Identifying the Top 5 Types of Gum Diseases
Explore the five common types of gum diseases, their symptoms, causes, and treatments. Early detection and proper oral hygiene are key to preventing severe complications like tooth loss. Regular dental visits help identify and manage periodontal issues effectively, ensuring healthier gums and overall oral health.
Sponsored
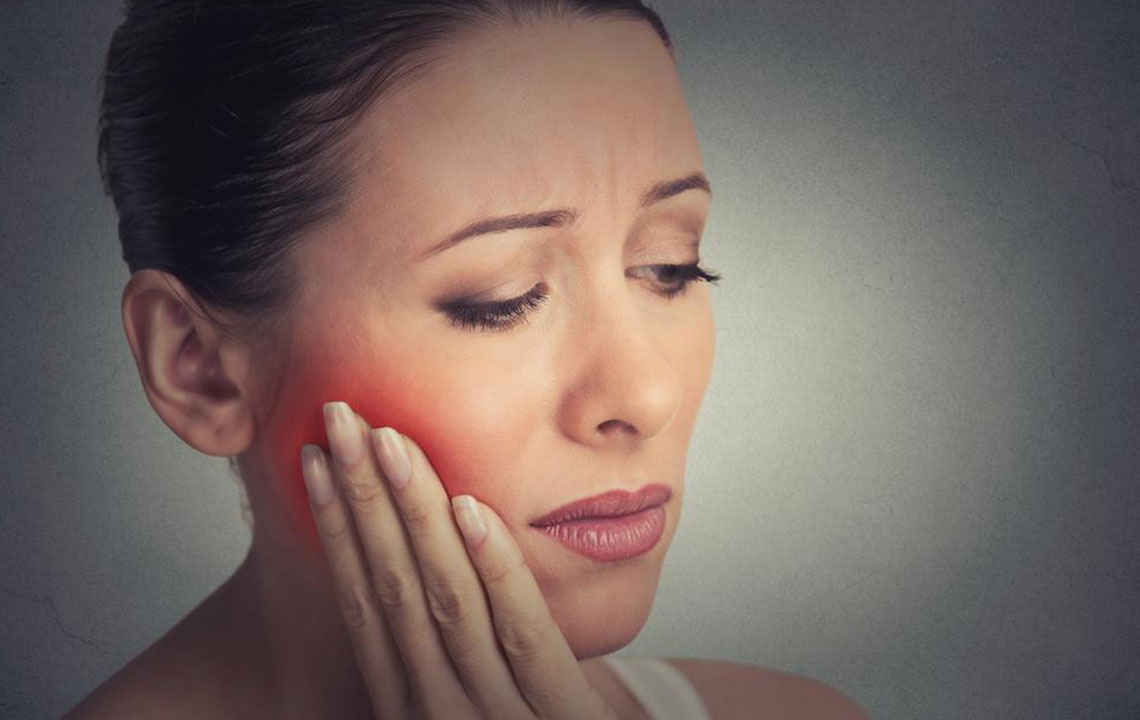
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a progressive infection that impacts the tissues supporting the teeth, including the gums and jawbone. If untreated, it can cause pain, sensitivity, and tooth loss. Early diagnosis and professional dental care are essential for effective treatment and prevention of serious complications.
Below are five common periodontal conditions everyone should be aware of.
Gingivitis: The mildest form of gum infection caused by plaque toxins. Good oral hygiene, including regular brushing and professional cleanings, can effectively treat gingivitis.
Chronic Periodontal Disease: Commonly affecting adults over 45, this condition involves inflammation beneath the gums leading to tissue and bone loss. Gums may recede, making teeth appear longer. Treatment often includes deep cleaning procedures like scaling and root planing, along with antimicrobial therapy per dentist recommendations.
Aggressive Periodontal Disease: Characterized by rapid gum deterioration, this form frequently affects smokers and those with a family history of gum issues. Extensive surgical treatments are often necessary, and regular dental checkups are crucial.
Periodontal Disease Linked to Systemic Illnesses: Conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, and lung problems can contribute to gum degeneration. Dentists should coordinate with other healthcare providers to address underlying health issues alongside dental treatments.
Necrotizing Periodontal Disease: Seen in individuals with compromised immunity, malnutrition, stress, or smoking, this rare but severe infection can destroy gum tissues and spread to the jawbone. Treatment involves comprehensive dental intervention.
Maintaining good oral hygiene from an early age greatly reduces the risk of severe gum diseases and the need for invasive treatments.