Four Key Strategies to Reduce Heart Disease Risk
Discover four effective strategies to lower your risk of heart disease. Incorporate regular exercise, adopt a nutritious diet, quit smoking, and manage health conditions like diabetes to promote a healthier heart and reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications.
Sponsored
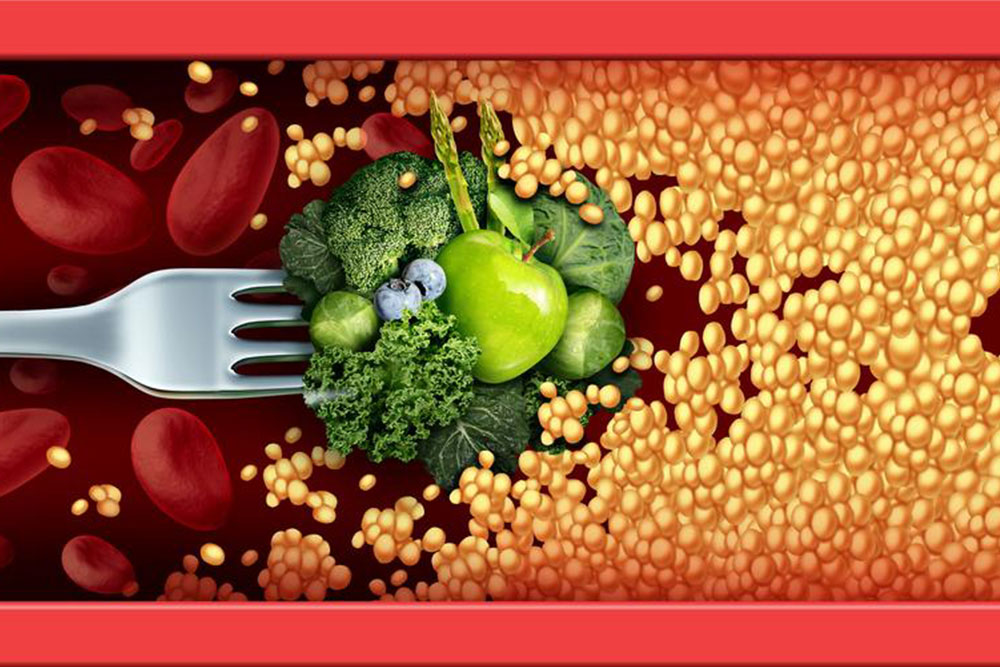
Heart disease remains the primary cause of mortality in the United States, claiming over 600,000 lives annually. This broad category includes various heart-related conditions that can affect individuals of all ages, even children. Fortunately, nearly 80% of these conditions—such as heart attacks, heart failure, and strokes—are preventable through consistent lifestyle adjustments. To lower your risk, consider incorporating these essential habits into your daily routine.
Stay physically active
Engaging in regular movement helps regulate blood pressure and reduces heart disease risk. Experts recommend at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise, five days a week, to strengthen your cardiovascular health. Activities like swimming, cycling, and rowing are excellent ways to keep your heart in shape. Using fitness apps and smart gadgets can motivate you to meet daily activity goals.
Adopt a heart-healthy diet
Diet significantly influences heart health, regardless of genetic risk factors. Begin with small, manageable changes—incorporate more raw fruits and vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 rich foods like fish. Limit red meat intake, or eliminate it if possible, and substitute with plant-based proteins such as legumes and nuts. Maintaining a balanced diet supports cardiovascular well-being and reduces the likelihood of heart issues.
Quit smoking
For smokers, this is one of the most impactful steps toward lowering heart disease risk. Smoking promotes plaque buildup in arteries, leading to atherosclerosis. It damages organs, decreases beneficial HDL cholesterol, and elevates blood pressure, increasing the chances of heart attacks. Quitting smoking improves blood circulation, oxygen delivery, and can normalize blood pressure levels, drastically improving overall heart health.
Control diabetes and related conditions
Unmanaged diabetes can cause significant damage to organs and increase the risk of heart disease, strokes, and peripheral artery disease. Regular medical checkups, a healthy diet, and physical activity are crucial for management. Medications prescribed by your doctor can help reduce the impact of diabetes and lower cardiovascular risk. Additionally, managing high blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar is vital to prevent heart complications. Regular consultations are recommended for appropriate control.