Effective Strategies for Alleviating Lower Back Discomfort
Discover effective methods to relieve lower back pain, including rest, heat and cold therapy, medical treatments, and exercises. Tailored strategies can help manage discomfort, improve mobility, and promote long-term spinal health. Consult healthcare providers for personalized advice and ensure safe exercise routines to prevent future issues.
Sponsored

Lower back discomfort affects the nerves, muscles, and bones in the lumbar region and is a widespread issue encountered by many. Also known as lumbago, this condition involves the complex interplay of joints, muscles, ligaments, and nerves that support the upper body. Muscles in the L1 to L5 vertebrae facilitate mobility and rotation of the hips, playing a vital role in daily movement.
The nerves and muscles in this area support limb movement. Strain or injury can hinder routine activities such as standing, bending, or twisting, leading to pain. Symptoms may range from dull ache to sharp, stabbing sensations, affecting mobility. Acute episodes often result from injuries or health issues, but with time, swelling and inflammation may subside. Persistent pain lasting weeks becomes chronic, necessitating targeted interventions.
Ways to Manage Lower Back Pain
Rest
Resting reduces strain on the lower back, giving muscles and tissues time to recover. Taking a few days off physical and mental exertion often alleviates pain.
Heat and Cold Therapy
Applying heat improves circulation, delivering nutrients and oxygen to promote healing. Use hot packs, hot water bottles, or take warm baths to relax muscles. Cold therapy diminishes inflammation and numbs nerves, reducing spasms. Alternating heat and cold treatments optimizes relief—use heat before activity and cold during rest for best results.
Medical Interventions
Medical options can provide significant relief, often combined with physical therapy. Common treatments include:
Epidural Steroid Injections – Steroid injections temporarily reduce nerve root inflammation, offering pain relief through guided x-ray procedures.
Muscle Relaxants – These medications ease muscle tightness by blocking pain signals sent to the brain, facilitating movement.
Narcotic Painkillers – Opioids alter pain perception temporarily, providing short-term relief.
Supportive Braces – Back braces stabilize the lumbar area, reducing strain and promoting healing alongside physical therapy.
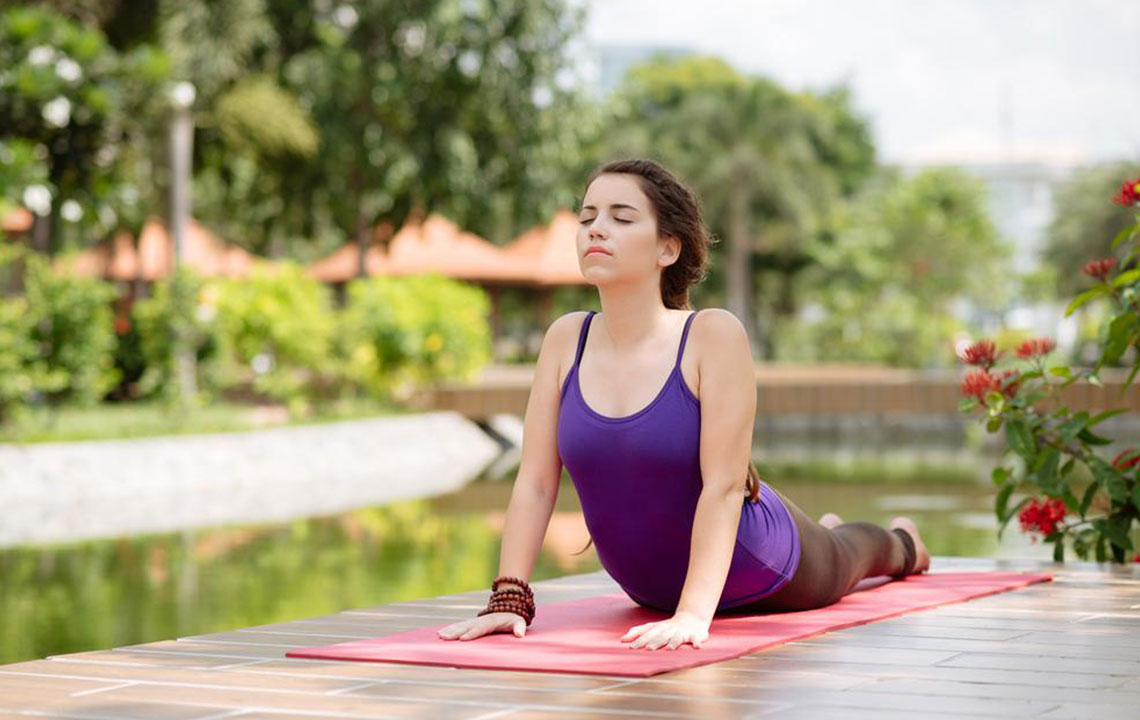
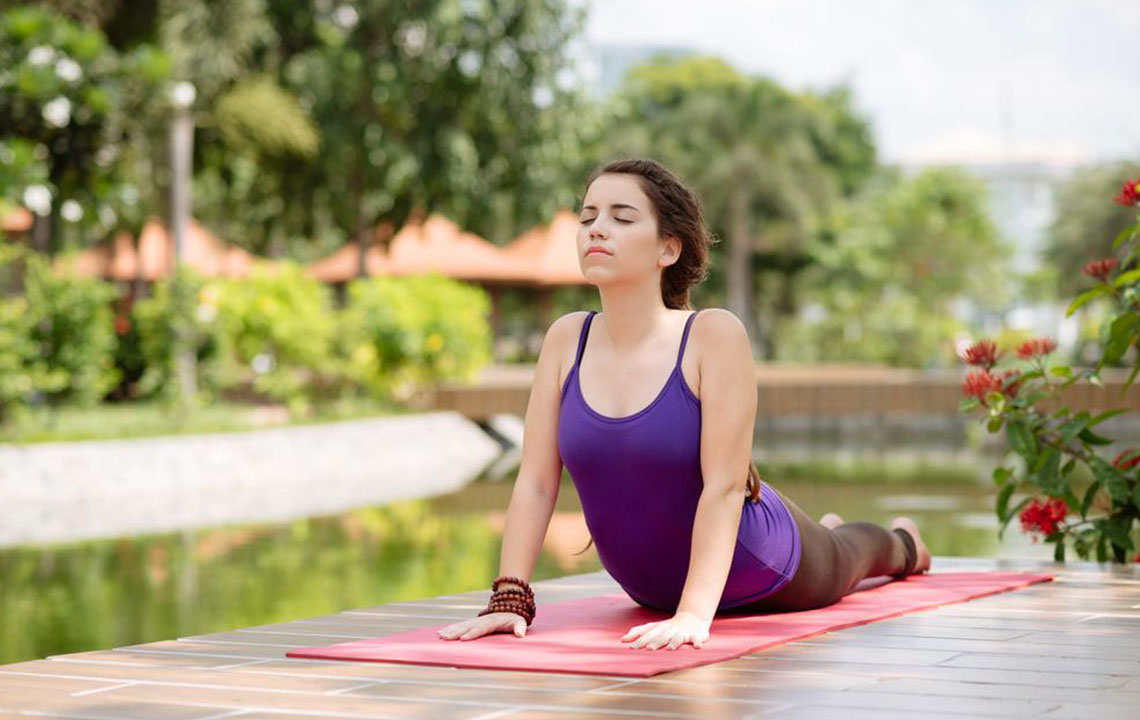
Regular Exercise
Engaging in targeted exercises helps manage long-term back pain by releasing endorphins—the body's natural painkillers. Suitable activities include:
Stretching – Gentle stretches improve flexibility of the hips and hamstrings, reducing pressure on the lower back.
Core Strengthening – Strengthening abdominal, hip, and glute muscles provides essential support to the spine, preventing future discomfort.
Remember to consult a healthcare professional before starting any medication or exercise program for back pain.