Understanding Gum Disease: Symptoms, Causes, and Effective Remedies
This article offers a comprehensive overview of gum disease, detailing its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. Recognizing early signs and maintaining good oral hygiene are essential for prevention. Dental professionals can provide effective treatment, including cleaning, medication, and surgical procedures, to manage and cure gum infections. Regular dental check-ups and lifestyle adjustments play a crucial role in maintaining healthy gums and overall oral health.
Sponsored
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, affects many individuals and involves infection and inflammation of the tissues supporting the teeth. The oral cavity is particularly vulnerable to various infections compared to other body parts. Common issues such as gingivitis and periodontitis require prompt attention from dental specialists. Recognizing the signs, understanding the causes, and exploring treatment options are crucial steps toward maintaining healthy gums and teeth.
• Causes: The primary cause of gum disease is inadequate oral hygiene. Failing to brush twice daily and floss regularly allows bacteria and debris to accumulate, promoting infection and decay. Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy and menopause can also increase susceptibility. Additionally, underlying health conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and acid reflux, along with lifestyle habits like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, further elevate risk.
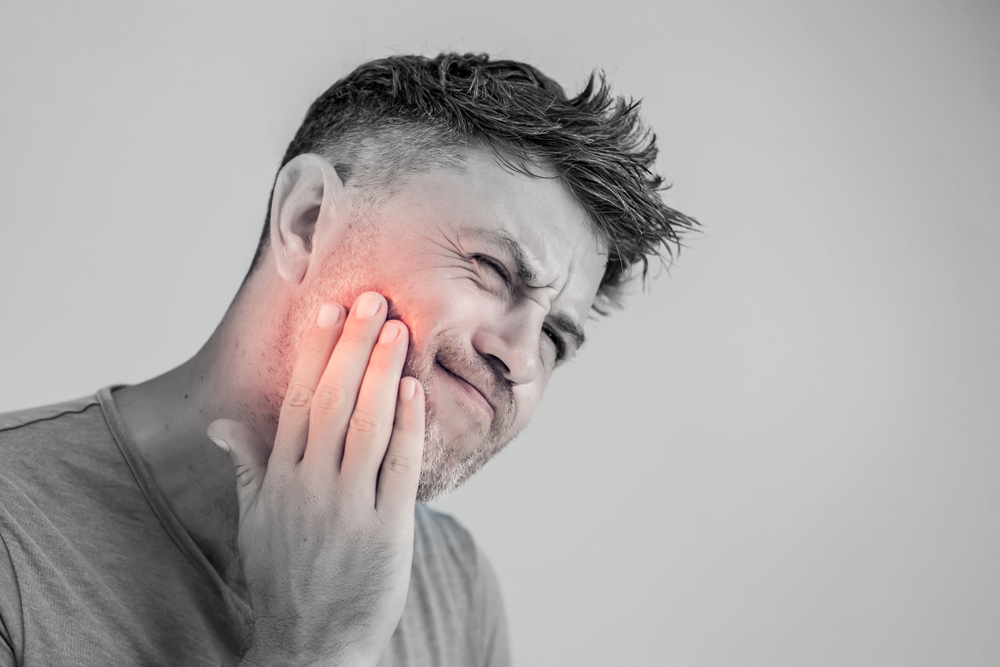
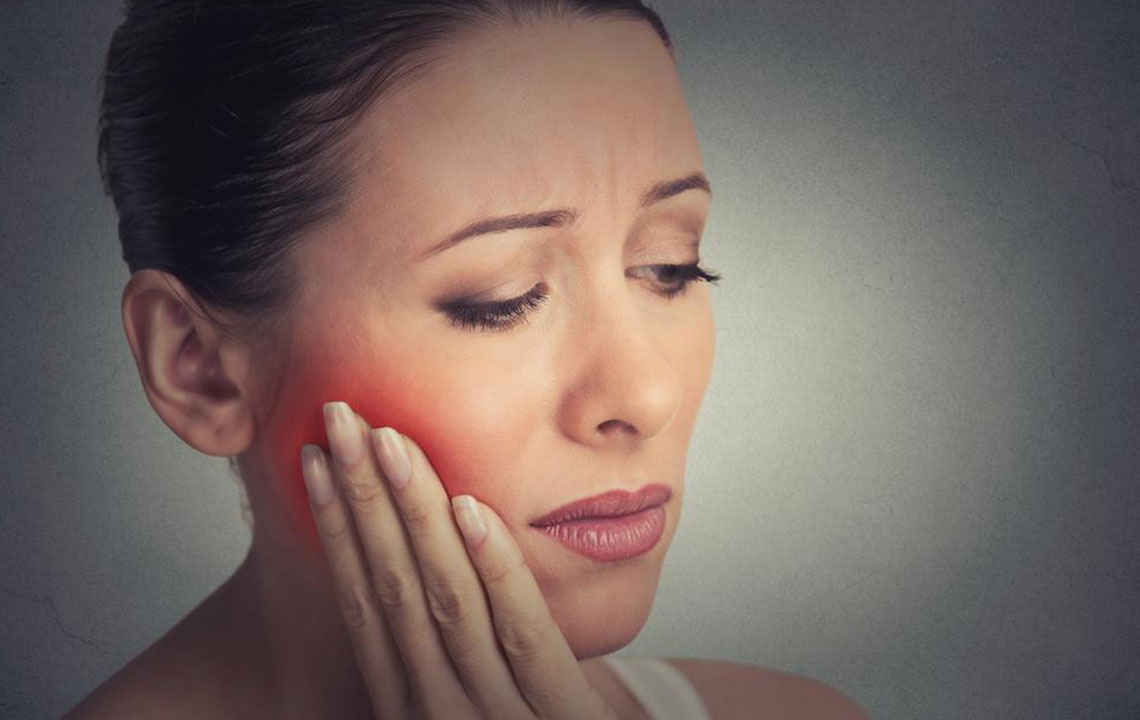
• Symptoms: Signs of gum disease include bleeding gums, persistent bad breath, and plaque buildup. Other symptoms may involve loose teeth, swelling, and reduced immunity. Recognizing these early indicators is vital for timely intervention.
