Understanding Gum Disease: Symptoms, Causes, and How to Treat It
This article explores the signs, causes, and treatment options for gum disease, emphasizing the importance of proper oral hygiene and early intervention to prevent severe periodontal issues.
Sponsored
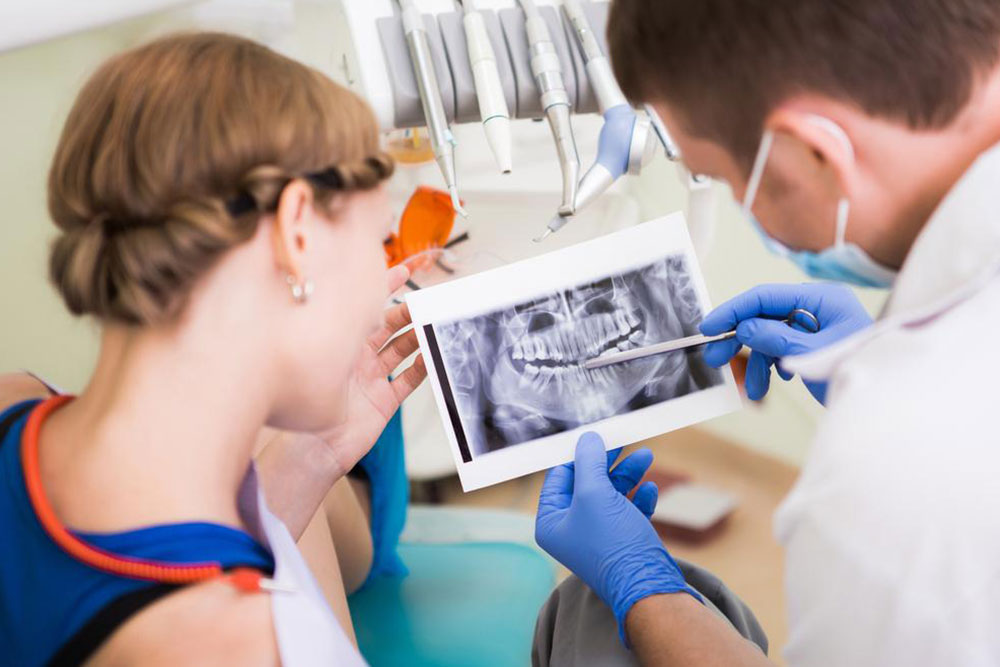
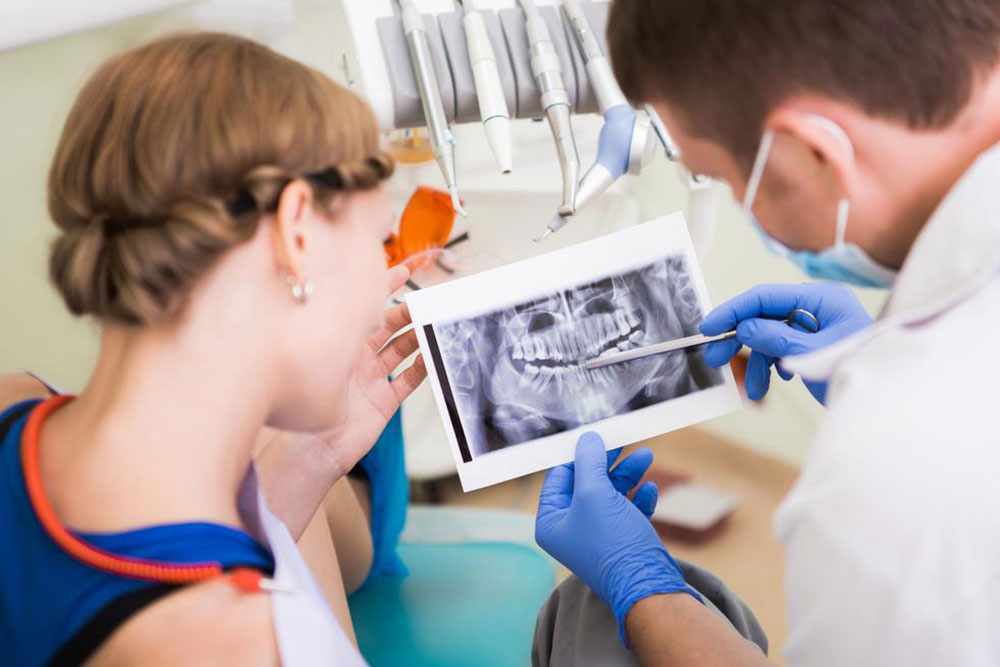
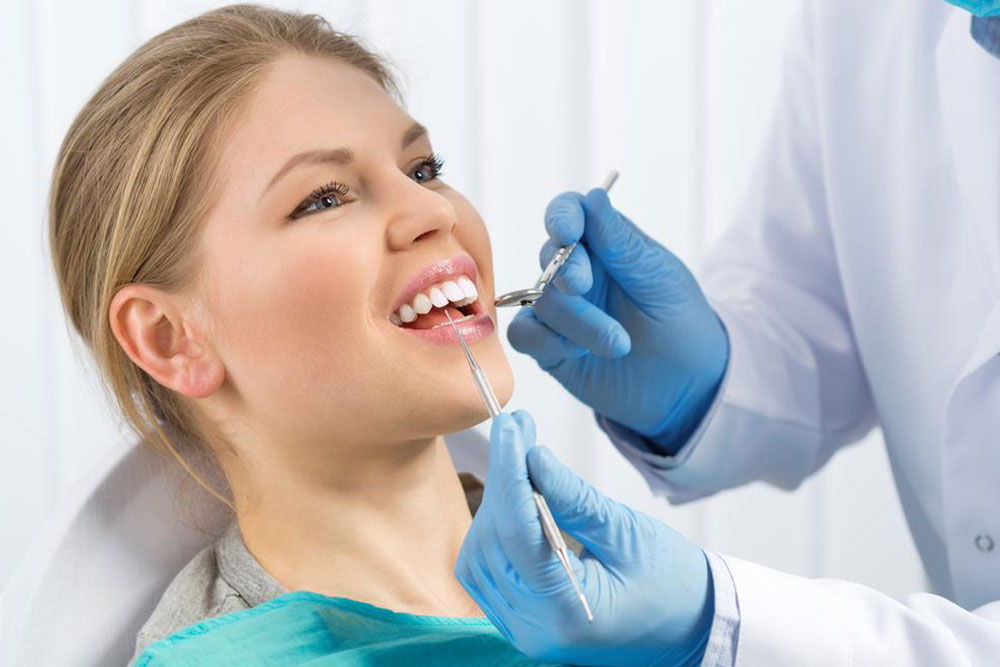
The mouth is highly exposed to external factors, making it susceptible to various infections and conditions, especially gum diseases like gingivitis and periodontitis. These common oral health issues require attention from dental professionals. Gum disease typically results from poor oral hygiene, such as inadequate brushing and flossing, which allow bacteria to accumulate around the gums. Hormonal shifts during pregnancy or menopause, alongside illnesses like heart disease and diabetes, can also increase risk. Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption further contribute. Symptoms include bleeding gums, bad breath, plaque buildup, and loose teeth. Differentiating between gingivitis and periodontitis is essential, as untreated gingivitis can develop into more severe gum infection. Treatment involves professional cleaning, improving diet, and sometimes medication or surgery to halt disease progression and restore gum health.