Key Insights on Managing and Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels
This article covers essential aspects of blood glucose management, including normal ranges, testing methods, and lifestyle strategies. It emphasizes personalized targets and gradual control to prevent complications. Key tips include diet modifications, regular exercise, and consistent monitoring, making it a comprehensive guide for maintaining optimal blood sugar levels and improving overall health.
Sponsored
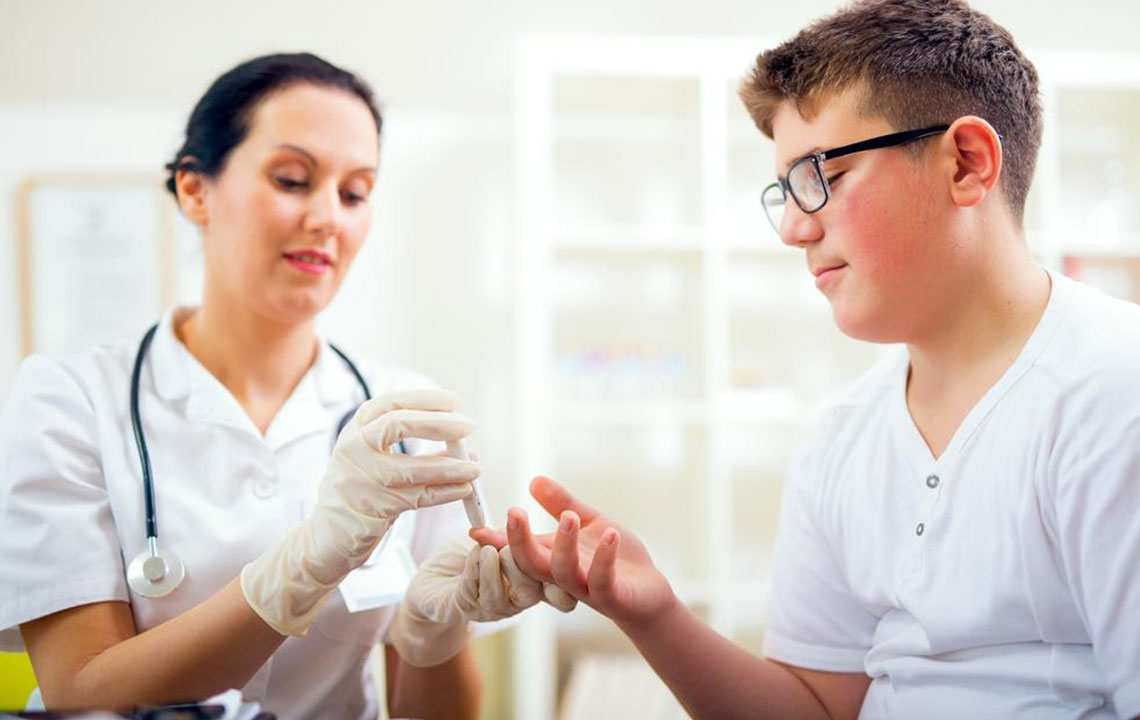
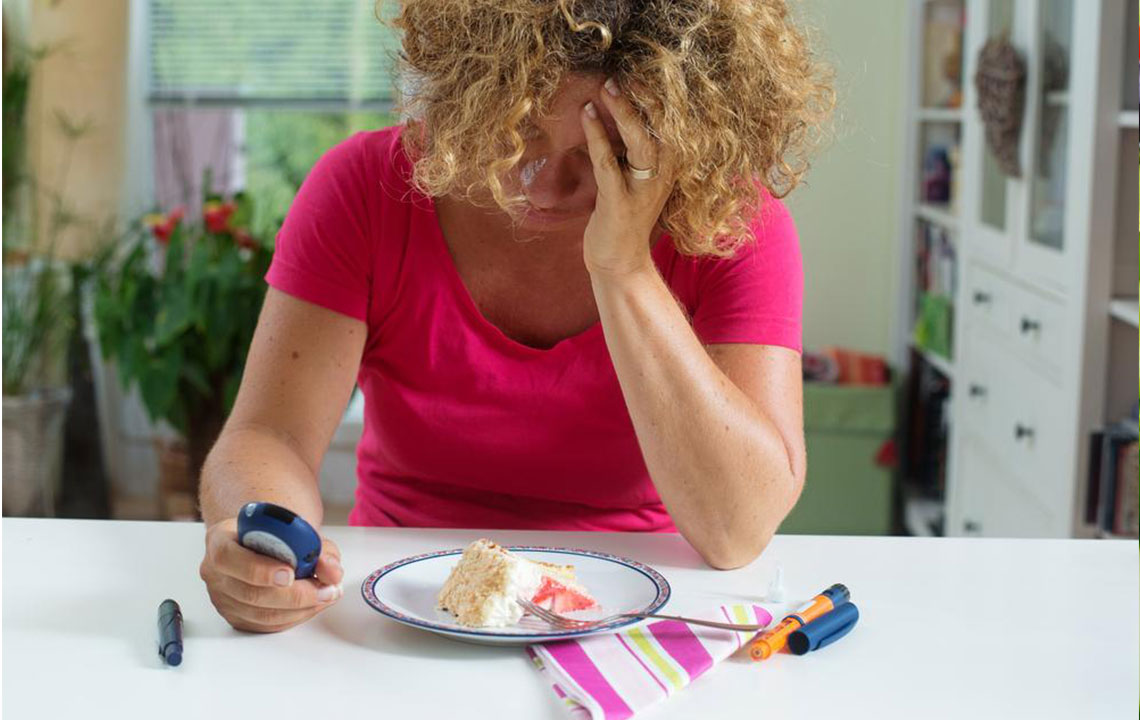
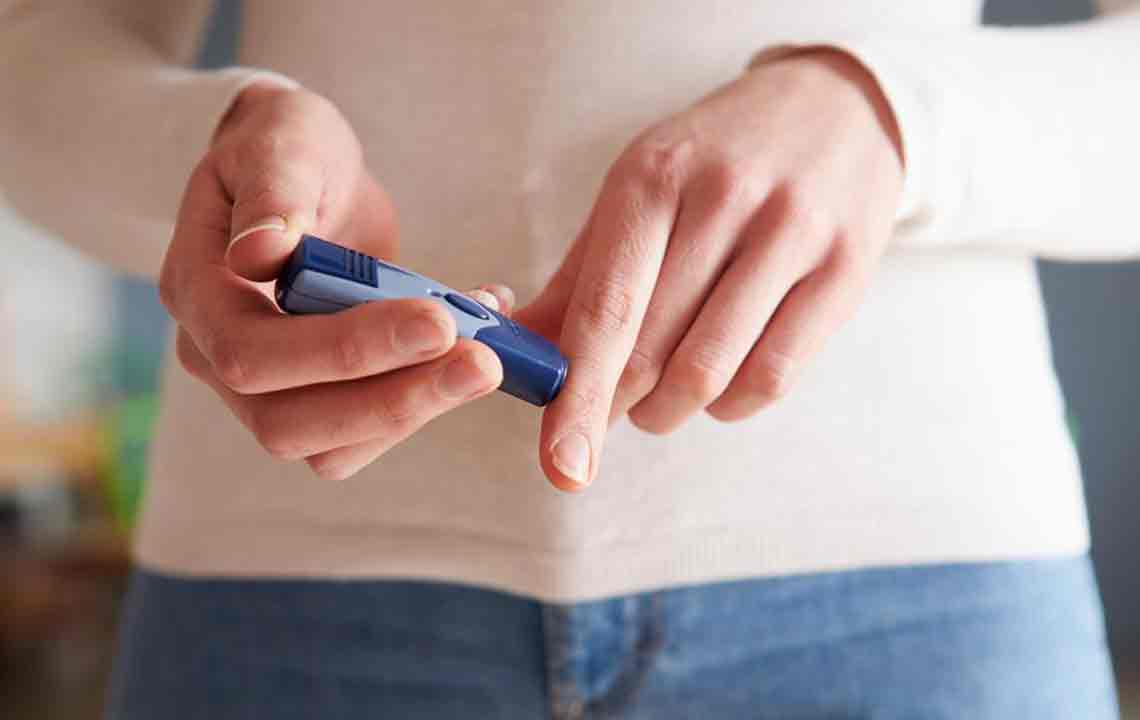
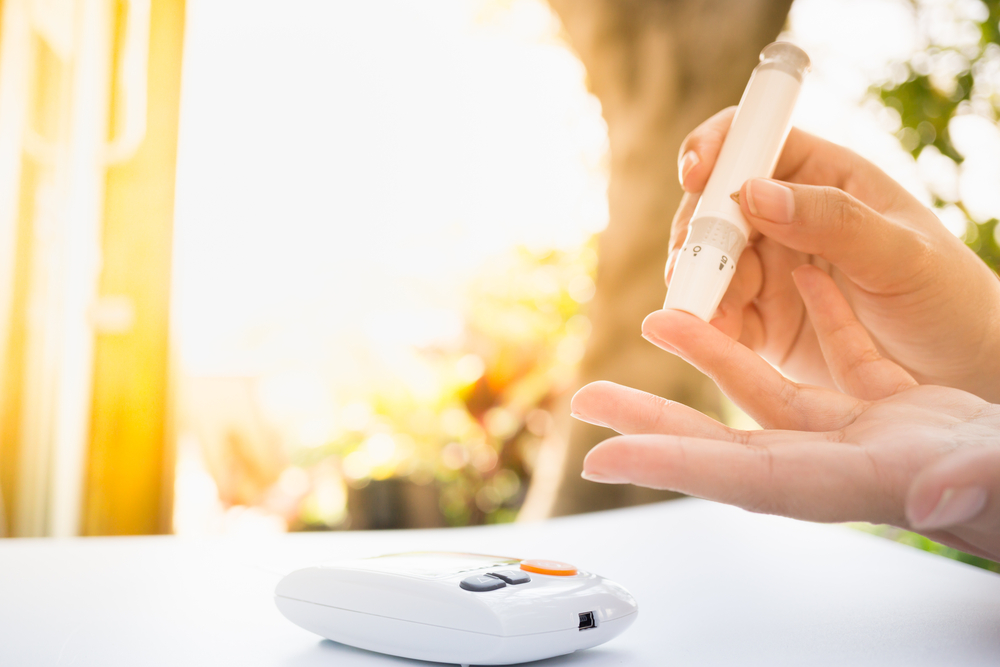
Blood glucose levels reflect the amount of glucose in the bloodstream, acting as a vital energy source. They depend on the body’s insulin production and sugar metabolism. Measured in mg/dL, normal levels typically range from 70 to 100 mg/dL, rising up to 120 mg/dL after eating. Blood sugar testing involves fasting measurements and post-meal readings. Normal ranges indicate good health, while deviations may signal pre-diabetes or diabetes. Managing blood glucose through diet, exercise, and regular monitoring is crucial for preventing complications. Personalized targets help achieve optimal control and overall well-being.
Maintaining levels within recommended ranges reduces health risks. Typically, fasting blood sugar should be between 70-130 mg/dL, and post-meal levels below 180 mg/dL. For those with diabetes, goal adjustments are necessary, often starting with higher targets. Monitoring helps detect lows and highs to prevent hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia. Lifestyle changes like consistent exercise, reducing carbohydrate intake, and increasing fiber consumption support blood sugar regulation. Small, gradual adjustments are safer and more effective in achieving and maintaining ideal glucose levels, ensuring long-term health benefits.