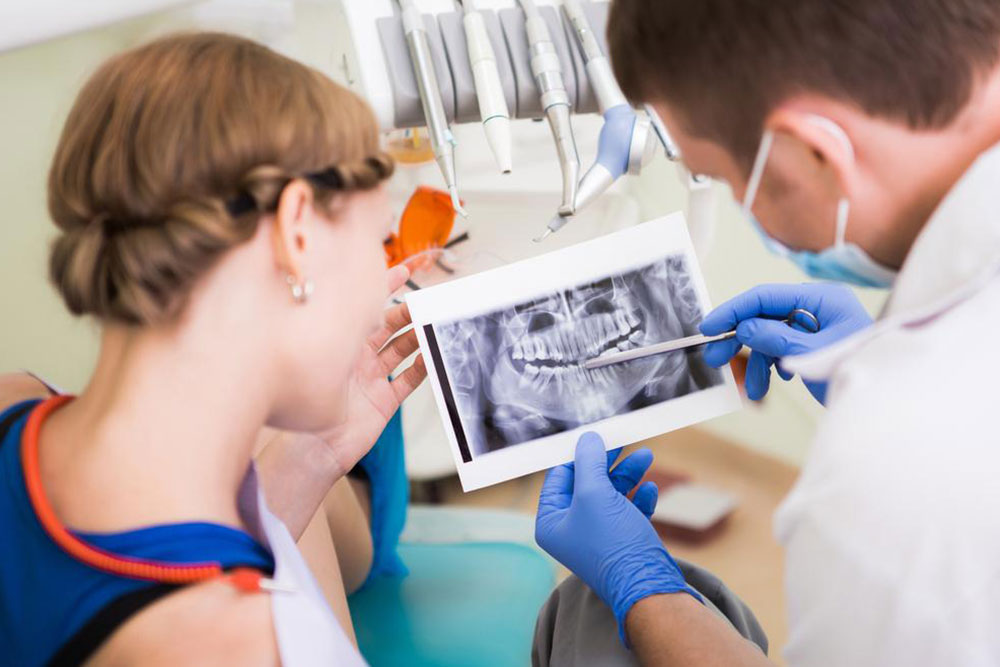
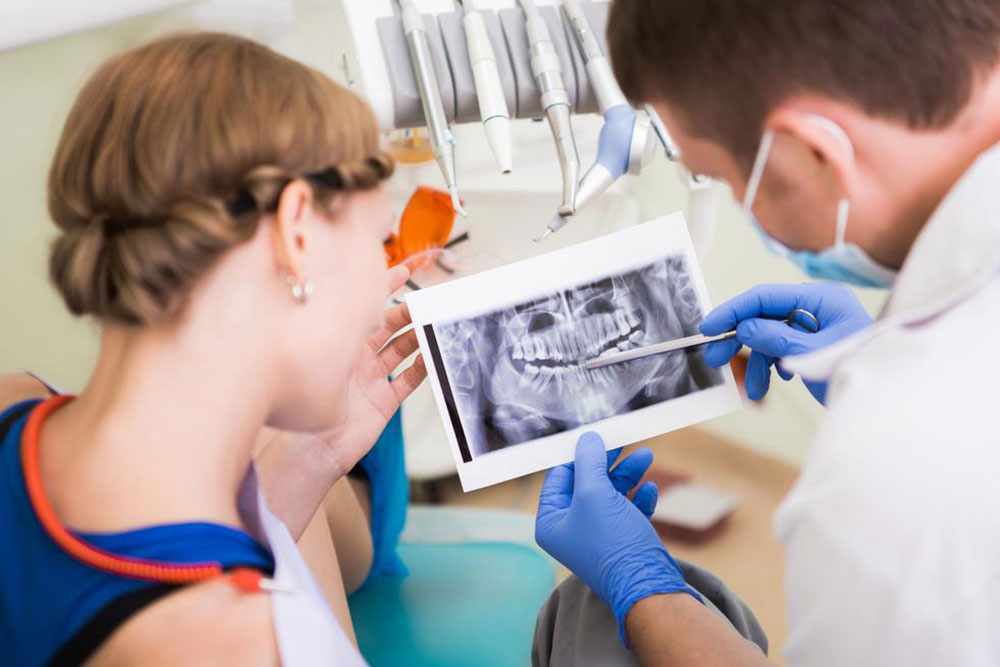
• Gingivitis and Periodontitis: Gingivitis refers to gum inflammation characterized by redness and swelling, which can evolve into periodontitis—a more severe form involving tissue and bone loss. Proper dental evaluation, including X-rays, helps differentiate between these conditions. Left untreated, gingivitis can develop into periodontitis, leading to irreversible damage.
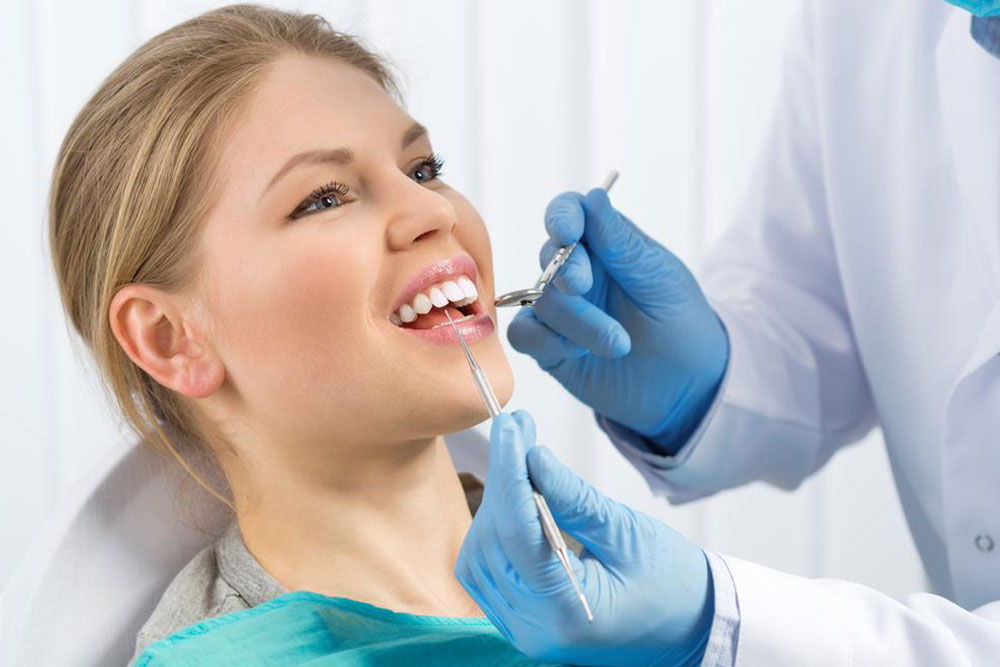
• Treatment Approaches: Treatment begins with thorough dental assessments and cleaning procedures to remove plaque and tartar. Improving oral hygiene practices, adopting a balanced diet, and avoiding smoking are key preventive measures. Advanced cases may require medication or surgical intervention to restore gum health and prevent further deterioration.