Effective Strategies to Normalize Your A1C Levels
Discover effective strategies to lower A1C levels, including lifestyle modifications, diet improvements, and regular monitoring. Maintaining optimal A1C levels is essential for preventing diabetes complications and enhancing overall health. Consult your healthcare provider for personalized guidance to manage your blood sugar effectively and prevent future health risks.
Sponsored

Managing diabetes effectively is crucial for overall health and preventing complications. Regular A1C testing is essential for identifying prediabetes, and for monitoring and controlling existing diabetes.
What is an A1C Test?
The A1C blood test reflects your average blood sugar over the past two to three months, expressed as a percentage. A higher percentage indicates higher blood sugar levels over time.
Purpose of the A1C Test
This test helps in diagnosing diabetes and assessing how well your treatment is working. It also predicts the risk of developing diabetes in the future. When glucose attaches to hemoglobin in red blood cells, it indicates blood sugar levels. The more glucose bound, the higher the A1C percentage.
Understanding your A1C levels
The normal A1C range is below 5.7%. An A1C between 5.7% and 6.4% indicates prediabetes, increasing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes within a decade. However, with lifestyle changes, this risk can be reduced. An A1C of 6.5% or above confirms a diabetes diagnosis.
For those with diabetes, maintaining an A1C below 7% can significantly lower the risk of complications.
How to Lower Your A1C Naturally
To achieve healthier A1C levels, consider these approaches:
Develop a personalized plan
Identify key challenges like weight management, physical activity, nutrition, and stress control, and plan actions accordingly.
Losing excess weight
Engaging in regular exercise
Following a balanced diet
Managing stress effectively
Create a structured diabetes management plan
Include medical guidance, medication schedules, blood sugar targets, emergency contacts, and strategies for correcting hypoglycemia.
Adopt a nutritious diet with appropriate portions
Prioritize non-starchy vegetables, fruits, healthy fats, proteins, and complex carbs like potatoes and bread. Limit processed foods, sugary beverages, and sodas.
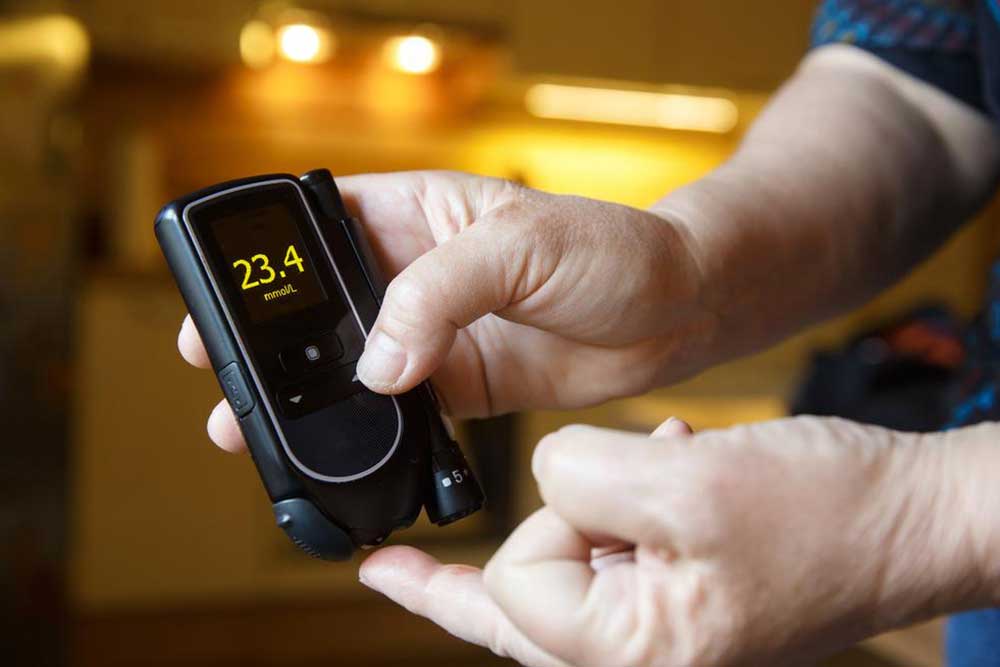
Monitor blood sugar levels closely
Work with your healthcare provider to determine the frequency of testing and adjust your lifestyle accordingly.