Identifying Key Symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome
This article outlines key symptoms of Irritable Bowel Syndrome, including abdominal pain, changes in bowel habits, and gas, emphasizing the importance of early diagnosis for effective treatment. Recognizing these signs can lead to timely medical intervention, reducing discomfort and complications related to IBS.
Sponsored

Recognizing Common Signs of Irritable Bowel Syndrome
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) impacts millions annually, predominantly affecting women between their late teens and early 40s. Characterized by abdominal discomfort paired with irregular bowel movements, IBS can cause diarrhea or constipation. Monitoring specific symptoms is vital for early detection and management.
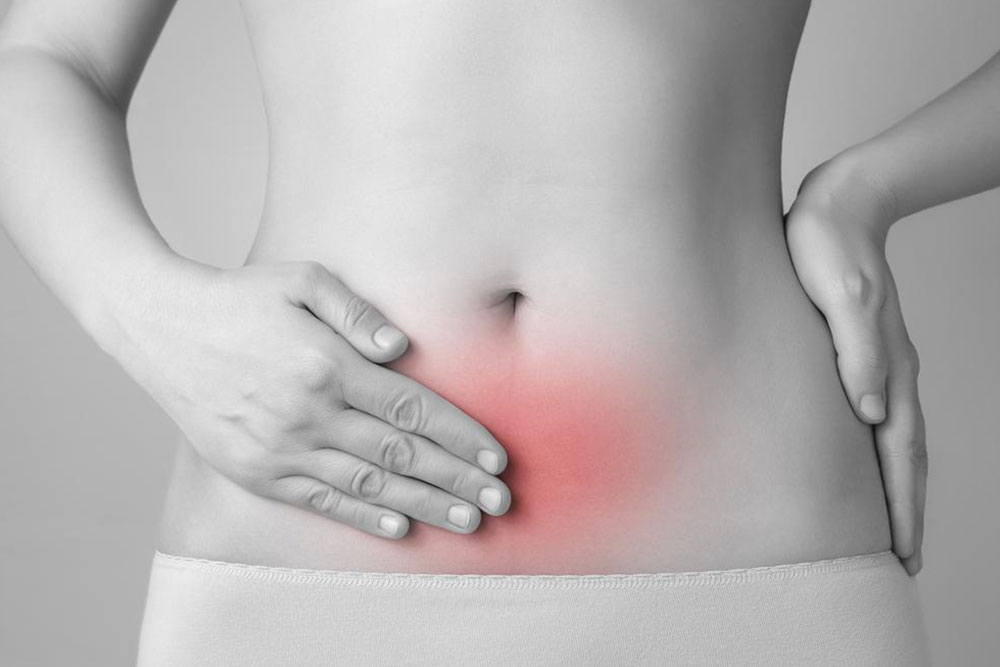
Lower abdominal discomfort
A prevalent symptom involves varying degrees of pain and cramping in the lower abdomen, often worsening after eating and alleviating after a bowel movement. Nighttime pain may also occur.
The discomfort typically intensifies post-meals and subsides following bowel movements. Severe abdominal pain, especially at night, is common.
Intense constipation or diarrhea
Fluctuations between constipation and diarrhea are typical. Stools may become abnormally hard or loose, with some individuals experiencing alternating episodes.
Excessive gas and bloating
Excess gas production leads to bloating and discomfort, often making the abdomen feel swollen and distended.
Unusual stool features
Presence of mucus in stool is common, sometimes accompanied by blood, signaling a need for prompt medical attention.
In severe cases, rectal bleeding may occur, requiring immediate medical evaluation. Symptoms tend to worsen during menstrual periods in women, and significant weight loss can sometimes be observed. Although IBS is chronic for many, episodes of severity call for prompt diagnosis and treatment. Early recognition of symptoms is crucial for effective management, helping patients recover faster and improve quality of life.