blood sugar regulation.
Extra-Virgin Olive Oil
Contains oleic acid, which helps reduce triglycerides and increase 'good' HDL cholesterol, beneficial for heart health in diabetics.
Broccoli
Contains sulforaphane, which reduces inflammation and may lower A1C levels while protecting against cardiovascular complications.
Eggs
A good protein source that, when eaten in moderation, can help reduce heart disease risk and support A1C reduction.
Remember, your diet directly affects your health. Making informed food choices is crucial for managing blood sugar and maintaining overall wellness.