Understanding Your Ideal Blood Sugar Range and How to Maintain It
This article provides comprehensive guidance on normal blood sugar levels for both healthy individuals and diabetics. It highlights the importance of regular monitoring, describes testing methods, and discusses the health risks associated with uncontrolled blood sugar. By understanding these key points, readers can take proactive steps to manage their blood glucose and prevent serious health complications.
Sponsored

Maintaining balanced blood sugar levels is essential for overall health and can prevent the development of diabetes or help manage it effectively. Fluctuations in blood glucose can lead to serious health issues, making it vital to monitor and regulate your levels through mindful eating and lifestyle choices.
Knowing what constitutes normal blood sugar levels, both for non-diabetic and diabetic individuals, is crucial. Regular testing helps ensure your levels stay within healthy ranges and reduces the risk of complications.
Normal Blood Sugar for Healthy Individuals
Blood sugar levels are typically checked at three key points:
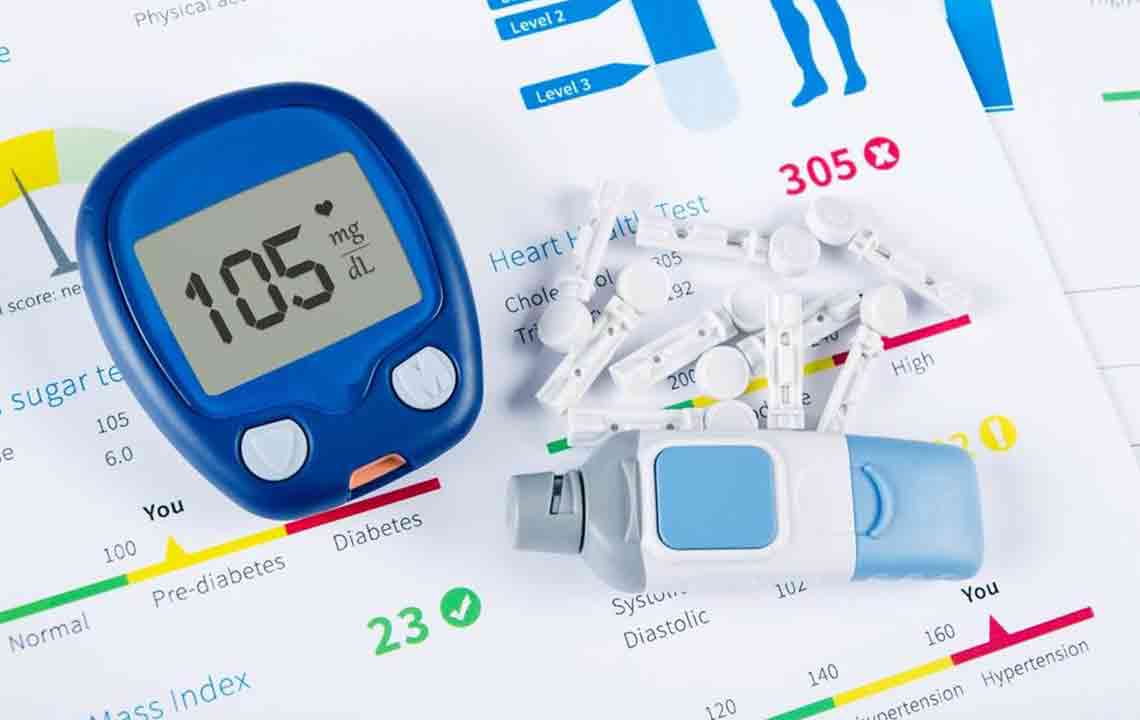
Fasting blood sugar is measured after at least 10 hours without eating—ideally in the morning before breakfast. Normal fasting levels should be between 70-99 mg/dL.
Post-meal blood sugar is checked approximately 1.5 to 2 hours after eating lunch. The normal range here is 90-140 mg/dL.
Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) levels provide an average of blood sugar over the past 2-3 months and should be below 5.7% for healthy individuals.
Blood Sugar Targets for Diabetes Patients
People with diabetes often have elevated blood sugar levels that need close monitoring. Fasting levels should be maintained between 80-130 mg/dL, while post-meal levels should stay below 180 mg/dL. The goal HbA1c level for diabetics is generally under 7.0%.
Regularly checking blood sugar levels helps manage the condition and avoid complications.
Signs of High Blood Sugar or Diabetes
Common symptoms indicating high blood sugar include constant fatigue, increased hunger, frequent urination, dry or itchy skin, and blurred vision. These signs signal the importance of timely blood sugar testing and medical consultation.
Monitoring Techniques
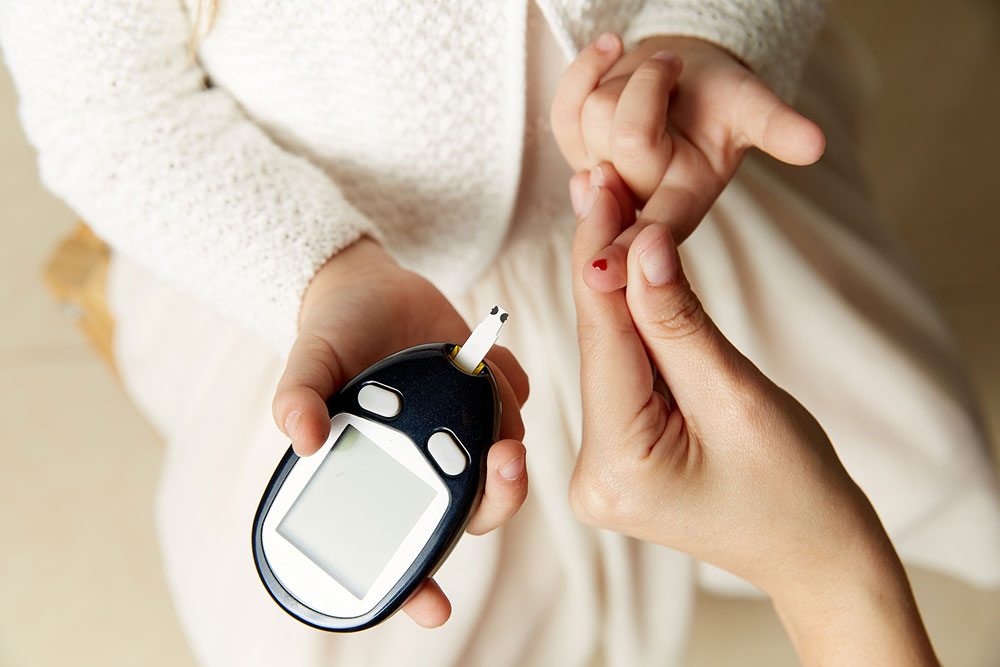
Diabetic individuals should utilize Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGM), inserted under the skin near the abdomen, for ongoing blood sugar tracking. Alternatively, traditional finger-prick tests with a glucose meter can be performed to check levels periodically. For non-diabetics, routine blood tests every few months help keep track of glucose status.
Risks of Uncontrolled High Blood Sugar
High blood sugar can cause nerve damage, kidney issues, and vascular problems. It can also harm tiny blood vessels in the eyes, leading to vision impairment. Maintaining proper level is vital to reduce these health risks and promote long-term wellness.
Keep these guidelines in mind to maintain healthy blood sugar levels and ensure a healthier lifestyle.